Executive Office Agencies L-4
advertisement

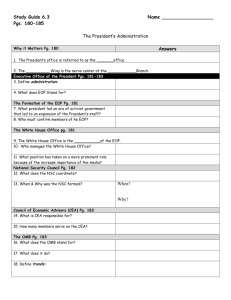
12/1/2015 networks ­ Print Lesson Print Decisions made by people working in the executive branch affect many areas of life. Executive Office Agencies SS.7.C.3.3, SS.7.C.3.8, SS.7.C.4.3, LA.7.1.6.1, LA.7.1.7.3 What offices make up the Executive Office of the President? In 1801 President Thomas Jefferson had a tiny staff. Only a few advisers, a messenger, and a part­time secretary helped him. Today thousands of experts, advisers, secretaries, and clerks assist the president. Most of these people work in the Executive Office of the President (EOP). They are all part of what is called the president’s administration. The EOP was set up under Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1939. Its purpose was to help the president do his job. The office has grown since its beginning. Today it has nearly 2,000 employees. Its budget is around $400 million. The president’s staff has come a long way. The White House Office The EOP is overseen by the president’s chief of staff. This person takes care of the president’s schedules. The chief of staff also decides who is allowed to meet with the president. The chief of staff, along with the deputy chiefs of staff and senior advisers, serve as the president’s closest advisers. The heart of the EOP, however, is the White House Office. This group is made up of about 500 people who work directly for the president. Their many tasks include helping the president develop policy and communicate with Congress and the general public. Office of Management and Budget The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) prepares the federal budget. The budget shows the president’s spending plans for the coming year. It also monitors, or oversees, spending in all the agencies of the executive branch. The director of the OMB works closely with the president. National Security Council The National Security Council (NSC) advises the president on matters of national security. The NSC includes the vice president, the secretaries of state and defense, and the chairperson of the Joint Chiefs of Staff. The Joint Chiefs of Staff are the top commanders from the four parts of the armed services. The Director of National Intelligence also serves on the NSC. Intelligence is information about the actions and plans of other governments. The National Security Advisor, appointed by the president, heads the NSC. Council of Economic Advisers The Council of Economic Advisers (CEA) helps the president carry out the role, or job, of economic leader. The president names people to the CEA, but the Senate must approve them. The CEA gives advice on economic policy. It addresses such matters as job growth, prices, and trade. Identifying Which officials make up the National Security Council? The NSC includes the vice president, the secretaries of state The President’s Cabinet SS.7.C.3.3, SS.7.C.3.8, SS.7.C.4.3 What role does the president’s cabinet play in the government? The EOP is only a small part of the president’s administration.Thousands more people work in 15 large units called departments. The heads of those departments form the group of presidential advisers known as the cabinet. The head of the Department of Justice is called the attorney general. All other department heads are called secretaries. As you can see from the chart, the 15 departments work in many different areas. http://connected.mcgraw­hill.com/ssh/book.printNarrative.do?bookId=NB4BRZZPV92X3JQT173BJVERP4&bookEdition=STUDENT&narrativeContainerId=X8… 1/4 12/1/2015 networks ­ Print Lesson Article II, Section 2, of the Constitution mentions that the president may require “in writing” the opinion of the heads of each of the executive departments “upon any Subject relating to the Duties of their respective Offices.“ It does not, however, specifically mention the cabinet. Meeting with a cabinet is tradition, or custom. The tradition began with President George Washington. He met regularly with the heads of the first four departments. These were the attorney general and the secretaries of state, war, and the treasury. Later presidents followed this example. As more executive departments were created over the years, the cabinet grew. Cabinet Responsibilities Cabinet members give the president advice on matters that touch the departments they lead. The secretary of agriculture, for example, works with the president on issues that have an effect on farmers. Cabinet members also carry out the president’s plans within their departments. Suppose that the president wants to start new programs for job training. The secretary of labor will be given the task of putting that plan into action. The president decides when the cabinet is to meet. The president may also ask the vice president and other top aides to join meetings of the cabinet. Meetings may be held as often as once a week or hardly at all. Many presidents have not relied heavily on their cabinets. They often have felt free to ignore cabinet advice. They expect the department heads to carry out their policies, though. Cabinet members spend most of their time directing the activities in their departments. To hold their posts, the department heads must be approved by the Senate. Department of Homeland Security In 2002, President Bush signed the Homeland Security Act. That law set up the new Department of Homeland Security. The task of this department is to protect the nation from attacks by terrorists. Part of that work is to gather information about terrorists and their plans. This was the first new department set up since 1989. That year, the Department of Veterans Affairs was formed. It runs programs for former members of the armed forces. The Vice President For many years, presidents gave little authority to their vice presidents. That has changed, though, in recent times. Vice President Al Gore, for example, served as a close adviser to President Bill Clinton about the environment. Vice President Dick Cheney advised President George W. Bush on foreign policy. Under President Obama, Vice President Joseph Biden led a team that tried to find ways to help families have a better standard of living. Stating When does the cabinet meet? the president decides, it can be up to once a week. Florida CONNECTION Cabinet The Department of Justice is headed by the U.S. attorney general. The attorney general is the nation’s chief law enforcement officer. Florida native Janet Reno became the first woman attorney general of the United States in 1993. She was also the longest­ serving attorney general of the 1900s. The Federal Bureaucracy SS.7.C.3.3, SS.7.C.3.8 What is the federal bureaucracy? The executive branch also has hundreds of agencies. They deal with everything from running the space program to deciding what can be used to make hot dogs. Together, the agencies and employees of the executive branch are called the federal bureaucracy (byu•RAH•kruh•see). About 3 million people work in the executive branch. These workers do three basic kinds of tasks. Through these tasks, they help make government policy. First, agencies write rules that put laws passed by Congress into practice. Laws are often written in very general terms. The agencies have to turn those guidelines into specific rules. That way, people and businesses can know what to do to follow the law. Second, departments and agencies carry out the day­to­day activities of the federal government. Some workers deliver the http://connected.mcgraw­hill.com/ssh/book.printNarrative.do?bookId=NB4BRZZPV92X3JQT173BJVERP4&bookEdition=STUDENT&narrativeContainerId=X8… 2/4 12/1/2015 networks ­ Print Lesson mail, some collect taxes, and some take care of national parks. Others perform thousands of other services. Third, federal agencies oversee certain activities. For example, they watch banks to make sure that they obey the rules about banking. They decide if products are safe to use. They establish rules that protect our health and the environment. Agencies cannot simply take this work on for themselves. Congress must pass a law to give them the power to do their work. Independent Agencies The executive branch has many independent agencies. They are called independent because they are not part of a cabinet department. These agencies can be grouped into three types: executive agencies, government corporations, and regulatory commissions. Executive agencies are independent agencies that deal with certain specific areas within the government. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), for example, runs the space program. The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) provides policy makers with intelligence information. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) establishes and enforces regulations that protect human health and the environment. Some agencies are government corporations. These are businesses that are owned by the government. Like any business, they provide goods or services and charge people to buy those goods or services. The difference is that these corporations are not supposed to make a profit. The United States Postal Service is one example. The Tennessee Valley Authority is another. It sells energy to people living in a certain part of the country. The job of regulatory commissions is to protect the public. They make and enforce rules that an industry or group must follow. For instance, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) makes rules for television and radio stations. The U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission establishes safety standards for thousands of types of consumer products. Unlike the other two types of independent agencies, regulatory commissions do not report to the president. The president does name the people who head these commissions. He or she cannot fire them, though. Only Congress can remove them. Government Workers The top jobs in a department or agency usually go to political appointees. These are people chosen by the president. Some are picked because they have experience in the work the department does. Some are named because they supported the president during the election. People in these jobs usually leave office when the president does. About 90 percent of those who work in the federal government are civil service workers. Unlike political appointees, civil service workers usually have permanent jobs. These people might be clerks or lawyers or park rangers. They are hired through the civil service system. This is the practice of hiring government workers on the basis of open, competitive examinations and proven ability. Before 1883, many federal jobs fell under the spoils system. In this practice, people won government jobs as a reward for political support. Each new president fired many government workers and replaced them with supporters. The idea was, “To the victor belong the spoils [jobs].” Under the spoils system, appointees were not always qualified to perform their jobs. In response, Congress passed the Civil Service Reform Act of 1883. That law created the civil service system. It also placed limits on the number of jobs a new president could give to friends and backers. The Office of Personnel Management (OPM) directs the civil service system today. It sets standards for federal jobs. It also gives tough tests to people who want those jobs. The civil service system is a merit system. Government officials hire new workers from lists of people who have passed the tests or otherwise met civil service standards. Describing Which jobs go to political appointees today? These are people chosen by the president. Some are LESSON 4 REVIEW Review Vocabulary 1. What is the difference between an executive agency and a regulatory commission? LA.7.1.6.1 2. How are the civil service system and the merit system connected? http://connected.mcgraw­hill.com/ssh/book.printNarrative.do?bookId=NB4BRZZPV92X3JQT173BJVERP4&bookEdition=STUDENT&narrativeContainerId=X8… 3/4 12/1/2015 networks ­ Print Lesson LA.7.1.6.1 Answer the Guiding Questions 3. Explaining Why is the work of the Office of Management and Budget so important? SS.7.C.3.8 4. Identifying What are the main functions of the members of the cabinet? SS.7.C.3.8 5. Explaining How does a government corporation operate? SS.7.C.3.3 6. PERSUASIVE WRITING Federal agencies enforce thousands of regulations that affect our lives. Some people say the government plays too large a role in society. Write a paragraph on whether you agree with this viewpoint and why. SS.7.C.3.8 http://connected.mcgraw­hill.com/ssh/book.printNarrative.do?bookId=NB4BRZZPV92X3JQT173BJVERP4&bookEdition=STUDENT&narrativeContainerId=X8… 4/4