Things that make you go hmmm:
advertisement

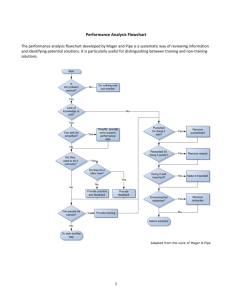
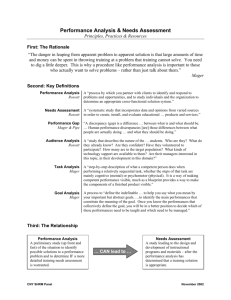
Things that make you go hmmm: Managing Performance Program overview • • • • • Welcome and introductions Performance management issues What is performance management anyway? Recognising and promoting good performance Responding to poor performance: – Causes of poor performance – An analysis framework (Mager and Pipe) • Self-management and support for supervisors • Close Groupwork • Discuss the following questions: – What are the performance management issues facing you in your workplace? – What is easier – managing good performance or poor performance? – What are we more likely to notice and respond to – good performance or poor performance? • Feedback to whole group What is performance management? • http://www.flinders.edu.au/ppmanual/staff/performance-management/gen-staff-perfreview-and-dev-procedures.cfm • The Performance Review and Development process is the central element of performance management at Flinders University – Provides a clear framework for understanding expectations and roles/responsibilities – Documents the annual discussion of performance outcomes and objectives – Often misunderstood as a “once-a-year” event, instead of a holistic approach to managing the workplace Yes, but what’s it for? • Performance management frameworks traditionally serve 3 purposes: – Strategic – linking employee activities with the organisational goals – Developmental – developing employees who are effective at their jobs – Administrative – helps make important decisions, eg: increments, promotions, retention, termination, retrenchment and recognition • Which of these purposes does the Flinders University model serve? Reference: De Cieri, H (2008) Human resource management in Australia: Strategy people, performance, North Ryde NSW: McGraw‐Hill Australia Pty Ltd. Managing staff performance High Ability Low Ability High Motivation Low Motivation Solid performers Reward good performance Identify development opportunities Provide honest and direct feedback Misdirected effort Coaching Frequent performance feedback Goal setting Training or temporary assignment for skill development Restructured job assignment Under-utilisers Give honest and direct feedback Provide counselling Use team building and conflict resolutions Link rewards to performance outcomes Offer training for needed knowledge or skills Stress management Deadwood Withholding pay increases Demotion Outplacement Firing Specific, direct feedback on performance problems Reference: De Cieri, H (2008) Human resource management in Australia: Strategy people, performance, North Ryde NSW: McGraw‐Hill Australia Pty Ltd. Sharing the love: good performers • http://www.flinders.edu.au/hr/recognising-rewarding-staff-guidelines-forsupervisors.cfm • Key strategies for general staff outlined in policy and procedures: – – – – – – – – Attraction and retention allowance Accelerated confirmation of probation Incremental progression Accelerated progression through linked positions Higher duty / temporary secondment General staff conference scheme Professional development and training opportunities Awards – University and cost-centre • Anything else? When performance goes bad • Poor performance can be the result of a combination of influences: – – – – Organisational policies and practices Job concerns Personal problems External factors • Understanding the cause of poor performance provides a framework for appropriate management strategies • Not all causes of poor performance can be remedied Reference: Nankervis A R, Compton RL & Baird, M (2008) Human resource management: Strategies and processes, South Melbourne Vic: Thomson Learning Australia. Groupwork • Discuss what issues and factors can be considered under each of the 4 sources of ineffective performance: – Organisation policies and practices; eg ineffective recruitment – Job concerns, eg unclear or constantly changing work requirements – Personal problems, eg conflict between work demands and family demands – External factors, eg union-management conflict • Feedback to large group Analysing performance problems • Framework from Mager and Pipe (2007) • Identifies a process for working through performance problems including some strategies • Flow chart based, but not necessarily linear • Solutions can be broader than those described (but the answer to performance problems is not always more training!) Stage I: What’s the problem? • Whose performance is at issue? • Why do I (or someone else) think there’s a problem? • Describe the perceived performance discrepancy, eg: – What is the actual performance at issue? – What is the desired performance? Reference: Mager R F & Pipe P (2007) Analyzing performance problems or you really oughta wanna, 3rd ed, Atlanta, Georgia : CEP Press. Stage II: Is it worth pursuing? • What would happen if I left it alone? • Are my expectations reasonable? • Does the discrepancy still exist? If so: – List the consequences – Calculate the cost of each outcome and total – Is the cost high enough that a solution is required? Reference: Mager R F & Pipe P (2007) Analyzing performance problems or you really oughta wanna, 3rd ed, Atlanta, Georgia : CEP Press. Stage III: Explore “fast fixes” • Do staff know what is expected of them? • Can they tell you what the expectations are? • Are there obvious obstacles, eg: resources, work environment? • What kind of feedback do staff get about their performance? Reference: Mager R F & Pipe P (2007) Analyzing performance problems or you really oughta wanna, 3rd ed, Atlanta, Georgia : CEP Press. Stage IV: Explore consequences • Consider these questions: – Is good performance punishing, eg: has unfavourable consequences? – Is poor performance rewarding, eg: has favourable consequences? – Are there any consequences at all? • Change the consequences to change the behaviour Reference: Mager R F & Pipe P (2007) Analyzing performance problems or you really oughta wanna, 3rd ed, Atlanta, Georgia : CEP Press. Stage V and VI: Address other causes • Genuine skill deficiency • A skill or ability that has been lost due to lack of practice or lack of feedback • Task complexity • Other issues impacting on performance, eg: personal problems • Does the person have the potential to change? Reference: Mager R F & Pipe P (2007) Analyzing performance problems or you really oughta wanna, 3rd ed, Atlanta, Georgia : CEP Press. Choosing a solution • Collect all the potential solutions revealed by the analysis • Work out cost of each solution • Select the solution(s) that will add the most value • Draft an action plan describing solutions Reference: Mager R F & Pipe P (2007) Analyzing performance problems or you really oughta wanna, 3rd ed, Atlanta, Georgia : CEP Press. Life support for supervisors • Performance management is a complex area, involving: – Multiple policies and procedures, and has legal implications – Emotional consequences, eg: increased stress and potential problems across the team • Use PRD as your framework for establishing clear expectations • Seeking support to deal with ineffective / poor performance is key survival strategy: – Consult with HR Adviser – Talk to your line manager Close • Any questions? • Feedback • Thank you for your participation