Solutions Exercises Lecture 1
advertisement
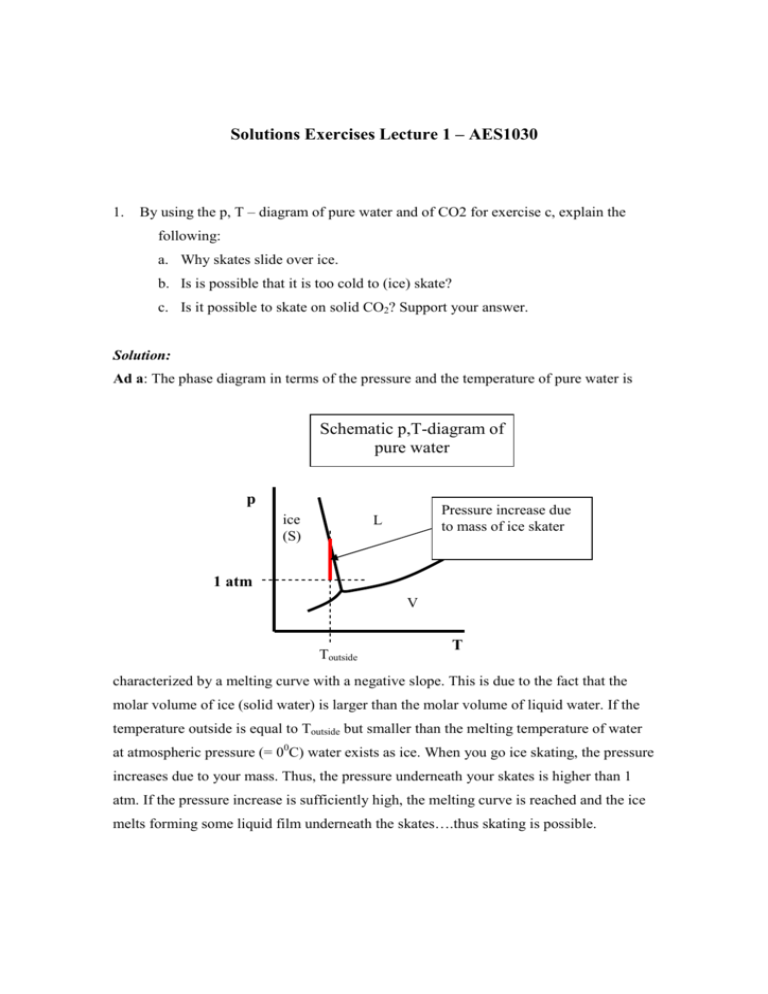
Solutions Exercises Lecture 1 – AES1030 1. By using the p, T – diagram of pure water and of CO2 for exercise c, explain the following: a. Why skates slide over ice. b. Is is possible that it is too cold to (ice) skate? c. Is it possible to skate on solid CO2? Support your answer. Solution: Ad a: The phase diagram in terms of the pressure and the temperature of pure water is Schematic p,T-diagram of pure water p ice (S) Pressure increase due to mass of ice skater L 1 atm V Toutside T characterized by a melting curve with a negative slope. This is due to the fact that the molar volume of ice (solid water) is larger than the molar volume of liquid water. If the temperature outside is equal to Toutside but smaller than the melting temperature of water at atmospheric pressure (= 00C) water exists as ice. When you go ice skating, the pressure increases due to your mass. Thus, the pressure underneath your skates is higher than 1 atm. If the pressure increase is sufficiently high, the melting curve is reached and the ice melts forming some liquid film underneath the skates….thus skating is possible. Ad b: If the temperature outside is very low, then it might happen that the mass of the skater is not sufficient to increase the pressure sufficiently to reach the melting curve. Thus, there is no liquid film underneath the skates so that skating becomes ‘impossible’. Ad c: The schematic p,T-diagram of CO2 is given below. It can be seen that the melting curve has a positive slope. Thus if the temperature is such that CO2 exists as solid, then pressure increase does not induce the formation of liquid as it was the case for water. Thus, one cannot skate on solid CO2. Schematic p,T-diagram of pure CO2 p Pressure increase due to mass of skater L S 1 atm V Toutside T 1. The following variables are related to a homogeneous system: Pressure, volume, temperature, heat, heat capacity CP, internal energy, enthalpy and work. a) Which of these variables are extensive and which intensive? b) Which of these variables depend on the path and which not? c) Which of the mentioned variables are state functions? Oplossing: a) Extensive properties (dependent on the amount of the component forming the system): volume, heat capacity, internal energy, enthalpy, work, heat Intensive properties (independent of the amount of component forming the system): pressure, temperature b) + c) Path dependent property: heat capacity, heat and work Path independent property (= state function): pressure, volume, temperature, internal energy, enthalpy