HiPer® Protein Estimation Teaching Kit (Quantitative)
advertisement

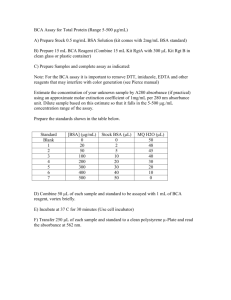
HiPer® Protein Estimation Teaching Kit (Quantitative) Product Code: HTBC005 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment Protocol Biuret assay:1 hour Folin – Lowry Assay: 2 hours Bradford assay: 1 hour Storage Instructions: The kit is stable for 6 months from the date of receipt Store all the kit contents as specified in the brochure 1 Index Sr. No. Contents Page No. 1 Aim 3 2 Introduction 3 3 Materials Required But Not Provided 3 4 Storage 3 5 Biuret Assay 3 6 Folin – Ciocalteau (Lowry) Assay 7 6 Principle Kit contents Important Instructions Procedure Observation and Result Interpretation Dye Binding (Bradford) Assay 8 Principle Kit contents Important Instructions Procedure Observation and Result Interpretation 9 Principle Kit contents Important Instructions Procedure Observation and Result Interpretation Troubleshooting Guide 12 2 Aim: To determine the concentration of a protein by three commonly used methods: 1. Biuret Assay 2. Folin – Ciocalteau (Lowry) Assay 3. Dye Binding (Bradford) Assay Introduction: HiPer® Protein Estimation Teaching Kit is designed for rapid and accurate determination of proteins by three most commonly used techniques, each having features that suit it to a particular use. It enables the determination of the concentration of proteins which is frequently required in biochemical work. There is no completely satisfactory single method to determine the concentration of protein in any given sample. Most protein assays take advantage of a reaction between a reagent dye and the protein of interest that will shift or increase the absorbance of a particular wavelength. The choice of the method depends on the nature of the protein, the nature of the other components in the protein sample, desired speed, accuracy and sensitivity of the assay. Materials Required But Not Provided: Glass wares: 1 ml and 10 ml Pipettes, cuvettes, test tubes Reagents: Distilled Water Other requirements: Spectrophotometer/Colorimeter to determine the absorbance in given range, Micropipette and tips, test tube stand Storage: HiPer® Protein Estimation Teaching Kit can be stored at 2-8oC for up to 6 months without showing any reduction in performance. Read Important Instructions before starting the experiment. Store all the reagents as specified in the brochure. 1. Biuret Assay for Protein Estimation: Principle: The Biuret is a general protein assay for batches of material for which yield is not a problem. In Biuret reaction peptides containing three or more amino acid residues form a colored chelate complex with cupric ions (Cu2+) in an alkaline environment containing sodium potassium tartrate. This became known as the biuret reaction because it is chemically similar a complex that forms with the organic compound biuret (NH2-CO-NH-CO-NH2) and the cupric ion. Biuret, a product of excess urea and heat, reacts with copper to form a light blue tetradentate complex. Fig 1: Biuret Reaction 3 Single amino acids and dipeptides do not give the biuret reaction, but tripeptides and larger polypeptides or proteins will react to produce the light blue to violet complex that absorbs light at 540 nm. One cupric ion forms a colored coordination complex with four to six nearby peptide bonds. The intensity of the color produced is proportional to the number of peptide bonds participating in the reaction. Thus, the biuret reaction is the basis for a simple and rapid colorimetric reagent of the same name for quantitatively determining total protein concentration. Kit Contents: Table 1: Enlists the materials provided in this kit for Biuret assay with their quantity and recommended storage Quantity Sr. No. Product Code Materials Provided Storage 5 expts 4 ml -200C Biuret Reagent 110 ml 2-80C TKC228 Protein Sample 1 1.2 ml -200C TKC229 Protein Sample 2 1.2 ml -200C 1 TKC226 Protein Standard (50 mg/ml) 2 TKC227 3 4 Important Instructions: 1. Read the entire procedure carefully before starting the experiment. 2. All glasswares must be clean and protein free, otherwise it will interfere with the assay. 3. The unknown and standard samples should be treated identically for accurate results. 4. The assay should be carried out at the same time and in the same buffer conditions. 5. Protein test samples provided are of different concentrations. (Protein Sample 1 and 2) Procedure: 1. Take nine tubes and label them as Blank and 1 to 8. 2. Make dilutions of Protein (BSA) standards with concentrations of 10, 8, 6, 4, 2, 1 mg/200 ul by transferring respective amount of BSA from the standard protein solution (50 mg/ml) and adjusting it to a total volume of 200 µl by adding distilled water as mentioned in table 2. 3. Add 2 ml of Biuret reagent to each test tube including the Blank and Unknown tubes. Mix well. 4. Keep at room temperature for 10 minutes. 5. Switch on the Spectrophotometer, select the wavelength at 540 nm and let it warm before taking the absorbance (OD). First take the OD of Blank and make it zero. 4 6. Remove Blank tube and take the OD of all the tubes and record it. Wash the cuvette after taking OD of each sample. Table 2: Tube No. Conc. of BSA (mg) Amt of Stock (µl) Amt of Distilled Water (µl) Amt of Biuret reagent (ml) Blank 1 2 3 4 5 6 0.0 1 2 4 6 8 10 0.0 20 40 80 120 160 200 200 180 160 120 80 40 0.0 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 7 Test sample 1 8 Test Sample 2 200 µl 200 µl 2 2 Keep at room temperature for 10 minutes Absorbance at 540 nm 7. Plot a Standard Curve of absorbance at 540 nm on “Y” axis versus concentration of protein mg/200 µl on “X” axis. 8. Record the value “x” of Unknown from graph corresponding to the optical density reading of the test sample. Deatermination of Protein Concentration in Unknown Sample: Protein concentration can be calculated using following formula: Concentration of Unknown in “mg” Protein Concentration in Test Sample = -------------------------------------------- x 1000 mg/ml Volume of sample in “µl” Observation and Result: 1 2 3 Fig 2: In Biuret Protein Assay the intensity of the colour increases with increasing protein concentration 5 Absorbance at 540 nm Standard Curve for Protein Estimation by Biuret Method 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Protein Concentration m g/200µl Interpretation: The Biuret method is carried out by preparing a set of solutions with known protein concentrations and mixing them with the Biuret reagent. A standard curve can be made and the concentrations of unknown protein sample can be derived from the standard curve 2. Folin – Ciocalteau (Lowry) Assay for Protein Estimation: Principle: The Lowry’s method utilizes phenol reagent of Folin and Ciocalteau. This is essentially phosphotungstic phosphomolybdic acid which can be reduced by phenols and many other substances with phenolic rings to ‘molybdenum blue’. Proteins reduce phenol reagent, which may be used therefore for their determination. However, the amount of colour varies greatly with different proteins because it is entirely proportional to their content of tyrosine and tryptophan, other amino acids having little effect. Pretreatment of proteins with alkali and a trace of copper salt greatly increases the colour that is absorbed maximally at 750 nm. Fig 3: Folin Lowry Reaction 6 Kit Contents: Table 3: Enlists the materials provided in this kit for Lowry assay with their quantity and recommended storage Quantity Sr. No. Product Code Materials Provided 1 TKC230 Protein Standard (1mg/ml) 2 3 TKC231 TKC232 Folin’s Reagent (2N) Solution A 4 TKC233 Solution B 5 6 7 TKC329 TKC234 TKC235 Solution C Protein Sample 1 Protein Sample 2 5 expts Storage 4 ml -200C 15 ml 180 ml RT RT 2 ml RT 2 ml 1.2 ml 1.2 ml RT -200C -200C Important Instructions: 1. Read the entire procedure carefully before starting the experiment. 2. All glasswares must be clean and protein free, otherwise it will interfere with the assay. 3. The unknown and standard samples should be treated identically for accurate results. 4. The assay should be carried out at the same time and in the same buffer conditions. 5. Protein test samples provided are of different concentrations. (Protein Sample 1 and 2) 6. Preparation of 1N Folin’s Reagent (5ml): Dilute Folin’s reagent (2N) with equal amount of Distilled water on the day of use. ( 2.5 ml of Folin’s reagent + 2.5 ml of Distilled water) 7. Preparation of Alkaline Copper Reagent (30 ml): Mix 29.4 ml of Solution A with 0.3 ml of Solution B and 0.3 ml of Solution C on the day of use. Procedure: 1. Take ten tubes and label them as Blank and 1 to 9. 2. Make dilutions of Protein (BSA) standards with concentrations of 200, 160, 120, 80, 40, 20, 10 µg/200 ul by transferring respective amount of BSA from the standard protein solution (1 mg/ml) and adjusting it to a total volume of 200 µl by adding distilled water as mentioned in table 4. 3. Add 3 ml of Alkaline Copper reagent to each test tube including the Blank and Unknown tubes. Mix well. 4. Keep at room temperature for 10 minutes. 5. Add 0.5 ml of 1N Folin’s reagent to each test tube. Vortex the tubes and keep in Boiling Water Bath for 10 minutes 6. Switch on the Spectrophotometer, select the wavelength at 750 nm and let it warm before taking the absorbance (OD). First take the OD of Blank and make it zero 7 7. Remove Blank tube and take the OD of all the tubes and record it. Wash the cuvette after taking OD of each sample. Table 4: Tube No. Conc. of BSA (µg) Amt of Stock (µl) Amt of diluent (µl) Alkaline Copper Reagent Blank 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Test sample 1 9 Test Sample 2 0.0 10 20 40 80 120 160 200 0.0 10 20 40 80 120 160 200 200 190 180 160 120 80 40 0.0 200 µl 200 µl 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 0.5 0.5 0.5 Keep at Room temperature for 10 minutes Amt of Folin’s Reagent (ml) 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 Vortex and keep in Boiling Water Bath for 10 minutes Absorbance at 750 nm 8. Plot a Standard Curve of absorbance at 750 nm on “Y” axis versus concentration of protein µg/200 µl on “X” axis. 9. Record the value “x” of Unknown from graph corresponding to the optical density reading of the test sample. Deatermination of Protein Concentration in Unknown Sample: Protein concentration can be calculated using following formula: Protein Concentration in Test Sample = Concentration of Unknown in “µg” ------------------------------------------ x 1000 µg/ml Volume of sample in “µl” Observation and Result: 1 2 3 Fig 4: In Folin Lowry Protein Assay the intensity of the colour increases with increase in protein concentration 8 Absorbance at 750 nm Standard Curve for Protein Estimation by Folin Lowry Method 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 50 100 150 200 250 Protein Concentration µg/200 µl Interpretation: The Lowry’s method of protein estimation is carried out by preparing a set of solutions with known protein concentrations and mixing them with the Folin’s reagent. A standard curve can be made and the concentrations of unknown protein sample can be derived from the standard curve. 3. Bradford Assay for Protein Estimation: Principle: Bradford Assay for protein estimation is a rapid, simple and sensitive method for estimation. The dye used in this method, Coomassie brilliant Blue G – 250 has an absorbance maximum of 465 nm in unbound state. When it interacts with proteins, the dye turns blue in colour and the complex formed has a λ max of 595 nm. Thus proteins can be estimated at 595 nm and the coloured complex formed is stable for one hour. Fig 5: Bradford reaction 9 Kit Contents: Table 5: Enlists the materials provided in this kit for Bradford assay with their quantity and recommended storage Sr. No. Product Code Quantity Materials Provided Storage 5 expts 1 TKC230 Protein Standard (1 mg/ml) 0.4 ml -200C 2 TKC236 Bradford’s Reagent 45 ml 2- 80C 3 TKC237 Protein Sample 1 1.2 ml -200C 4 TKC238 Protein Sample 2 1.2 ml -200C Important Instructions: 1. Read the entire procedure carefully before starting the experiment. 2. All glasswares must be clean and protein free, otherwise it will interfere with the assay. 3. The unknown and standard samples should be treated identically for accurate results. 4. The assay should be carried out at the same time and in the same buffer conditions. 5. Protein test Samples provided are of different concentrations. (Protein Sample 1 and 2) Procedure: 1. Take eight tubes and label them as Blank and 1 to 7. 2. Make dilutions of Protein (BSA) standards with concentrations of 20, 16, 12, 8, 4 µg/200 µl by transferring respective amount of BSA from the standard protein solution (1mg/ml) and adjusting it to a total volume of 200 µl by adding distilled water as mentioned in table 6. 3. Add 1ml of Bradford’s reagent to each test tube including the Blank and Unknown tubes. Mix the contents of each tube thoroughly by vortexing the tubes and incubate at RT for 10 minutes. 4. Switch on the Spectrophotometer, select the wavelength at 595 nm and let it warm before taking the absorbance (OD). First take the OD of Blank and make it zero. 5. Remove Blank tube and take the OD of all the tubes within one hour and record it. Wash the cuvette after taking OD of each sample. 10 Table 6: Tube No. Conc. of BSA (µg) Amt of Stock (µl) Amt of diluent (µl) Amt of Bradford Reagent (ml) Blank 1 2 3 4 5 0.0 4 8 12 16 20 0.0 4 8 12 16 20 200 196 192 188 184 180 1 1 1 1 1 1 6 Test sample 1 7 Test Sample 2 200 µl 200 µl 1 1 Vortex the tubes and incubate at RT for 10 minutes Absorbance at 595 nm 6. Plot a Standard Curve of absorbance at 595 nm on “Y” axis versus concentration of protein µg/200 µl on “X” axis. 7. Record the value “x” of Unknown from graph corresponding to the optical density reading of the test sample. Deatermination of Protein Concentration in Unknown Sample: Protein concentration can be calculated using following formula: Protein Concentration in Test Sample = Concentration of Unknown in “µg” -------------------------------------------- x 1000 µg/ml Volume of sample in “µl” Observation and Result: 1 2 3 Fig 6: In Bradford Assay the intensity of colour increases with increasing protein concentration 11 Absorbance at 595 nm Standard Curve for Protein Estimation by Bradford Method 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 Protein Concentration µg/200 µl Interpretation: The Bradford’s method of protein Estimation is carried out by preparing a set of solutions with known protein concentrations and mixing them with the Bradford reagent. A standard curve can be made and the concentrations of unknown protein sample can be derived from the standard curve. Trouble shooting Guide: Sr.No. 1. Problem Standards and Samples give lower OD values than expected although the Blank is ok Possible Cause Solution Biuret, Folin’s and Bradford’s reagents were not stored properly Always store reagents as mentioned in the brochure Samples were cold while performing the reaction Allow samples to come to RT before starting the reaction Dye Precipitation was seen in Bradford’s reagent Filter the reagent before use Absorbance was not measured at correct wavelength Measure absorbance at correct wavelength as mentioned in the brochure Technical Assistance: At HiMedia we pride ourselves on the quality and availability of our technical support. For any kind of Technical assistance mail at mb@himedialabs.com 12 Notes: Sr No Biuret Assay 1 Reproducibility 2 Sensitivity 3 Accuracy 4 Range of Protein Concentration 5 Specificity 6 Interfering Agents Low Folin Lowry Assay Moderate Bradford’s Assay High 1 – 20 µg (Micro assay) & 20 – 200 µg (Macro Assay) 1 – 50 mg Wide Range Low Moderate High Ammonium Salts Strong Acids , Buffers Ammonium Sulphate Surfactants PIHTBC005_O/0514 HTBC005-03 PROTEIN 13