August 18, 2015
AMB Country Risk Report
Our Insight, Your Advantage.
Germany
Country Risk Tier
• The Country Risk Tier (CRT) reflects A.M. Best’s assessment
of three categories of risk: Economic, Political and Financial
System Risk.
CRT-1
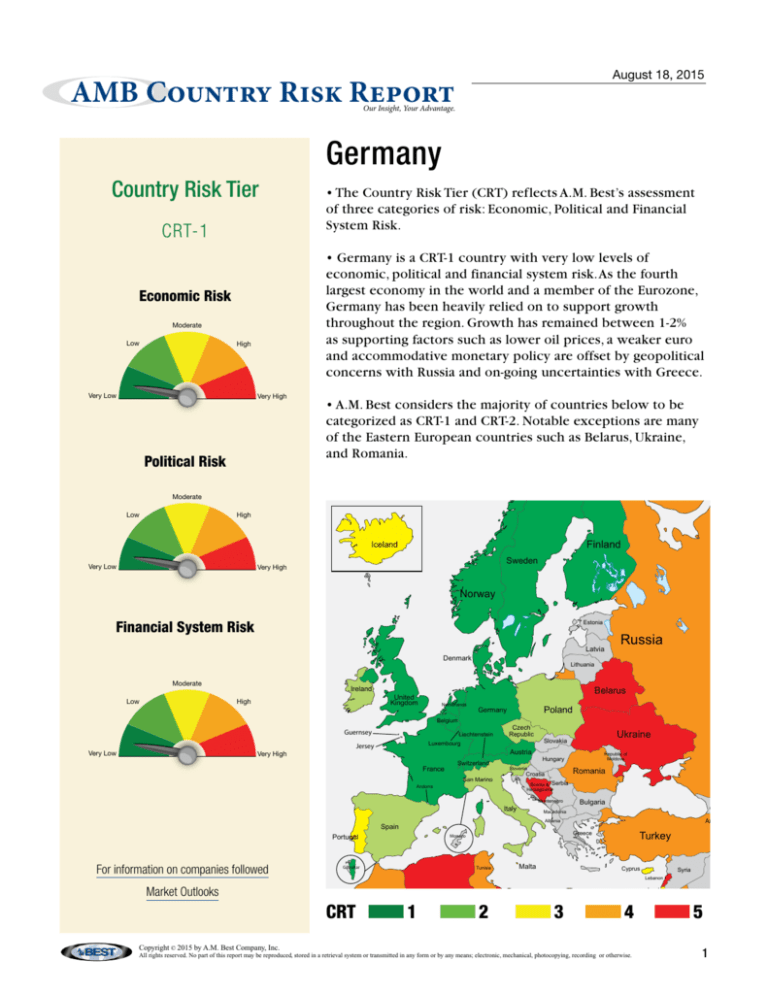
• Germany is a CRT-1 country with very low levels of
economic, political and financial system risk. As the fourth
largest economy in the world and a member of the Eurozone,
Germany has been heavily relied on to support growth
throughout the region. Growth has remained between 1-2%
as supporting factors such as lower oil prices, a weaker euro
and accommodative monetary policy are offset by geopolitical
concerns with Russia and on-going uncertainties with Greece.
Economic Risk
Moderate
Low
High
Very Low
Very High
• A.M. Best considers the majority of countries below to be
categorized as CRT-1 and CRT-2. Notable exceptions are many
of the Eastern European countries such as Belarus, Ukraine,
and Romania.
Political Risk
Moderate
Low
High
Iceland
Greenland
Finland
Iceland
Greenland
Very Low
Sweden
Very High
Norway
Norway
Financial System Risk
Estonia
Isle of Man
Isle of Man
Moderate
Low
Ireland
Denmark
United
Germany
Kingdom
Belgium
Liechtenstein
Guernsey
Luxembourg
Jersey
Very High
Switzerland
San Marino
Slovenia
Croatia
France
Portugal
For information on companies followed
Market Outlooks
Copyright © 2015 by A.M. Best Company, Inc.
as
Dominican
Macedonia
Monaco
Tunisia
Malta
Canary
Islands
Tunisia
Russia
Bulgaria
Macedonia
Turkey
Greece
Cyprus
Malta
Syria
Cyprus
Lebanon
Iraq
Israel
Morocco
Algeria
Azerbaija
Turkey
CRT 1 2 3 4 5
Canary
Islands
Georgia
Armenia
Albania
Monaco
Gibraltar
Morocco
Montenegro
Greece
Portugal
Gibraltar
Bosnia & Serbia
Herzegovina
Italy
Albania
Spain
Romania
Croatia
Bulgaria
Republic of
Moldova
Hungary
Slovenia
Bosnia & Serbia
Herzegovina San Marino
Italy
Ukraine
Republic of
Switzerland
Romania
Montenegro
Azores
Poland
Czech
Ukraine
Republic
Slovakia
Moldova
Austria
Hungary
Andorra
Spain
Belarus
Germany
CzechBelgium
Republic
Slovakia
Liechtenstein
Russia
Lithuania
Poland
Netherlands
Andorra
Azores
Latvia
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Austria
Jersey
France
Estonia
Belarus
Netherlands
Guernsey
Russia
Latvia
Denmark
Ireland
United
Kingdom
High
Very Low
Finland
Sweden
Lebanon
Israel
Jordan
Libya
Algeria
Libya
Egypt
All rights reserved. No part of this report may be reproduced, stored inWestern
a retrieval system
or transmitted in any form or by any means; electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise.
Sahara
(Occupied by Morocco)
Western Sahara
(Occupied by Morocco)
Jordan
Kuwa
Bahrain
Egypt
Saudi
1 Arabia
Qat
AMB Country Risk Report
Germany
Regional Summary: Western Europe
Vital Statistics 2014
• Western Europe is a highly developed
and affluent region. The 28 countries of
the European Union (EU) accounted for
25% of world GDP in 2014. The EU is
facilitating a single European market with
standardized regulatory systems and free
movement of people, goods, services and
capital. The 17 EU members of the eurozone use the euro as their currency.
Nominal GDP
Population
GDP Per Capita
Real GDP Growth
Inflation Rate
Premiums Written (Life)
Premiums Written (Non-Life)
Premiums Growth (2013 - 2014)
USD bn
mil
USD
%
%
USD mil
USD mil
%
3859.55
81.1
47,590
1.6
0.8
118,475
136,170
2.8
Regional Comparison
• Western Europe has been experiencing
a prolonged period of slow economic
growth, with the EU growing 1.4% in
2014. Growth is largely expected to
remain muted at 1.8% and 1.9% in 2015
and 2016 respectively. On-going concerns
over Greece’s economic and political
future have increased the potential
downside risks to growth and stability
throughout the European Union.
Country Risk Tier
CRT-1
CRT-1
CRT-2
CRT-2
CRT-1
CRT-1
Germany
France
Italy
Spain
Switzerland
United Kingdom
Source: IMF, Axco, Swiss Re and A.M. Best
• In March 2015 the European Central
Bank (ECB) launched a program of
Quantitative Easing, expected to last
through September 2016.The program
entails the purchase of 60 Billion EUR of
assets monthly in an effort to boost growth,
encourage lending and increase inflation.
Economic Growth
Economic Risk: Very Low
• Germany is a large, diversified,
competitive and modern economy.
• Unlike most of Europe, Germany enjoys
low unemployment, strong consumer
demand and solid wage growth. Higher
incomes have led to higher savings rates,
consumer deleveraging and a pick up in
consumer spending, as consumers have
gained confidence. It is expected that this
pent-up demand will provide support for
the economy going forward.
• Growth is expected to remain below 2%
near-term, as credit growth remains tepid
and trading partners in the EU continue
to struggle for growth.
6
Real GDP
CPI Inflation
4
2
0
%
2006
2007
2008
2009
2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
2019
2020
-2
-4
-6
-8
Source: IMF World Economic Outlook and A.M. Best
2
AMB Country Risk Report
Germany
Political Risk: Very Low
Political Risk Summary
• Germany is a member of the European
Union and one of the original 11 countries
to adopt the euro as its currency in 1999.
Score 1 (best) to 5 (worst)
Germany
World Average
International Transactions
Policy
5
4
Legal System
• After using expansionary fiscal policy to
help jump-start the economy in 2009, the
government has only modestly tightened
it into 2014. Germany’s public finances,
however, are in much better shape than
most other European countries due to
strong tax revenues, better economic
performance and accommodative
monetary policy. Germany enjoyed a
public-sector surplus of 0.7% in 2014.
Monetary Policy
3
2
1
Regional Stability
Fiscal Policy
0
Social Stability
Business Environment
Government Stability
• Germany will continue to take a lead
role in resolving Eurozone financial
and political issues as it remains one
of the most stable and powerful global
economies. Efforts will concentrate on
more centralized control over budgets
and economic policies as well as strict
budget discipline among member states as
opposed to a collectivization approach.
Labor Flexibility
Source: A.M. Best
• The “grand coalition” government,
comprising 80% of Parliament, has
recently increased spending on pensions,
transportation infrastructure and a new
nationwide minimum wage, which is to be
fully implemented by January 2017.
GDP Per Capita and Population
for Selected Countries
90
100,000
GDP Per Capita
Population
90,000
Financial System Risk: Very Low
80
80,000
• The German insurance sector is
regulated by the Bundesanstalt für
Finanzdienstleistungsaufsicht (BaFin).
70
70,000
60
60,000
40
40,000
30
30,000
20
20,000
10
10,000
0
Germany
France
Source: IMF and A.M. Best
Italy
Spain
Switzerland
United Kingdom
Millions
USD
50
50,000
• The IMF has recently voiced concern
over the German life insurance industry
as persistently low interest rates may give
rise to financial vulnerabilities.The Life
Insurance Reform Act, passed in 2014, is
addressing some of these concerns by
ensuring that life insurance companies
maintain sufficient capital buffers.
0
• Financial regulation and enforcement
are transparent and effective.
3
AMB Country Risk Report
Germany
GUIDE TO BEST’S COUnTry rISk TIErS
A.M. Best defines country risk as the risk that country-specific factors could adversely affect the claims-paying ability of an insurer. Country risk is
evaluated and factored into all Best’s Credit Ratings. Countries are placed into one of five tiers, ranging from “CRT-1” (Country Risk Tier 1), denoting
a stable environment with the least amount of risk, to “CRT-5” (Country Risk Tier 5) for countries that pose the most risk and, therefore, the greatest
challenge to an insurer’s financial stability, strength and performance.
A.M. Best’s Country Risk Tiers are not credit ratings and are not directly comparable to a sovereign debt rating, which evaluates the ability and
willingness of a government to service its debt obligations.
Country risk Tiers
Country risk Tier
Definition
CRT-1
Predictable and transparent legal environment, legal system and business infrastructure; sophisticated financial
system regulation with deep capital markets; mature insurance industry framework.
CRT-2
Predictable and transparent legal environment, legal system and business infrastructure; sufficient financial system
regulation; mature insurance industry framework.
CRT-3
Developing legal environment, legal system and business environment with developing capital markets; developing
insurance regulatory structure.
CRT-4
Relatively unpredictable and nontransparent political, legal and business environment with underdeveloped capital
markets; partially to fully inadequate regulatory structure.
CRT-5
Unpredictable and opaque political, legal and business environment with limited or nonexistent capital markets; low
human development and social instability; nascent insurance industry.
Country risk reports
A.M. Best Country Risk Reports are designed to provide a brief, high-level explanation of some of the key factors that determine a country’s Country
Risk Tier assignment. It is not intended to summarize A.M. Best’s opinion on any particular insurance market or the prospects for that market.
Categories of risk
Country Risk Reports provide scores for three categories of risk for each country. These scores are (1) Very Low; (2) Low; (3) Moderate; (4) High
and (5) Very High.
Category of risk
Definition
Economic Risk
The likelihood that fundamental weaknesses in a country’s economy will cause adverse developments for an insurer.
A.M. Best’s assessment of economic risk evaluates the state of the domestic economy, government finances and
international transactions, as well as prospects for growth and stability.
Political Risk
The likelihood that government or bureaucratic inefficiencies, societal tensions, inadequate legal system or
international tensions will cause adverse developments for an insurer. Political risk comprises the stability of the
government and society, the effectiveness of international diplomatic relationships, the reliability and integrity
of the legal system and of the business infrastructure, the efficiency of the government bureaucracy, and the
appropriateness and effectiveness of the government’s economic policies.
Financial System Risk
Financial system risk (which includes both insurance and non-insurance financial system risk) is the risk that financial
volatility may erupt due to inadequate reporting standards, weak banking system or asset markets, and/or poor
regulatory structure. In addition, it includes an evaluation of whether the insurance industry’s level of development and
public awareness, transparent and effective regulation and reporting standards, and sophisticated regulatory body will
contribute to a volatile financial system and compromise the ability of an insurer to pay claims.
Political risk Summary
To provide additional detail on the political risk in a given domicile the Country Risk Reports include the Political Risk Summary. The Political Risk
Summary is a radar chart that displays scores for nine different aspects of political risk scored on a scale of one to five with one being the least
amount of risk and five being the highest amount of risk.
Category
Definition
International Transactions
Policy
Measures the effectiveness of the exchange rate regime and currency management.
Monetary Policy
Measures the ability of a country to effectively implement monetary policy.
Fiscal Policy
Measures the ability of a country to effectively implement fiscal policy.
Business Environment
Measures the overall quality of the business environment and ease of doing business.
Labor Flexibility
Measures the flexibility of the labor market, including the company’s ability to hire and fire employees.
Government Stability
Measures the degree of stability in a government.
Social Stability
Measures the degree of social stability, including human development and political rights.
Regional Stability
Measures the degree of stability in the region.
Legal System
Measures the transparency and level of corruption in the legal system.
Country risk Tier Disclosure
A Country Risk Tier (CRT) is not a credit rating, rather it represents a component of A.M. Best’s Credit Rating Methodology that is applied to all
insurers. A CRT is not a recommendation to purchase, hold or terminate any security, insurance policy, contract or any other financial obligation
issued by a government, an insurer or other rated issuer, nor does it address the suitability of any particular policy, contract or other financial
obligation for a specific purpose or purchaser.
Copyright © 2015 by A.M. Best Company, Inc.
Version 091714
Copyright © 2015 by A.M. Best Company, Inc.
All rights reserved. No part of this report may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means; electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise.
4












