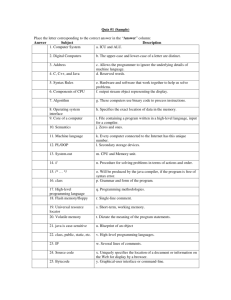
• Operating system software • Utility programs • Library programs
advertisement

• Operating system software • Utility programs • Library programs • Translator software (Compiler, assembler, interpreter). System software (or systems software) is computer software designed to operate and control the computer hardware and to provide a platform for running application software.[ The operating system (prominent examples being z/OS, Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X and Linux), allows the parts of a computer to work together by performing tasks like transferring data between memory and disks or rendering output onto a display device. It also provides a platform to run high-level system software and application software. An Operating System is special software that enables users to communicate with the computer system. Tasks of an operating system are: 1. controlling the operation of the input, output and backing storage devices 2. supervising the loading, running and storage of application programs 3. dealing with errors that occur in applications programs 4. maintaining security of the whole computer system 5. maintaining a computer log, which contains details of computer usage 6. allowing communication between user and the computer system (user interface ) There are two main types of user interface: 1. Command line interface (CLI) 2. Graphical User Interface (GUI) e.g. WINDOWS (WIMP – Windows Icons Menus Pointing device) Utility software helps to analyze, configure, optimize and maintain the computer. Utility software categories Anti-virus utilities scan for computer viruses. Archive utilities output a stream or a single file when provided with a directory or a set of files. Archive utilities, unlike archive suites, usually do not include compression or encryption capabilities. Some archive utilities may even have a separate un-archive utility for the reverse operation. Backup utilities can make a copy of all information stored on a disk, and restore either the entire disk (e.g. in an event of disk failure) or selected files (e.g. in an event of accidental deletion). Cryptographic utilities encrypt and decrypt streams and files. Data compression utilities output a shorter stream or a smaller file when provided with a stream or file. Utility software categories Data synchronization utilities establish consistency among data from a source to a target data storage and vice versa. There are several branches of this type of utility: File synchronization utilities maintain consistency between two sources. They may be used to create redundancy or backup copies but are also used to help users carry their digital music, photos and video in their mobile devices. Revision control utilities are intended to deal with situations where more than one user attempts to simultaneously modify the same file. Disk checkers can scan operating hard drive. Disk cleaners can find files that are unnecessary to computer operation, or take up considerable amounts of space. Disk cleaner helps the user to decide what to delete when their hard disk is full. Disk compression utilities can transparently compress/uncompress the contents of a disk, increasing the capacity of the disk. Disk defragmenters can detect computer files whose contents are broken across several locations on the hard disk, and move the fragments to one location to increase efficiency. Utility software categories Disk partitions can divide an individual drive into multiple logical drives, each with its own file system which can be mounted by the operating system and treated as an individual drive. Disk space analyzers for the visualization of disk space usage by getting the size for each folder (including sub folders) & files in folder or drive. showing the distribution of the used space. Disk storage utilities File managers provide a convenient method of performing routine data management tasks, such as deleting, renaming, cataloging, uncataloging, moving, copying, merging, generating and modifying data sets. Hex editors directly modify the text or data of a file. These files could be data or an actual program. Utility software categories Memory testers check for memory failures. Network utilities analyze the computer's network connectivity, configure network settings, check data transfer or log events. Registry cleaners clean and optimize the Windows registry by removing old registry keys that are no longer in use. Screensavers were desired to prevent phosphor burn-in on CRT and plasma computer monitors by blanking the screen or filling it with moving images or patterns when the computer is not in use. Contemporary screensavers are used primarily for entertainment or security. System monitors for monitoring resources and performance in a computer system. System profilers provide detailed information about the software installed and hardware attached to the computer. Library Programs In computer science, a library is a collection of nonvolatile resources used by programs on a computer, often to develop software. These may include configuration data, documentation, help data, message templates, pre-written code and subroutines, classes, values or type specifications. Library Programs Most compiled languages have a standard library although programmers can also create their own custom libraries. Most modern software systems provide libraries that implement the majority of system services Library Programs Most compiled languages have a standard library although programmers can also create their own custom libraries. Most modern software systems provide libraries that implement the majority of system services Translator software (Compiler, assembler, interpreter). A compiler is a computer program (or set of programs) that transforms source code written in a programming language (the source language) into another computer language (the target language, often having a binary form known as object code). The most common reason for wanting to transform source code is to create an executable program. The name "compiler" is primarily used for programs that translate source code from a high-level programming language to a lower level language (e.g., assembly language or machine code). If the compiled program can run on a computer whose CPU or operating system is different from the one on which the compiler runs, the compiler is known as a crosscompiler. A program that translates from a low level language to a higher level one is a decompiler. A program that translates between high-level languages is usually called a language translator, source to source translator, or language converter. A language rewriter is usually a program that translates the form of expressions without a change of language. A compiler is likely to perform many or all of the following operations: lexical analysis, preprocessing, parsing, semantic analysis (Syntaxdirected translation), code generation, and code optimization. An assembly language is a low-level programming language for a computer, microcontroller, or other programmable device, in which each statement corresponds to a single machine code instruction. Each assembly language is specific to a particular computer architecture, in contrast to most high-level programming languages, which are generally portable across multiple systems. Assembly language is converted into executable machine code by a utility program referred to as an assembler; the conversion process is referred to as assembly, or assembling the code. Assembly language uses a mnemonic to represent each low-level machine operation or opcode. Some opcodes require one or more operands as part of the instruction, and most assemblers can take labels and symbols as operands to represent addresses and constants, instead of hard coding them into the program. Macro assemblers include a macroinstruction facility so that assembly language text can be pre-assigned to a name, and that name can be used to insert the text into other code. Many assemblers offer additional mechanisms to facilitate program development, to control the assembly process, and to aid debugging. Assembly Language Example Interpreter A program that executes instructions written in a high-level language. There are two ways to run programs written in a high-level language. The most common is to compile the program; the other method is to pass the program through an interpreter. An interpreter translates high-level instructions into an intermediate form, which it then executes. In contrast, a compiler translates high-level instructions directly into machine language. Compiled programs generally run faster than interpreted programs. The advantage of an interpreter, however, is that it does not need to go through the compilation stage during which machine instructions are generated. This process can be time-consuming if the program is long. The interpreter, on the other hand, can immediately execute high-level programs. For this reason, interpreters are sometimes used during the development of a program, when a programmer wants to add small sections at a time and test them quickly. In addition, interpreters are often used in education because they allow students to program interactively. Both interpreters and compilers are available for most high-level languages. However, BASIC and LISP are especially designed to be executed by an interpreter. In addition, page description languages, such as PostScript, use an interpreter. Every PostScript printer, for example, has a built-in interpreter that executes PostScript instructions. A compiler translates code from a source language (e.g. C, C++, Java) to a target language, which can then be executed by a (virtual or physical) machine. An interpreter reads code in an interpreted language (e.g. PHP, Perl, JavaScript) and directly executes the contained instructions. Compiler characteristics: •spends a lot of time analyzing and processing the program •the resulting executable is some form of machine- specific binary code •the computer hardware interprets (executes) the resulting code •program execution is fast Interpreter characteristics: •relatively little time is spent analyzing and processing the program •the resulting code is some sort of intermediate code •the resulting code is interpreted by another program •program execution is relatively slow