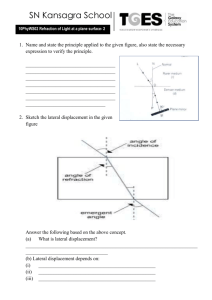
Properties of Matter Physical properties = a property that describes
advertisement

Properties of Matter Physical properties = a property that describes the behavior of a substance without reference to any other substance. - You look at the substance by itself, not combined with anything else. Weight, color, volume, boiling point, melting point, hardness, etc. Chemical property = a property that describes the behavior of a substance when it reacts or combines with another substance. - Burn it or add chemicals to it to make it react. We can measure both physical and chemical properties. - 2 things many have some properties that are the same, but not all of them. We do tests until we get only one substance with all of the properties. The Metric System - Scientists have used this system for over a century. Created in 1791, it is based on units of 10. The English system is not based on any unit. - It is based on things that change. 1 foot changed depending on whose foot it is. It is only used by the U.S.A. The metric system is used in every other country. In the metric system you can change from one unit to another by just moving the decimal. - EX. – 1 meter = 1000ml, 100cm. 10dm, .1dkm, .01hm, .001km Nature of Matter Matter = anything that has mass and takes up space. - Matter is made of atoms. The simplest form of matter is the element. - Elements are made of only one type of atom. Everything that is matter is made of 2 or more of these elements. Periodic Table = a chart of all the known elements arranged in a systematic fashion. Vertical columns are called groups or families. - Things in the same column have similar properties Each element has a letter or letters as a symbol. - Many of the elements names and symbols are Latin. EX) Gold’s symbol is Au, for Aurum, which is Latin for gold When we combine elements we get compounds. - Most everything on the planet is a compound or made of compounds Carbon Dioxide is written as CO2, which means it is made of 1 Carbon and 2 oxygen atoms. Carbon dioxide is a new substance. - Carbon is a sold and oxygen is a gas. Carbon dioxide is a gas that does not act like either of these. States of Matter There are 3 states of physical matter – solid, liquid and gas. Solids - The molecules in a solid are very tightly packed in a 3-D form. The molecules are moving, but only barely vibrating. This gives solids a definite shape and a definite volume. Liquids - The molecules in a liquid move much faster than in a solid. They move so fast that the 3 – D form breaks down into chains of molecules. They have no definite shape, but have a definite volume. Gases - The molecules are now moving very quickly. The liquid chains now are moving so fast they break into individual molecules. The have no definite shape and no definite volume. Changing states of matter - You can change from one state of matter to another by adding or taking away energy. EX – water – heat liquid water past 100°C and you get water vapor (a gas) Remove heat from liquid water until you get to 0°C and it turns into ice (a solid) Through all of this it is still H2O. Sometimes a solid can turn directly into a gas. - This is called sublimation EX – dry ice is solid CO2 and will change into a gas at room temperature without ever turning into a liquid. Scientists are constantly combining compounds and elements in all their phases to try to make new and useful products. - Most do not work, and some are dangerous. When there is a definite boundary between two substances, it is called a Phase. - ex – oil and water This is one way forensic scientists tell what a substance will be. Theory of Light Knowing how light works is important in forensics. There are two theories as to how light works – one as a wave and one as a particle. Wave Theory - This says light travels in waves, like water. It has crests (high points) and troughs (low points) Wavelength = the distance between to crests. - Its symbol is the Lambda (λ) and is measured in millionths of meters (.0000001) Frequency = how many times a wave passes a point in a given amount of time. - Its symbol is f f = c ÷ λ or frequency = the speed of light/ wavelength Visible light (sunlight) is made of many different wavelengths. - Each wavelength is a different color. When we use a prism, it splits the light into different wavelengths. - This is called dispersion. The spectrum of visible light has 7 main colors (red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet) When light goes through something (glass, water, etc.) it slows down. - This causes the light to bend. Depending on what it is going through it may bend a little or a lot This is called Refraction. When light bounces off something it is called reflection. - Everything you see is reflected light. If a shirt is blue, it is reflecting blue and absorbing the other colors. White reflects all of the colors, and black absorbs all of the colors. Light absorption is an important part of forensics. - Certain chemicals will absorb and reflect certain colors. The electromagnetic spectrum - This includes every wavelength that comes from the sun. Every wavelength from the sun travels at the speed of light (300 million meters/second) This ranges from things that have a high frequency and short wavelength, to low frequency and long wavelength. The highest frequency waves belong to gamma rays. - These kill life because they have so much energy. X-rays have a slightly lower wavelength. - It still has enough energy to push through muscles and bounce off of bone. Given enough dosage, X-rays can cause cancer. Ultraviolet rays have a frequency that is only a little higher than visible light. - “ultra” is Latin for “above” - This can cause skin cancer Visible light (what we can see) is a very tiny part of the E.M.S. Things that have a lower frequency and longer wavelength than visible light are infrared (heat), microwaves, and radio waves. Normally, light waves are not in step with each other. - They bump into and interfere with one another. We have found a way to make the rays stay in step with each other. - This creates a light with only one wavelength. This is a laser = light amplification by stimulated emissions of radiation. Light as a particle In space, light acts like a wave. - When it is absorbed by something, it acts as a particle Photon = energy particles Each photon has a specific amount of energy E = hf - E is the energy of the photon f is the frequency of the wavelength h is Plank’s Constant In other words, the higher the frequency of light, the more energy their photons will have. EX) X-rays have higher energy photons than infrared rays do. We can tell what photons of light are absorbed by something by using spectrophotometry. - This is very useful when figuring out what kind of drugs are on a scene. Refractive index When light changes speed, it bends (refraction) EX) A quarter in a pool - Light bounces off the quarter, through the water, and into the air. When it hits the air, it speeds up a lot, and bends. This is why, when you try to pick up the quarter, it is not where you think it is. Refractive index = the velocity of light in a vacuum ÷ the velocity of light through some medium. The refractive index for any substance changes based on its temperature and lighting conditions. - So in order to do tests, the conditions have to be very carefully controlled. Almost all refractive indices use a wavelength of 589.3 nanometers. - This gives us a standard for doing tests. Anything light passes through has a refractive index. - If it goes from one gas to another, it changes speed. Same for liquids and solids. If you put a solid into a liquid that has the same refractive index, the solid disappears. In a crystal, there can be two different refractive indices. - If you turn the crystal, the refractive index changes. Crystals have a repeating pattern as to how their atoms are arranged. Glass is not a crystal - Its atoms are randomly arranged. Knowing if what you are looking at is a crystal or not will change how you figure out the refractive index. Forensic Analysis of Glass We look at the composition of the glass, the glass fragments themselves, the density, the refractive index and the glass fractures. Density and refractive index are the two most easily done tests, and are the most accurate of the tests. Glass composition Glass is made of sand mixed with various metal oxides as well as other minerals. Soda (sodium carbonate) is usually mixed with the sand to lower its melting point and make it easier to work with. Lime is added to the mixture to keep it from dissolving in water. This soda-lime glass is used in most window and bottle glass. This mixture is cooled on top of liquid tin. - This is called “float glass” The metal oxides in glass are generally sodium, calcium, magnesium and aluminum. - Specialized glass uses other metals. Heat resistant glass uses boron oxide to keep it from shattering from heat. Tempered glass is made rapidly heating and cooling the glass so it breaks into “dices”. - These are small, cube pieces that break off. This is used in the rear and side windows of cars. Laminated glass is made by putting a layer of plastic between two layers of glass. - This makes it very strong and resistant to cracking. It is used in the windshields of cars.