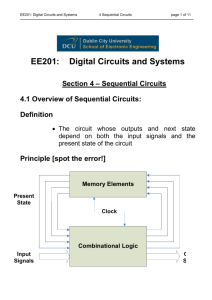
EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems
advertisement

EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems EE201: Introduction page 1 of 7 Digital Circuits and Systems Seán Marlow Room: S337 Phone: (01-700) 5120 E-mail: marlows@eeng.dcu.ie Module co-ordinator: Dr. Seán Marlow Web page: http://www.eeng.dcu.ie/~ee201 Objective of the course: Enable successful students to: • Analyse and understand combinational and sequential logic circuitry • Design combinational and sequential logic circuitry • Design digital systems • Design interfaces to digital computer systems EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems Introduction page 2 of 7 Computer Architecture: Memory Unit CPU (RAM, ROM, HDD) I/O Units (Mouse, Keyboard, Monitor, Printer, etc.) Registers Arithmetic Logic Unit Control Unit Course Content: • Combinational Logic: o Encoders/Decoders o Multiplexers/Demultiplexers • Computer Codes: o o o o BCD and ASCII Gray Codes Parity and Hamming codes Error detection and correction • Binary Arithmetic: o Addition Ripple-carry adder Carry look-ahead adder o Multiplication o Division o Floating point arithmetic o Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) o Accumulator EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems Introduction page 3 of 7 • Sequential Logic: o Analysis and design using state diagram and state table; o State assignment and reduction. o Implementation using gates • Digital Circuitry: o TTL, ECL, IIL and MOS technologies o Comparison of technologies in terms of: Speed Power consumption Noise margin Loading Cost o Methods of data bussing • Digital Storage: Bi-stable latch Single word memory Organisation of memory systems Static and dynamic RAM o ROM o o o o • Programmable Logic Devices: o ROM o PLA o PAL o GAL • Microprocessor Interfacing o Parallel I/O o Serial I/O o Video controllers o Timers EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems Introduction page 4 of 7 EE201 consists of: • Lectures (2 hours/week) • Tutorials (1 hour/week) • Practicals (3 hours every 2 weeks) • Web site (anytime) • Private study (minimum 2 hours/week) Duration: • 12 weeks Assessment: • Laboratory Reports (25%) • Exam (75%) Pass: • Final grade at least 40% Recommended Resources: • Web site: http://www.eeng.dcu.ie/~ee201 • Libraries (e.g. http://library.dcu.ie/) • Bookshops • Search engines (e.g. http://www.google.com) EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems Introduction page 5 of 7 Recommended Textbooks: • Tocci, R. J., "Digital Systems", Prentice Hall, 1995 • Floyd, T. L., "Digital Fundamentals", Merrill, 1994 • Katz, R. H., "Contemporary Logic Design", Benjamin, 1994 • Cahill, S. J., "Digital and Microprocessor Engineering", Ellis-Horwood, 1993 • Peatman, J. B., ”Design of Digital Systems” • Pappas, N. L., “Digital Design” • Quinn, J., “6800 Microprocessor“ • Tinder, R. F., “Digital Engineering Design“ • Mano, M. M., “Digital Design” • Mano, M. M., “Logic and Computer Design” • Mano, M. M., “Digital Logic and Computer Design” • Brey, B. B., “Microprocessors and Peripherals” • Olesky, J. E., “Microprocessors and Digital Computer Technology” EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems Introduction page 6 of 7 Advice: • Attend lectures o The lecturer presents the most important material o Your presence is strongly recommended o Take notes and read them at home o Keep them and review them later on • Attend tutorials o Read lecture notes and textbooks before tutorials o Prepare questions and ask them o Your presence is strongly recommended as you can clarify some aspects not fully understood • Do not miss any practical o Practicals are compulsory o You have an opportunity to exercise theoretical knowledge • Buy the laboratory manual o You need it during the lab sessions o You can get it from Hodges & Figgis bookshop (campus) o You also need a lab notebook EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems Introduction page 7 of 7 • Borrow books from the library o Read them! o Take notes o Exercise • Ask questions o Lecturer – after the lectures o Tutor – during the tutorial o Demonstrators – during lab sessions • Work on your own o Solve problems o Save solutions o Devise your own problems o Try to solve them o Practice as much as you can • Prior knowledge o Binary Arithmetic: 2’s comp Add/Sub o Combinational Logic: logic gates, KM o Sequential Logic: flip-flops, shift registers, counters