Superposition and Wave interference
advertisement

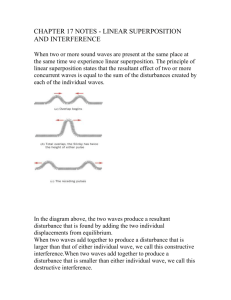
SPH3UW Notes Superposition and Interference Page 1 of 6 Physics Tool box Constructive Interference: refers to when waves build up each other, resulting in the medium having larger amplitude. Destructive interference: occurs when waves diminish one another and the amplitude of the medium is less than it would have been for either of the interfering waves acting alone. Superposition: the simple algebraic sum of the values of a wave. Node: : a point that remains at rest Antinode: point midway between the nodes where maximum constructive interference occurs. When waves are combined, only certain allowed frequencies can exist on systems with boundary conditions. It is the understanding of this behaviour that demonstrates why a large array of musical instruments can produce he sounds they generate. When two sound waves having nearly the same frequency interfere, we hear a variation in the loudness of the tone (called beats). The beat frequency corresponds to the rate of alternation between constructive and destructive interference between the waves. Superposition and Wave interference In nature most interesting wave phenomena cannot be produced by single travelling waves, Instead, we need to analyse the interactions of multiple traveling waves. The analysis of the combination of these multiple travelling waves requires the application of the Superposition Principle. When two or more traveling waves are moving through a medium, the resultant value of the wave function at any point is simply the algebraic sum of the values of the wave functions of the individual waves. One of the amazing consequences of the superposition principle is that two traveling waves can actually pass through each other without being destroyed or even altered.as seen on the image on the right. Wave interference is the phenomenon that occurs when two waves meet while traveling along the same medium. The interference of waves causes the medium to take on a shape that results from the net effect of the two individual waves upon the particles of the medium. This type of interference is probren down into two types Constructive Interference is a type of interference that occurs at any location along the medium where the two interfering waves have a displacement in the same direction. In this case, both waves have an upward displacement; consequently, the medium has an upward displacement that is greater than the displacement of the two interfering pulses. Constructive SPH3UW Superposition and Interference Page 2 of 6 interference is observed at any location where the two interfering waves are displaced upward. But it is also observed when both interfering waves are displaced downward. Destructive interference is a type of interference that occurs at any location along the medium where the two interfering waves have a displacement in the opposite direction. The consequence of a destructive interference is a final displacement that is less than the displacement of the two interfering pulses. When we have a single generator producing two vibrating point sources, the created waves will have the same wavelength, amplitude and phase ( the particular point in the cycle of each wave is the same). As these wave move from their point souses they will interfere. Sometimes crest to crest and trough to trough, and at other times crest to trough. This will create patterns of contrastive and destructive interference. As the waves move out from the sources, a symmetrical pattern will be produced, creating nodal lines (areas of destructive interference where the point remains at rest) and areas of constructive interference. SPH3UW Superposition and Interference Page 3 of 6 You will notice that the nodal lines appears to be straight lines, but actually they are curved lines following a hyperbolic path. When the frequency of the sources is increased the wavelength also decreases thus bringing the nodal lines closer together (also increasing the number). Node: a point that remains at rest Antinode: point midway between the nodes where maximum contructive interference occurs. Standing Wave If two waves with identical wavelengths and amplitudes are traveling in the opposite directions, the resulting interference patterns will produce some interesting interactions. A standing wave, such as the one shown in Figure below , is an oscillation pattern with a stationary outline SPH3UW Superposition and Interference Page 4 of 6 that results from the superposition of two identical waves traveling in opposite directions. Example If the wavelength of the wave generated is 0.25 m, and the frequency of generated wave is 4 Hz, what is the waves speed? Solution: v f 4 Hz 0.25m 1.0 m s Example The distance between two successive nodes in a vibrating rope is 20cm. The frequency of the source is 40 Hz. What is the wavelength? What is the speed of the nodes? Solution: The distance between any two successive nodes is Therefore 1 20cm 2 40cm v f 40 Hz 40cm 1.6 102 cm s Mechanical Resonance 1 2 SPH3UW Superposition and Interference Page 5 of 6 SPH3UW Superposition and Interference Extra Notes and Comments Page 6 of 6