PHP Development – MySQL
advertisement

PHP Development - Introduction
Php Hypertext Processor
• PHP stands for PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor
• PHP is a server-side scripting language, like ASP
• PHP scripts are executed on the server
• PHP supports many databases (MySQL, Informix,
Oracle, Sybase, Solid, PostgreSQL, Generic ODBC,
etc.)
• PHP is an open source software
Php Hypertext Processor
Php Hypertext Processor
Php Hypertext Processor
Php Hypertext Processor
Taken from Udemy.com
Php Hypertext Processor
Taken from Udemy.com
Php Hypertext Processor
• PHP files can contain text, HTML tags and
scripts
• PHP files are returned to the browser as
plain HTML
• PHP files have a file extension of ".php“
(most common), ".php3", or ".phtml"
Php Scripts
• Php script starts with <?php
• Ends with ?>
• Php script can be placed anywhere in
document
• File ends in .php
• Each instruction must end with a semicolon ;
• Semicolon acts as a separator between
instructions
Hello World
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<?php
echo "Hello World!";
?>
</body>
</html>
Hello World
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
Hello World!
</body>
</html>
Comments
• Comments help make code more readable/understandable
• Beneficial for third party to understand code
• Ignored by compiler
• Use // to create a single line comment
• Use /* ….. */ to create a multiple line comment
Comments
<html>
<body>
<?php
//This is a comment
/*
This is
a comment
block
*/
?>
</body>
</html>
Outputting Strings
• The echo() function outputs one or more strings
• The print() function can also be used
• echo() is faster than print()
<?php
echo "This text
spans multiple
lines.";
?>
This text spans multiple lines.
Outputting Strings
<?php
$str = "What’s my name?";
echo $str;
echo "<br />";
echo $str."<br />I don't know!";
?>
What’s my name?
What’s my name?
I don't know!
PHP Development – MySQL
Dr. Mark Hughes
Why Databases
Some examples of PHP and MySQL being used together are:
•
Banner Rotation. On this site, where each banner is, a PHP script is
called. This opens a database and picks a random banner from it to
show the visitor.
•
Forums. Hundreds of forums (message boards) on the internet are run
using PHP and MySQL.
•
Databases. One quite obvious example is sites which get all there
information from a database. Websites. If you have a large website
and you want to change the design it can take a very long time to
update and upload all the pages. With PHP and MySQL your whole
website could be just one or two PHP scripts.
Creating Databases
Creating Databases
• Retrieve all users from Shenyang
• Retrieve all users from Dublin who are under 30
• Retrieve all users who have a username that begins with j
• Retrieve all users that have a yahoo email address
• Print out users under 30 by order of their age
Phpmyadmin Access Denied Issue
• Go to C:\wamp\apps\phpmyadmin3.5.1
• Open file called config.inc.php
• Change lines
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['user'] = '';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['password'] = ‘’
To username and password of mysql installed
on local machine
Connecting to Databases
Before you can access data in a database, you must create
a connection to the database.
In PHP, this is done with the mysql_connect() function.
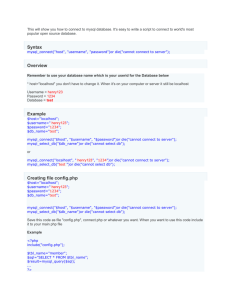
Syntax
mysql_connect(servername,username,password);
Connecting to Databases
Parameter
Description
servername
Optional. Specifies the server to connect to. Default
value is "localhost:3306"
username
Optional. Specifies the username to log in with. Default
value is the name of the user that owns the server
process
password
Optional. Specifies the password to log in with. Default
is ""
Connecting to Databases
<?php
$con =
mysql_connect("localhost",“username",“password")
;
if (!$con)
{
die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error());
}
// some code
?>
Closing a connection
<?php
$con =
mysql_connect("localhost",“username",“password")
;
if (!$con)
{
die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error());
}
// some code
mysql_close($con);
?>
Database Connection
<?php
$db_hostname = ‘localhost’;
$db_database = ‘mydatabase’;
$db_username = ‘’username’
$db_password = ‘password’;
?>
<?php
require_once ‘login.php’;
$database = mysql_connect($db_hostname,
$db_username, $db_password);
…..
……
?>
Creating Databases
• The CREATE DATABASE statement is used to create a
database in MySQL.
Syntax
CREATE DATABASE database_name
Can be executed in three ways:
• Phpmyadmin
• MySQL command line
• Php Code
Creating Databases
•
<?php
$con = mysql_connect("localhost",“username",“password");
if (!$con)
{
die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error());
}
if (mysql_query("CREATE DATABASE my_db",$con))
{
echo "Database created";
}
else
{
echo "Error creating database: " . mysql_error();
}
mysql_close($con);
?>
Creating Databases
The CREATE TABLE statement is used to create a table in
MySQL.
Syntax
CREATE TABLE table_name
(
column_name1 data_type,
column_name2 data_type,
column_name3 data_type,
....
)
Creating Databases
<?php
$con = mysql_connect("localhost",“username",“password");
if (!$con)
{
die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error());
}
// Create database
if (mysql_query("CREATE DATABASE my_db",$con))
{
echo "Database created";
}
else
{
echo "Error creating database: " . mysql_error();
}
// Create table
mysql_select_db("my_db", $con);
$sql = "CREATE TABLE Persons
(
FirstName varchar(15),
LastName varchar(15),
Age int
)";
// Execute query
mysql_query($sql,$con);
mysql_close($con);
?>
Creating Databases
• The INSERT INTO statement is used to add new records to a
database table.
Syntax
It is possible to write the INSERT INTO statement in two forms.
• The first form doesn't specify the column names where the data
will be inserted, only their values:
INSERT INTO table_name
VALUES (value1, value2, value3,...)
• The second form specifies both the column names and the values
to be inserted:
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3,...)
VALUES (value1, value2, value3,...)
Inserting into Databases
<?php
$con =
mysql_connect("localhost",“username",“passw
ord");
if (!$con)
{
die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error());
}
mysql_select_db("my_db", $con);
mysql_query("INSERT INTO Users (FirstName,
LastName, email)
VALUES (‘James',
‘Murphy',’james.murphy@yahoo.com’)");
mysql_close($con);
?>
Database Querying
$query="SELECT * FROM contacts";
$result=mysql_query($query);
• In this case the whole contents of the database
is now contained in a special array with the
name $result.
• Before you can output this data you must
change each piece into a separate variable.
There are two stages to this.
Database Querying
<?php // Make a MySQL Connection
mysql_connect("localhost", "admin", "1admin")
or die(mysql_error());
mysql_select_db("test")
or die(mysql_error());
// Retrieve all the data from the "example" table $result =
mysql_query("SELECT * FROM example")
or die(mysql_error());
// store the record of the "example" table into $row
$row = mysql_fetch_array( $result );
// Print out the contents of the entry echo "Name: ".$row['name'];
echo " Age: ".$row['age']; ?>
Database Querying
'$row = mysql_fetch_array( $result );‘
• mysql_fetch_array returns the first row in a MySQL Resource
in the form of an associative array.
• $result is now a MySQL Resource containing data from your
MySQL table, "example". Data is being stored in $result, but
it is not yet visible to visitors of your website.
• When we pass $result into the mysql_fetch_array function -mysql_fetch_array($result) -- an associative array (name,
age) is returned.
Database Querying
'$row = mysql_fetch_array( $result );‘
• In a MySQL table "example," there are two fields :
name and age. These names are the keys to extracting
the data from our associative array. To get the name we
use $row['name'] and to get the age we
use $row['age'].
• PHP is case sensitive when you reference MySQL
column names, so be sure to use capitalization in your
PHP code that matches the MySQL column names!
Database Querying
<?php
// Make a MySQL Connection
$query = "SELECT * FROM example";
$result = mysql_query($query) or die(mysql_error());
while($row = mysql_fetch_array($result)){
echo $row['name']. " - ". $row['age'];
echo "<br />";
}
?>
Database Querying
<?php
// Make a MySQL Connection
$query = "SELECT * FROM example";
$result = mysql_query($query) or die(mysql_error());
$no_of_rows = mysql_num_rows($result);
For(int $i = 0; $i < $no_of_rows; $i++)
{
$row = mysql_fetch_array($result);
// process rows here
}
?>
MySQLi
MySQL Extensions
• Object Oriented Extensions to MySQL functionality
• Recommended approach to use
• Original procedural approach no longer being maintained
$db = new mysqli('localhost', 'user', 'pass', 'demo');
if($db->connect_errno > 0)
{
die('Unable to connect to database [' . $db>connect_error . ']');
}
MySQL Extensions
$query = "SELECT * FROM `users` WHERE `status`='bonkers'";
$result = $db->query($query)
if($result->num_rows > 0) {
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
echo stripslashes($row['username']);
}
}
else {
echo 'NO RESULTS';
}
// CLOSE CONNECTION
$db->c
MySQL Extensions (Create Table)
<?php
// connect to the MySQL server
$conn = new mysqli('localhost', 'root', 'pass', 'tests');
// check connection
if (mysqli_connect_errno())
{
exit('Connect failed: '. mysqli_connect_error());
}
// sql query for CREATE TABLE
$sql = "CREATE TABLE `users` ( `id` INT(6) UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, `name`
VARCHAR(25) NOT NULL, `pass` VARCHAR(18) NOT NULL, `email` VARCHAR(45), `reg_date`
TIMESTAMP ) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci";
// Performs the $sql query on the server to create the table
if ($conn->query($sql) === TRUE)
{
echo 'Table "users" successfully created';
}
else
{
echo 'Error: '. $conn->error;
}
$conn->close();
?>
MySQL Extensions (Insert Statement)
<?php
// connect to the "tests" database
$conn = new mysqli('localhost', 'root', 'pass', 'tests');
// check connection if (mysqli_connect_errno())
{
exit('Connect failed: '. mysqli_connect_error());
}
// sql query for INSERT INTO users
$sql = "INSERT INTO `users` (`name`, `pass`, `email`) VALUES ('Marius', 'faith',
'name@domain.net')";
// Performs the $sql query on the server to insert the values
If ($conn->query($sql) === TRUE)
{
echo 'users entry saved successfully';
}
else
{
echo 'Error: '. $conn->error;
}
$conn->close(); ?>
MySQL Extensions