Chapter 24: Lipids, Fatty Acids & Triglycerides
advertisement

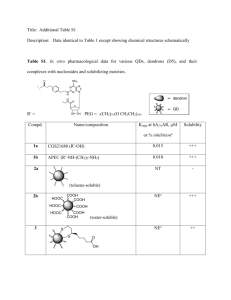
Chapter 24: Lipids, Fatty Acids & Triglycerides Lipids • Organic compounds not soluble in water Vague, overly general definition Waxes Triglycerides Steroids (inc. cholesterol) 1 Fatty Acids • Key components of “triglycerides” • Long-chain carboxylic acids Typically C10 – C20 chain with –COOH group at end • Also phosphoric fatty acids (less common) O O HO – C – (CH2)n – CH3 HO – P – (CH2)n – NH3+ Carboxylic Fatty Acid O– Phosphoric Fatty Acid Lauric Acid, CH3(CH2)10COOH O HO-C ‒ CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 - Polar - Reactive group - Nonpolar - Insoluble in water - Non-reactive - Longer chains ⇒ higher melting Temp (stick to themselves) • Since not water-soluble, not easily ejected by body once consumed (not soluble in blood) • Can be burned by body to generate energy Fatty Acid + O2 CO2 + H2O + energy 2 Saturated Fatty Acid – no double bonds CH3(CH2)16 - COOH COOH Mono-unsaturated: one double bond in chain CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7 - COOH COOH Poly-unsaturated: multiple double bonds CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7 - COOH COOH Saturated Fatty Acid COOH COOH COOH Cis-unsaturated fats COOH COOH COOH Trans-unsaturated fats COOH COOH COOH COOH COOH Cis- fats do not stack Do not stick together Lower melting temperature Less of a health problem Stack together / Stick together Higher melting temperature Clogs arteriers 3 Common Saturated and Unsaturated Fatty Acids # C’s : Structure # Db Bd Common Name Position of Double Bond Melt Point (ºC) SATURATED FATTY ACIDS Lauric Acid 12 : 0 CH3(CH2)10COOH 44 Myristic Acid 14 : 0 CH3(CH2)12COOH 54 Palmitic Acid 16 : 0 CH3(CH2)14COOH 63 Stearic Acid 18 : 0 CH3(CH2)16COOH 70 UNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS Palmitoleic Acid 16 : 1 CH3(CH2)5CH=CH(CH2)7COOH cis-9 0 Oleic Acid 18 : 1 CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH cis-9 16 Linoleic Acid 18 : 2 CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7COOH cis-9,12 -5 Triglycerides • Fatty acids can be burned by body to create energy … But stored in body as triglycerides C-OH C-OH O + 3 C-OH glycerine (1,2,3-propanetriol) HO-C ‒ (CH2)nCH3 triglyceride fatty acid O C ‒ O-C ‒ (CH2)nCH3 O C ‒ O-C ‒ (CH2)nCH3 O C ‒ O-C ‒ (CH2)nCH3 + 3 H2O 4 Esterification Reaction Acid + alcohol → Ester + water ‒OH group and alcohol swap places O O HO ‒ CCH2CH3 CH3O ‒ CCH2CH3 + H2O Ester + CH3OH Esterification Reaction Acid + alcohol → Ester + water O O HO ‒ CCH2CH3 CH3O ‒ CCH2CH3 + H2O Ester + CH3OH O HO ‒ C ‒ (CH2)nCH3 O C-O ‒ C ‒ (CH2)nCH3 C-OH + C-OH C-O - H 2O C-OH C-O 2 more times Triglyceride 5 Fats and Oils • Both are triglycerides made up of fatty acids • Fats: have melting temp’s higher than 25ºC Are solids at room temperature • Oils: have melting temp’s less than 25ºC Are liquids at room temperature O C ‒ O-C ‒ (CH2)nCH3 Fat vs. oil depends on which fatty acids are present O C ‒ O-C ‒ (CH2)nCH3 O C ‒ O-C ‒ (CH2)nCH3 Composition of Common Fats & Oils Saturated C12 Lauric C14 C16 Myristic Palmitic Unsaturated C18 Stearic C18 Oleic (cis) C18 Linoleic (cis,cis) 44 58 63 70 4 -5 Lard - 1 25 15 50 6 Butter 2 10 25 10 25 5 Human fat 1 3 25 8 46 10 Whale blubber - 8 12 3 35 10 Corn - 1 8 4 46 42 Olive - 1 5 5 83 7 Peanut - - 7 5 60 20 Soybean - - 7 4 34 53 Melting Temp (C) Animal Fat Vegetable Oil 6