Link to Brain topography pdf
advertisement

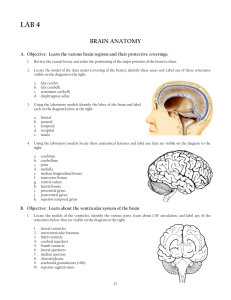
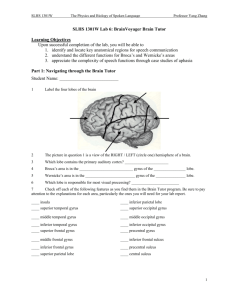
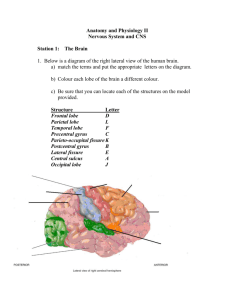
TOPOGRAPHY T1 Division of Cerebral Cortex into Lobes 1. Lateral View of Lobes in Left Hemisphere 2. Medial View of Lobes in Right Hemisphere PARIETAL FRONTAL INSULAR: buried in lateral fissure FRONTAL LIMBIC PARIETAL OCCIPITAL OCCIPITAL TEMPORAL TEMPORAL 3. Dorsal View of Lobes 4. Ventral View of Lobes PARIETAL TEMPORAL LIMBIC FRONTAL OCCIPITAL FRONTAL OCCIPITAL Comment: The cerebral lobes are arbitrary divisions of the cerebrum, taking their names, for the most part, from overlying bones. They are not functional subdivisions of the brain, but serve as a reference for locating specific functions within them. The anterior (rostral) end of the frontal lobe is referred to as the frontal pole. Similarly, the anterior end of the temporal lobe is the temporal pole, and the posterior end of the occipital lobe the occipital pole. TOPOGRAPHY T2 central sulcus central sulcus parietal occipital frontal lateral sulcus temporal lateral sulcus SUMMARY CARTOON: GYRI SUMMARY CARTOON: LOBES Lateral View of Left Hemisphere central sulcus superior frontal gyrus precentral gyrus postcentral gyrus superior parietal lobule intraparietal sulcus inferior parietal lobule: supramarginal and angular gyri middle frontal gyrus parieto-occipital sulcus incision for close-up below OP T inferior frontal gyrus: O-orbital T-triangular OP-opercular O cerebellum lateral sulcus preoccipital notch superior, middle and inferior temporal gyri Lateral View of Insula central sulcus insula cut surface corresponding to incision in above figure superior temporal gyrus Comment: Insula (insular gyri) exposed by removal of overlying opercula (“lids” of frontal and parietal cortex). TOPOGRAPHY T3 Language sites and arcuate fasciculus. MRI reconstruction from a volunteer. central sulcus supramarginal site (posterior Wernicke’s) Language sites (squares) approximated from electrical stimulation sites in patients undergoing operations for epilepsy or tumor removal (Ojeman and Berger). Broca’s site superior temporal site (anterior Wernicke’s) corpus callosum arcuate fasciculus supramarginal site (posterior Wernicke’s) superior temporal site (anterior Wernicke’s) Broca’s site Dissection of arcuate fasciculus transverse temporal gyrus central sulcus arcuate fasciculus visual radiation caudate Broca’s site arcuate fasciculus Broca’s region superior temporal gyrus supramarginal site (posterior Wernicke’s) TOPOGRAPHY T4 Lateral Dissections central sulcus cut surface of middle frontal gyrus supramarginal gyrus lateral fissure putamen middle temporal gyrus external capsule pons medulla spinal cord central sulcus pyramidal cell in precentral gyrus corona radiata internal capsule fiber in cerebral peduncle fiber in base of pons fiber in pyramid pyramidal decussation T5 TOPOGRAPHY Dorsal View of Brain LEFT HEMISPHERE RIGHT HEMISPHERE superior frontal gyrus longitudinal fissure middle frontal gyrus superior frontal sulcus precentral sulcus central sulcus precentral gyrus postcentral sulcus postcentral gyrus superior parietal lobule intraparietal sulcus parieto-occipital fissure Posterior View of Brain occipital lobe longitudinal fissure parieto-occipital sulcus falx lies between the cerebral hemispheres in the longitudinal fissure occipital lobe tentorium lies between occipital lobes and cerebellum cerebellum medulla T6 TOPOGRAPHY B B central sulcus A parietooccipital fissure A lateral fissure A FRONTAL LOBE longitudinal fissure corpus callosum caudate nucleus thalamus central sulcus lateral fissure intraparietal sulcus parietooccipital fissure lateral ventricle: posteriorhorn OCCIPITAL LOBE B parietooccipital fissure occipital pole cerebellum parietooccipital fissure corpus callosum caudate nucleus thalamus lateral fissure lateral ventricle: inferior horn T7 TOPOGRAPHY Dorsal View of Brain LEFT RIGHT frontal lobe genu of corpus callosum body of corpus callosum genu of corpus callosum caudate nucleus occipital lobe splenium of corpus callosum internal capsule thalamus transverse temporal gyrus choroid plexus posterior horn of lateral ventricle splenium of corpus callosum T8 TOPOGRAPHY Dorsal View anterior horn of lateral ventricle caudate nucleus internal capsule thalamus amygdala inferior horn of lateral ventricle hippocampus fimbria corpus callosum internal capsule fornix caudate nucleus amygdala thalamus fornix inferior horn of lateral ventricle fimbria hippocampus posterior horn of lateral ventricle TOPOGRAPHY T9 Medial View of Right Hemisphere central sulcus cingulate gyrus parieto-occipital fissure corpus callosum: cuneus (cuneate gyrus ) body calcarine fissure splenium fornix genu septum pellucidum thalamus midbrain cerebellar vermis lingual gyrus pons subcallosal gyrus anterior commissure optic chiasm interventricular foramen and hypothalamus medulla cerebral aqueduct and fourth ventricle superior and inferior colliculi Medial View of Right Hemisphere: Brain Stem and Septum Pellucidum Removed cingulate gyrus corpus callosum fornix caudate isthmus of cingulate gyrus part of thalamus remaining after removal of brainstem subcallosal gyrus uncus fimbria at edge of hippocampus (not seen) anterior commissure parahippocampal gyrus lamina terminalis optic chiasm column of fornix entering dissected hypothalamus TOPOGRAPHY T10 Magnetic Resonance Scan: midline septum pellucidum corpus callosum cingulate gyrus parieto-occipital fissure calcarine fissure superior and inferior colliculi cerebral aqueduct fornix third ventricle midbrain optic nerve cerebellar vermis pituitary fossa pons medulla spinal cord fourth ventricle TOPOGRAPHY T11 1. Septum Pellucidum, Hypothalamus & Most of Thalamus Removed fornix parieto-occipital fissure body of corpus callosum cingulate gyrus calcarine sulcus head of caudate nucleus anterior commissure vermis pons 2. Remaining Thalamus & Fornix Removed cingulate gyrus thalamus uncus cerebral peduncle head of caudate nucleus genu of corpus callosum parieto-occipital fissure calcarine sulcus internal capsule vermis pons 3. Caudate Removed cingulum splenium of corpus callosum anterior commissure cingulate gyrus substantia nigra cerebral peduncle body of corpus callosum internal capsule anterior commissure vermis pons uncus substantia nigra cerebral peduncle uncus TOPOGRAPHY OF THE CNS T12 Ventral View of Brain frontal pole olfactory bulb and olfactory tract orbital gyri lateral sulcus FRONTAL LOBE optic nerve, optic chiasm and optic tract temporal pole inferior temporal gyrus collateral sulcus TEMPORAL LOBE floor of hypothalamus (tuber cinereum) lateral and medial occipitotemporal gyri BASE OF PONS cerebral peduncle mammillary mammillary body body of hypothalamus parahippocampal gyrus trigeminal nerve MEDULLA olive flocculus (part of cerebellum) CEREBELLUM pyramid tonsil (part of cerebellum) occipital pole Comment: The ventral surface of the brain is especially important. It is here that the blood supply to the brain enters. The brain stem and many of the cranial nerves are visible. In addition, one can see the cerebellum, portions of the frontal, temporal and occipital lobes, and the floor of the diencephalon. And it is also here that the pituitary gland (not shown) is attached to the hypothalamus by the small infundibulum (posterior to the optic chiasm). T13 TOPOGRAPHY Cranial Nerves: Numbers and Names I . Olfactory bulb: olfactory nerves (in the nasal epithelium) terminate in the bulb. orbital gyri Olfactory tract straight (rectus) gyrus II. Optic nerve: The cell bodies of origin are in the retina. Half the axons cross (optic chiasm) to the opposite optic tract, half continuing to help form the optic tract of the same side. infundibulum and tuber cinereum Optic chiasm and optic tract mammillary body (nucleus) III. Oculomotor nerve IV. Trochlear nerve cerebral peduncle pons middle cerebellar peduncle V. Trigeminal nerve VI. Abducens nerve VII. Facial nerve nerve VIII. Vestibulocochlear nerve pyramid XII. Hypoglossal nerve rootlets olive X. Vagus nerve rootlets IX. Glossopharyngeal and XI. Accessory (cranial) nerve rootlets are too small to see here: position is rostral and caudal to the vagus in the same line TOPOGRAPHY T14 Ventral View Dissections olfactory tract frontal pole optic chiasm hypothalamus temporal pole mammillary nucleus (body) amygdala optic tract hippocampus uncus cerebral peduncle parahippocampal gyrus substantia nigra cerebral aqueduct splenium of corpus callosum occipital pole olfactory bulb infundibulum amygdala optic tract inferior horn of lateral ventricle uncus hippocampus parahippocampal gyrus mammillary body cerebral peduncle midbrain posterior horn of lateral ventricle splenium of corpus callosum TOPOGRAPHY T15 Ventral Dissection: Optic Radiation RIGHT LEFT olfactory bulb and tract optic nerve, chiasm and tract middle cerebral artery infundibulum and hypothalamus hypothalamus dura cerebral peduncle oculomotor nerve optic radiation: temporal (Meyer’s) loop substantia nigra lateral geniculate medial geniculate parahippocampal gyrus pulvinar optic radiation splenium of corpus callosum midbrain dissected lower bank of calcarine fissure TOPOGRAPHY T16 BRAINSTEM 1. Medial view of right hemisphere corpus callosum fornix septum pellucidum pineal anterior commissure thalamus cerebellar vermis midbrain hypothalamus pons optic chiasm mammillary body superior & inferior colliculus cerebral aqueduct medulla fourth ventricle 3. Posterior view: cerebellum removed 2. Anterior view superior colliculus internal capsule striatum cerebral peduncle pons inferior olive inferior colliculus optic chiasm and tract cerebral peduncle hypothalamus superior cerebellar peduncle cerebellar hemisphere middle cerebellar peduncle VIII flocculus floor of 4th ventricle tonsil medulla pyramid 4. Lateral view from left side cerebral peduncle optic tract hypothalamus cerebellar hemisphere trigeminal nerve (V) flocculus pons tonsil pyramid inferior olive medulla inferior cerebellar peduncle