MDI-01 - The Insurance Institute of Ireland
advertisement

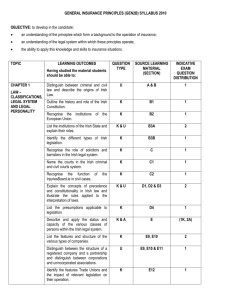
MDI-01 INSURANCE & BUSINESS LAW SYLLABUS 2016 10 INSURANCE AND BUSINESS LAW On completion of this module students should be able to : • Explain the Irish legal system (its characteristics, sources of law, effect of the EU, the Courts and legal personnel) and the concepts involved in legal personality; particularly status and capacity. • Describe the law of tort (nature of tort, main torts, defences, limitations, remedies and damages, the law of contract (formation, classification, validity, discharge, breach, privity and assignment). • Explain the nature of agency (including its creation, the relationships involved therein, the rights and responsibilities of the parties involved, termination and the application of agency to insurance). • Describe the general principles governing insurance contracts (general principles of contract law, utmost good faith, insurable interest and assignment). • Differentiate between void, voidable and illegal insurance contracts. • Discuss the issues surrounding insurance claims (the principles of proximate cause, utmost good faith and indemnity, subrogation and contribution). Each chapter in this textbook addresses a specific topic. The table below lists the learning outcomes for each chapter and these learning outcomes indicate what a student should have learned from their study of that particular chapter. The table below notes where these learning outcomes can be sourced in the text material. Each learning outcome is based on either a Knowledge (K), Understanding (U) or Application (A) basis (or in some cases a combination of these) and this is how they will be tested in the examination. This module is assessed by a 3 hour end-of-semester examination paper, which is in two parts. The whole paper carries 200 marks. In Part I, the student answers 14 short answer questions and in Part II, the student answers 2 essay questions. ASSUMED KNOWLEDGE It is assumed that the candidate already has knowledge of the fundamental principles of insurance as covered in PDI-01 (The Nature of Insurance) and PDI-07 (Practice of Claims and Loss Adjusting), or equivalent exams. IMPORTANT NOTES • Candidates should note that the examination will test the module syllabus alone. • The syllabus will be based on Irish law and practice. • The 2016 examination sessions will test the legal position as of November of the preceding year. FEEDBACK If you have any comments on this textbook or the material contained therein, The Insurance Institute of Ireland would appreciate your feedback. Please contact us on info@iii.ie © The Insurance Institute of Ireland 2015 10 MDI-01 INSURANCE AND BUSINESS LAW SYLLABUS CHAPTER 1: THE IRISH LEGAL SYSTEM Section A&B Learning outcome Knowledge rating State how laws are classified and outline the history of common law in Ireland and the effect of judicial precedent. K C Describe the sources and types of Irish and European Union law. U D Demonstrate the civil procedure in a personal injuries case and describe the structure of the Irish Court system and the legal professions operating therein. U E Discuss the rules for interpretation of written law. U CHAPTER 2: LEGAL PERSONALITY Section A Learning outcome Knowledge rating Explain the status and capacity of the various classes of legal persons. U B1 Describe the legal constitution and legal capacity of a juristic person (corporation). U B2 Explain the formal legal requirements of a juristic person (corporation). U B3 Differentiate between the types of companies that exist in Ireland. A C Explain the legal capacity of unincorporated associations. U D Summarise the legal capacity of partnerships and distinguish between the requirements of a limited company, a partnership and a Lloyd’s underwriter. U E Recognise the legal basis for and capacity of trade unions. K CHAPTER 3: LAW OF TORTS 1 Section Learning outcome Knowledge rating A Explain the nature of torts and recognise how they are classified. K&U B Describe the characteristics of the tort of negligence and the principles governing it. C Describe the characteristics of the tort of trespass and the forms it may take. D Differentiate between the torts of public and private nuisance and the key principles governing them. U E Explain the rule in Rylands v. Fletcher. U F Describe the nature of a ‘breach of statutory duty’ and illustrate its application to employers’ liability, occupiers’ liability and product liability. U G Describe the characteristics of the tort of defamation, the principles governing it and the unique defences available for it. U U U&A CHAPTER 4: LAW OF TORTS 2 Section Learning outcome Knowledge rating A Explain the principle of vicarious liability. U B Explain the main defences in tort. U C Outline the main remedies in tort. U D Describe the time limitation of actions in tort. U CHAPTER 5: THE LAW OF CONTRACT Section Learning outcome Knowledge rating A Define a contract and recognise the various classifications of contracts. K B Describe the elements essential to the formation of a valid contract. U C Describe how contract terms are classified and the effect of legislation on their classifications. D Describe the elements that affect the validity of contracts. U E Explain the circumstances in which a contract may be discharged. U F Describe the remedies for breach of contract. U G Outline the doctrine of privity of contract. U H Outline the key considerations in the assignment of a contract. U U&A CHAPTER 6: AGENCY Section Learning outcome Knowledge rating A Explain the nature of agency and its creation. U B Discuss the nature of an agent’s duties and state the remedies for the breach of such duties. C Discuss the nature of an agent’s rights. U D Discuss the nature of an agent’s authority. U E Describe the affect that the disclosed and undisclosed principles have on the relationships between agents, principals and third parties. U F Explain how an agency can be terminated and its effect. U K&U CHAPTER 7: INSURANCE CONTRACTS AND INSURABLE INTEREST Section A Learning outcome Apply the essential elements of contract formation to insurance. Knowledge rating A B Apply the law of agency to insurance. A C Explain the concept of insurable interest and why it is necessary. U D Describe the legal basis for the concept of insurable interest. U E Recognise how insurable interest is created and when it is required. K F Apply the principle of insurable interest to reinsurance and the major classes of insurance. A CHAPTER 8: UTMOST GOOD FAITH Section Learning outcome A Outline the doctrine of utmost good faith. B Identify the various forms of misrepresentation and distinguish between misrepresentation and non-disclosure. Knowledge rating U K&U C1 & C2 Discuss the duty of disclosure in the context of insurance. U C3–C5 Discuss the significance of material facts in insurance and outline which facts must and must not be disclosed. U C6 State when disclosure is required and how the timing of the duty of disclosure can be modified by policy wordings. K&U C7 Explain how the duty of disclosure operates with regard to compulsory insurances. U State the forms that breach of good faith may take and the remedies available. K Explain the effects of the Insurance Ireland Non-Life Insurance General Code and the Central Bank Consumer Protection Code on the duty of good faith. U State the objective and scope of the Law Reform Commission’s Report 2015. K D1 & D2 D3 E CHAPTER 9: INSURANCE CONTRACTS – WARRANTIES, CO-INSURANCE AND ASSIGNMENT Section A1–A4 Learning outcome Knowledge rating Differentiate between the meaning and use of warranties and conditions in insurance and non-insurance contracts. U Explain the effect of a breach of warranty or condition in insurance. U Explain the effects of Insurance Ireland Non-Life Insurance General Code, the Central Bank Consumer Protection Code and special conditions relating to compulsory insurance on the use and breach of warranties and conditions. U B State the difference between void and voidable insurance contracts. K C Distinguish between joint and composite insurance contracts and explain the rights under them. U D Illustrate the rules that govern the assignment of insurance contracts. A A5 A6–A8 CHAPTER 10: MAKING A CLAIM Section Learning outcome Knowledge rating A Discuss who can enforce an insurance contract and who benefits from it. U B Explain the rules governing notice and proof of loss. U C Explain the main rules governing the construction and interpretation of insurance contracts. U D Discuss the doctrine of proximate cause and explain the effect that specific policy wordings have on its operation. U CHAPTER 11: MEASURING THE LOSS – THE PRINCIPLE OF INDEMNITY Section Learning outcome Knowledge rating A Define indemnity. K B Explain the methods that insurers can use to provide indemnity. U C Explain the various methods of calculating the measure of indemnity for the main classes of insurance. U D Discuss and apply the factors which limit, reduce, extend or modify the principle of indemnity. A E Explain the doctrine of salvage. U F State how claim payments affect policy cover. K CHAPTER 12: SUBROGATION AND CONTRIBUTION Section Learning outcome Knowledge rating A Define the principle and nature of subrogation as a corollary of indemnity. K B Explain how subrogation operates and applies. C Discuss the source of subrogation rights and how they may be modified or denied. U D Describe the nature of double insurance and contribution. U E Explain when contribution arises at common law. U F Describe the operation of contribution at common law and the effect of common contribution conditions. U&A G1 & G2 Explain and apply the maximum liability and independent liability methods of contribution. U&A G3 & G4 Explain the methods of contribution used for property and liability insurance. U H State the effect of market agreements on the principles of subrogation and contribution. K U&A