Engineering Analysis (650201) lec(2) – CH 1 Separable DE

Philadelphia University/ Faculty of Engineering
Communication and Electronics Engineering
Engineering Analysis (650201) lec(2) – CH 1
Separable DE
Instructor: Eng. Nada
Email: nkhatib@philadelphia.edu.jo
Summary
Ordinary differential equation (ODE) , Partial differential equation (PDE) y
′′ +
4 y
=
0 ,
∂ 2 u /
∂ x
2 + ∂ 2 u /
∂ y
2 =
0
Order : highest derivative in equation dx
= dt x
+ t 1 st order equations d d t
2 x
2
+
3 dx
= t dt
Implicit solution, explicit solution
2 nd order equation y
= g ( x ) ( y
=
2 e
2 x
), G ( x , y )
=
0 ( x
2 + y
2 =
1 )
General solution, particular solution y
= ce
2 x
, y
=
2 e
2 x
٢ lec 2_ch1_Separable DE Nada khatib .
Eng
Separable DE
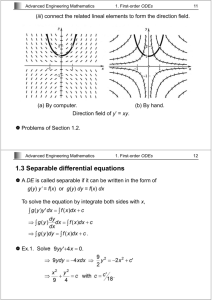
A separable DE is any DE that we can write in the following form.
g ( y ) dy
= f ( x ) dx
The variable y appears only on the left side
The variable X appears only on the right side
How to solve it?
٣ lec 2_ch1_Separable DE Nada khatib .
Eng
Separable DE
Step 1: rewrite the DE as the following form: g ( y ) dy
= f ( x ) dx
Step 2: integrate both sides
∫ g ( y ) dy
= ∫ f ( x ) dx
+ c lec 2_ch1_Separable DE Nada khatib .
Eng ٤
Examples lec 2_ch1_Separable DE Nada khatib .
Eng ٥
Reduction to Separable DE
Certain DEs are not separable but can be made separable by the introduction of a new unknown function.
We discuss this technique for a class of
ODEs of practical. DE of the form y
′ = f ( y x
) cos( y x
) , ( y x
)
3 lec 2_ch1_Separable DE Nada khatib .
Eng ٦
Reduction to Separable DE
The form of such an ODE suggests that we y set ; thus x
= y
= ux
By product differentiation
Substitution into
Then gives:
This can be separated:
٧ lec 2_ch1_Separable DE Nada khatib .
Eng
Examples lec 2_ch1_Separable DE Nada khatib .
Eng ٨