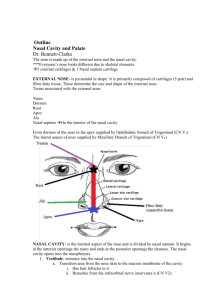
Nasal Cavity - Boundaries Nasal Cavity - Regions
advertisement
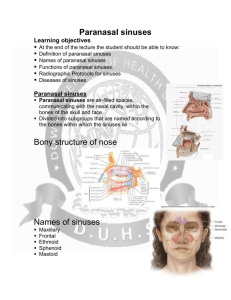
NOSE & PARANASAL SINUSES • NASAL CAVITY REVIEW • • • • • • Boundaries Concha Regions Innervation Blood Supply Paranasal Sinuses – General features – Clinical Relationships • PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA PREVIEW Gordon L. Todd, Ph.D. WH 2002 9-4241 gltodd@unmc.edu Nasal Cavity - Concha • Superior – Sphenoethmoidal recess – sphenoid sinus – Superior meatus – post. ethmoid air cells • Middle – Ethmoid bulla – middle ethmoid air cells – Hiatus semilunaris – frontal sinus, ant. ethmoid air cells and maxillary sinus Nasal Cavity - Boundaries • Roof – nasal, frontal, cribriform plate, sphenoid • Floor – Maxillary & palatine bones of hard palate • Septum – Septal cart., perpendicular plate of ethmoid, vomer (bottom) • Post – Choana • Lat – Nasal, lacrimal, maxillary, ethmoid, palatine, sphenoid and inf. concha Nasal Cavity - Regions • Vestibule • Olfactory – sup. concha & upper 1/3 of septum • Respiratory • Inferior – Inferior meatus – nasolacrimal duct 1 Nasal Cavity - Innervation • Olfactory n. • Ant. ethmoid n. (nasociliary n.) • Lat. nasal n. (greater palatine) – parasym. to glands & sensory (maxillary) • Nasopalatine (maxillary) - septum Nasal Cavity – Blood Supply • Sphenopalatine (maxillary)* • Ethmoids (ophthalmic) • Sup. labial, ascending palatine and lat. nasal (facial) • Descending palatine (maxillary) Greater & lesser palatine 2 Epistaxis • Epistaxis that “you can see” – septal brs. of sup. Labial and sphenopalatine • Epistaxis that “you cannot see” – post. sphenopalatine or post. ethmoid a. • Kiesselbach’s plexus – 90% of epistaxis • Initial treatment – pack with cotton & pinch • Extended treatment – gauze packing or balloon occluders • Severe recurrent epistaxis – ligate ext. carotid a. Pterygopalatine Fossa • • • • • • • Post. Med. – Pharyngeal canal Post. – Pterygoid canal Post. Lat. – Foramen rotundum Lat. – Pterygomaxillary fissure Ant. – Inf. Orbital fissure Med. – Sphenopalatine foramen Floor – Palatine canal 3 Paranasal Sinuses - General • 4 pairs of sinuses • Lined by mucous membrane continuous with nasal cavity • Secrete more than 500 ml / day • Cilia of respiratory epithelium clear mucus • Sinusitis – Inflammation of mucous memb. • “Useless products of human evolution.” Paranasal Sinuses - General 4 Maxillary Sinus • Tetrahedra shape, largest, 1st to develop • Aperture – middle meatus • Relations • • • • • Sup. – Infraorbital n. and orbit Med. – Nasal cavity Ant.& lat. – Cheek Post. – Infratemporal fossa, pterygopalatine fossa Inf. – Roots of premoloars & molars • Nerve supply – infraorbital n. • Blood supply – Maxillary a. • Clinical – Pain in forehead, cheek, teeth Frontal Sinus • Flattened tetrahedral shape • Aperture – Inferomed. angle of middle meatus • Relations • • • • • Sup. – Ant. Cranial fossa Ant. – Forehead, supraorbital & supratrochlear n. Med. – Other frontal sinuses Inf. – Orbit, ant. ethmoid sinuses Post. – Ant. cranial fossa • Nerve supply – Ophthalmic via supraorbital • Blood supply – Ophthalmic a. • Clinical – Pain around eyes & discomfort in forehead Ethmoid Sinus • 3-18 irregular-shaped cells • Aperture – middle meatus (Ant.), bulla (mid.), superior meatus (post.) • Relations • Med. – nasal cavity • Lat. – orbit • Sup. – ant. Cranial fossa • Nerve Supply – Ant. & post. ethmoids, nasal brs. (maxillary) • Blood Supply – Ant. & post. Ethmoids • Clinical – Pain in retro-orbital area, between eyes Sphenoid Sinus • Cuboidal shape across the midline • Aperture – Sphenoethmoidal recress • Relations • • • • • Med. – Sinus of opposite side Sup. – Hypophyseal fossa, pituitary gland, optic n. Lat. – Cavernous sinus, int. carotid a. Ant. – Nasal cavity Inf. – Nasopharynx, pterygoid canal • Nerve Supply – Post. Ethmoid (ophthalmic) & sphenopalatine (maxillary) • Blood Supply – Post. Ethmoid & sphenopalatine a. • Clinical – Pain at vertex, occipital, retro-orbital 5 Clinical Relationships Clinical Relationships Clinical Relationships 6