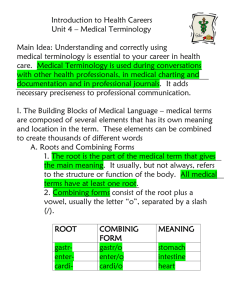
word root meaning example
advertisement

Medical Terminology - Medical terminology is the language used by physicians and other members of health team to: 1. Aid in communication. 2. Reduce the entire phrase into a single term. Eg. The condition of bluish discoloration of the hands and feet is called “acrocyanosis” Acro: limbs Cyan: blue Osis: condition It includes the medical words that describe or define a disease, a condition or clinical signs and symptoms. _ Medical terminology is essential and beneficial for: - 1- Students in medicine, pharmacy, nursing and in other allied health sciences. 2- Health professionals such as a- Pharmacists, b- Specialists in allied medical sciences - Nurses - Clinical laboratory professionals - Biomedical technologists, - Radiologists, - Community health specialists such as medical record administration, health educators and dieticians, - Medical secretaries and librarians and - People interested in translation and arabinisation of medical sciences. - The word building system 1 The medical words consists of three parts:- 1- The word root 2- The prefix 3- The suffix. 1- The word root: i Is the foundation of the word for example: peri/card/itis, endo/card/itis, cardio/megaly The part card ,means heart, is considered as the word root. In medical term, the word root may be an organ, tissue, cell, fluid or cavity. The word root: - - Indicate the organ or part that is modified by a prefix or suffix or both. “The medical term has 1 root or more” One: gastritis Two: gastr-o-enteritis Three: Oto-rhino-laryngology The compound word : - Is formed when two or more word roots are used to build the word e.g. Short/wave Short/hand This compound word has a specific meaning and could not be separated. The combining word : - Is formed of two word roots or more joined by a vowel such as Therm/o/meter Micr/o/scope The part of the word will retain its specific meaning irrespective of its presence in different words or positions in the words such as: Gastr/o/enter/o/logy Enter/o/col/itis - -In this two words, enter- means the small intestine in spite of the different positions in the two words. -Gastr- means stomach, while -logy means science, thus the meaning of gastroenterology is the science of digestive system (stomach and intestine). - In the enterocolitis, the part col means colon and itis means inflammation, so the meaning is inflammation of small intestine and colon. - 2- The suffix The suffix means an ending of the word which will convert word into: - A noun such as port/er - Adjective such as microscop/ic - Modify the meaning of the word such gaster/itis and gastro/logy. “Not all medical terms have suffixes” 3- The prefix - The prefix is the part that precedes the medical word and changes its meaning e.g. Tachy/cardia Brady/cardia Cardia means the heart and prefix tachy/ means increase in rate and brady/ means decrease in rate. Combining Vowel: A letter (usually O, occasionally E or I) may be added to: 1. Connect roots to suffixes & roots to other roots. 2. Make pronunciation easier. Notes: 1. When the suffix begins with a vowel, the combined vowel in the root is dropped. Eg. meningo & itis meningitis psychology & ic psychologic 2. When the suffix and the root have the same vowel, one vowel is dropped. Eg. cardi & it is carditis 3. Suffix Beginning with rh: When a suffix (rh) is added to a root, the r is doubled (rh) becomes (rrh) eg. haem/o = blood rhage = bursting haemorhage is wrong, the correct is hemorrhage Plural Endings: When we change a singular to a plural, usually we add “S” at the end of the word. Exceptionally, some plural endings do not follow this rule:- Formula Vertebra Formulae Vertebrae Lumen Lumina Index Indices Diagnosis Diagnoses Ganglion Ganglia Fungus Ovum Fungi Ova The most commonly used prefixes - Prefix aananteanticoncontradysect- Meaning without not before against together against difficult, painful outside, outer Example apnea anesthesia antepartum antipyretic connective tissue contraception dysuria ectopic beats Prefix endepiequiexhyperhypopolypara- Meaning Example inside, inner over, upon equal out above below many beside, near endocarditis epidermis equipotent expectorant hypertension hypotension polyarthritis parametrium - Prefix Meaning perperipreprosemisubsupratrans- through around before before half below over, excess across - Example percutaneous pericarditis precardium prognosis semicircular canal subnormal temp. suprarenal gland transabdominal Prefixes Pertaining to Colour Prefix Meaning Example Definition Cyan Blue Cyanosis Erythr Rubi Red Red Erythrocyte Rubella Bluish colouration of skin (lack of O2) Red blood cell Acute viral infectious disease caused by rubella virus Melan Black Melanin Xanth Yellow Xanthoma Dark pigment that colours the hair and skin Yellow raised area on skin Polio Grey Polioencephalitis An inflammation of the grey matter of brain Prefix Meaning Example Definition chloro green Chlorophyll The green pigment in plants Alb Leuk White White Albino rats Kind of experimental rats Leukemia - A serious disease in which the blood contains too many white cells causing weakness & death Leukocyte - White blood cells Cirrh gluco Orange yellow Silvery Liver Cirrhosis Glucoma Polio Grey Polioencephalitis One of the serious liver diseases One of the serious eye diseases An inflammation of the grey matter of brain The most commonly used suffixes 1 Suffix Meaning -algia -ectasia -ectomy -aemia -genic -graph -ic -itis pain expansion surgical excision blood origin to write pertaining inflammation Example myalgia gastroectasia nephroectomy anaemia myogenic electrocardiograph gastric gastritis Suffix Meaning -lithiasis -logy -lysis -malacia -mania -megaly -oid -oma stone in study of dissolution softening madness enlargement similar tumor - Example nephrolithiasis pharmacology haemolysis osteomalacia hypomania splenomegaly lipoid nephroma Suffix -pathy -penia -phobia -plasty -rhea -spasm -stomy Meaning disease decrease fear repair to flow contraction opening - Example neuropathy leucopenia hydrophobia hernioplasty rhinorrhea broncospasm gastrostomy The most commonly used word roots - word root meaning example adenangioarthrcardCerebrocholcost cyt - gland vessel joint heart brain bile rib cell adenoma angiogenesis arthritis cardiopathy cerebral cholilithiasis costal cartilage cytology word root meaning dermencephalentergastrglycoheamhepathyster- skin brain small intestine stomach sweet blood liver uterus - example dermatology encephalitis enteropathy gastroectasia glycosuria haemorrhage hepatomegaly hysterectomy word root meaning leuk(c)liplithmeningmynephrooculusophthalmosteo- white lipid (fat) stone membrane muscle kidney eye eye bone - example leukocytes lipoma lithiasis meningitis mylagia nephropathy ocular ophthalmitis osteoporosis word root meaning example - pneumproctpsychradiRensplenvas- lung rectum mind ray kidney spleen vessel viscer- internal organ pneumonia proctoscope psychology radiotherapy renal faliuer splenomegaly vasodilation vasoconstriction visceral The clinical description of disease - - Clinical is derived from (clin)= at bedside. - To describe a disease, some important headings are essential to know. Etiology - Eti = cause - Logy = study or science dealing with Thus, the word etiology means studying the cause of the disease and its predisposing factors such as tumor, allergy, infection….etc. Pathogenesis - Path- = disease genesis = origin Thus the word pathogenesis means the study of disease development from the start of the condition till the establishment of the disease. Pathology The science that deal with the cause and nature of the disease by microscopic and naked-eye examination. Symptoms - The feelings noticed by the patient due to the disturbances caused by the disease. Signs The features of the disease or deformation. It is observed by the physician, relatives or the patient himself. Diagnosis Dia- =through, -gnosis = knowledge The name of the disease is reached through knowledge of its sign and symptoms and through clinical investigation. Investigations _ The methods used to reach the definitive diagnosis such as laboratory tests which include : biochemical, bacteriological, histological, haematological and radiological. Clinical examinations Examination of the patient by using the physicians skills, his hands, stethoscope, blood pressure apparatus or other aids to know the physical signs of the disease. Anatomy _ The science that deal with the body systems regarding structure and relations. Prognosis Pro = beforehand gnosis = knowledge Thus, the meaning is the prediction of the progress, and termination of a disease. Complications Undesirable events in the progress of the disease such as bleeding from stomach ulcer. Prophylaxis - Protection from a disease. Prophylactic Protective against a disease. Syndrome Set of signs and symptoms running together. Disease A state of ill-health resulting from structural changes associated with functional alteration. Relapsing - Repeated recurrence of disease for several times. -Logist Specialist in type of study in health and disease. Surgeon Sur = hand geon = work Physician who uses instruments to remove or repair a diseased tissue or organ. Acute The severe signs and symptoms of the disease that occur in short duration. Chronic - The signs and symptoms of mild nature start slowly and gradually and maintained for a long time. Subacute The severity and duration of the signs and symptoms are between acute and chronic. Indications The use of drugs in the diagnosis, prevention or treatment of specific disease. Contra-indications - The disease in which the use of a drug will be harmful or will aggravate the condition. Inflammation Cellular, lymphatic and vascular reactions against an irritant in order to localize and remove the irritant. Repair A replacement of a damage tissue by a new one. Regeneration The division and reproduction of the cells. Degeneration A metabolic and morphological changes resulting from irritation not severe enough to kill cells. - Necrosis A local death of a mass of tissue which occur either directly or follow severe degeneration. Thrombosis The formation of compact body (from blood elements) inside a blood vessel or the heart. Embolism Insoluble body which circulates in the blood until it occlude a small vessel. Thrombo-embolism The movement of a thrombus from its site and production of embolism. - Edema Accumulation of excess fluid in tissue spaces, pulmonary alveoli or inside the cells. Ischemia A decrease of blood supply to an organ due to occlusion of its artery. Infarction An area of necrosis caused by sudden occlusion of the arterial supply by thrombosis or embolism. Haemorrhage - The escape of blood outside the blood vessels or the heart. Shock An acute circulatory failure i.e. hypotension and tissue hypoxia. Bacterial infection The invasion of the body by pathogenic bacteria and development of pathological changes. Toxaemia The presence of toxins in the circulating blood. Septicaemia - The presence of a large number of multiplying bacteria and their toxins in the blood due to low body resistance. Immunity The ability of the body to overcome infection by the microorganism by producing antibodies. Diabetes melletus Metabolic disease due to decrease or complete loss of insulin leading to increase in the blood glucose level (hyperglycemia). The clinical diagnostic signs - Stethoscope Instrument which is used to hear sounds elicited from heart, lungs or abdomen. Sphygmomanometer Instrument which is used to measure the blood pressure.