Nutrition and Digestion
advertisement

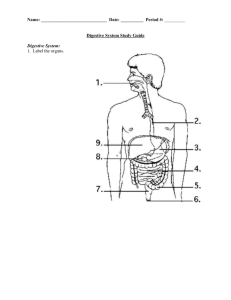
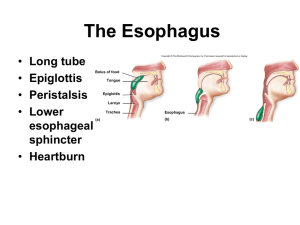
Nutrition and Digestion Pg. 428-429 Suspension-feeding: a baleen whale Ingesting food • • • • Omnivores - ingest plants and animals Herbivores -plant eaters Carnivores -animal eaters Suspension feeders-eat particles in the water column • Substrate feeder - live in or on food source • Fluid feeder- suck nutrient rich fluid from host • Bulk feeder- eat large pieces of food Figure 21.1 Substrate-feeding: a leaf miner Figure 2118 Fluid-feeding: a mosquito 21.1E Bulk-feeding: a python Food processing: 4 stages • 1 Eating • 2 Breakdown of food into small molecules for absorption • 3 Cells in the lining of the digestive tract absorb nutrient molecules • 4 Undigested materials pass out of the digestive tract Food processing: 4 stages • Ingestion -eating • Digestion-breakdown of food into small molecules for absorption • Absorption - cells in the lining of the digestive tract absorb nutrient molecules • Elimination - undigested materials pass out of the digestive tract Digestion occurs in specialized compartments Simple animals have a mouth and gastrovascular cavity Fig 21.3A More complex animals have an alimentary canal Typhlosole Omnivorous Herbivorous Mouth-pharynx-esophagus-crop-gizzard-stomach-intestine-anus Human digestive tract • Alimentary canal Main parts – Mouth,oral cavity,tongue,pharynx, esophagus,stomach,sm all intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus • Accessory structures – Salivary glands, pancreas, liver – Peristalsis, sphincters The oral cavity • Salivary juices – Lubricate, buffer, kill bacteria, begin digestion • Mechanical and Chemical digestion – Tooth types • Tongue – Manipulates food Food and breathing passages open to the pharynx • Pharynx open to windpipe most of the time • During eating the epiglottis closes off the windpipe Esophagus squeezes food to the stomach • Two muscle layers, circular and longitudinal • Peristalsis moves the food along • No digestive function (hiatal hernia) Stomach stores food and breaks it down 2-6 hours! • Involves acid and digestive enzymes • Can store 2L of food • Has pits, glands, and cells which produce acid and mucus Stomach stores food and breaks it down • Digestion in the stomach – Pepsinogen + HCl Epepsin acitvated – Proteins + pepsin E polypeptides • • • • Gastric glands secrete mucus, HCl and pepsinogen External stimuli (smell, sight) stimulate gastrin release Gastrin stimulates production of gastric juce Chyme forms from food and gastric juice mixed together Disorders of the stomach and esophagus • Acid reflux- back flow of acid into the esophagus - heartburn • Barrett’s esophagus - growth of abnormal tissue in the esophagus. • Gastric ulcers-digestive juice erodes the lining of the stomach wall creating open sores • H. pylori can cause ulcers also (gastritis) • Antibiotics can cure this Small intestine: major site of chemical digestion and nutrient absorption Small intestine: major site of chemical digestion and nutrient absorption • Pancreas -secretes 9 different enzymes that break down fat, protein, carbohydrate. Also produces an alkaline secretion that neutralizes acid chyme • Liver-produces bile that emulsifies fat • Bile- chemically emulsifies fat • Gallbladder- stores bile salts that emulsify fat • Duodenum- site of absorption Small intestine:Structure Tests • Starch • Place a sample of solution to be tested in the dish • Add a few drops of IKI • Maltose • Add benedicts to solution remaining in each test tube • Heat and observe color Test for Starch with IKI Before After • A dark brown color indicates the presence of starch Hydrolysis of Starch to Maltose Total hydrolysis No hydrolysis Partial hydrolysis Test for Maltose with Benedicts solution • Blue is negative • Orange is positive Large intestine • Cecum - blind pouch that stores bacteria • Appendix - immune function • Main function - water absorption - creates feces which become harder as water is absorbed • Vitamin production from E. coli • Rectum-terminal portion of the colon • Diarrhea / constipation Adaptations of the digestive system • Carnivore - short alimentary canal • Herbivore/omnivorelong alimentary canal – Special chambers to digest cellulose • Cow - the extreme herbivore - Ruminant 4 chambered stomach extracts maximum nutrients! 1+2 prokaryotes digest cellulose in rumen and reticulum Regurgitation and more chewing Swallow again - omasum absorbs water Abomasum - cow’s own enzymes complete digestion Nutrition • “If you find honey eat just enough - too much and you will vomit” Nutrition • Macronutrients – Carbohydrates, Fats, Proteins, Nucleic acids – Provide fuel for energy • Micronutrients – Vitamins and minerals Kilocalorie=calorie BMR = 1300-1800 kcal per day Liver makes and stores glycogen which is stored in muscles as well Excess energy is stored as fat Essential Amino Acids • Your body makes many amino acids, but not all of them • Some AA’s must be obtained from food = essential AA’s Vitamins/minerals • Chemical nutrients other than O, H, N, H • All minerals are essential • Too much of some can cause high blood pressure • An organic nutrient that is essential but required in smaller amounts • Coenzymes - part of the metabolic reactions in the body • Deficiencies cause specific sets of symptoms • Evaluations