Grading Recommendations In the summary table below and the rest
advertisement

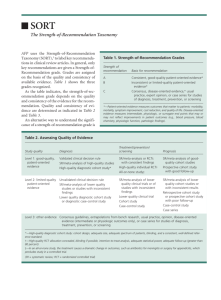
Grading Recommendations In the summary table below and the rest of this document we use the Strength of Recommendation Taxonomy (SORT) proposed by Ebell and colleagues (1) to grade recommendations based on the quality and consistency of relevant evidence: Strength of Recommendation A B C Best Available Supporting Evidence Consistent and good quality patient-oriented evidence1 Inconsistent and/or limited quality patient-oriented evidence Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented2 evidence or, case series 1 Patient-oriented evidence measures outcomes that matter to patients: morbidity, mortality, symptom improvement, cost reduction and quality of life. 2 Disease-oriented evidence measures intermediate, physiologic, or surrogate end points that may or may not reflect improvement in patient-oriented outcomes. Reference 1. Ebell MH, Siwek J, Weiss BD, Woolf SH, et al. Strength of recommendation taxonomy (SORT): A patient-centered approach to grading evidence in the medical literature. J Family Practice 2004;53:111-20.