Nasal Obstruction - Student Nurse Laura
advertisement
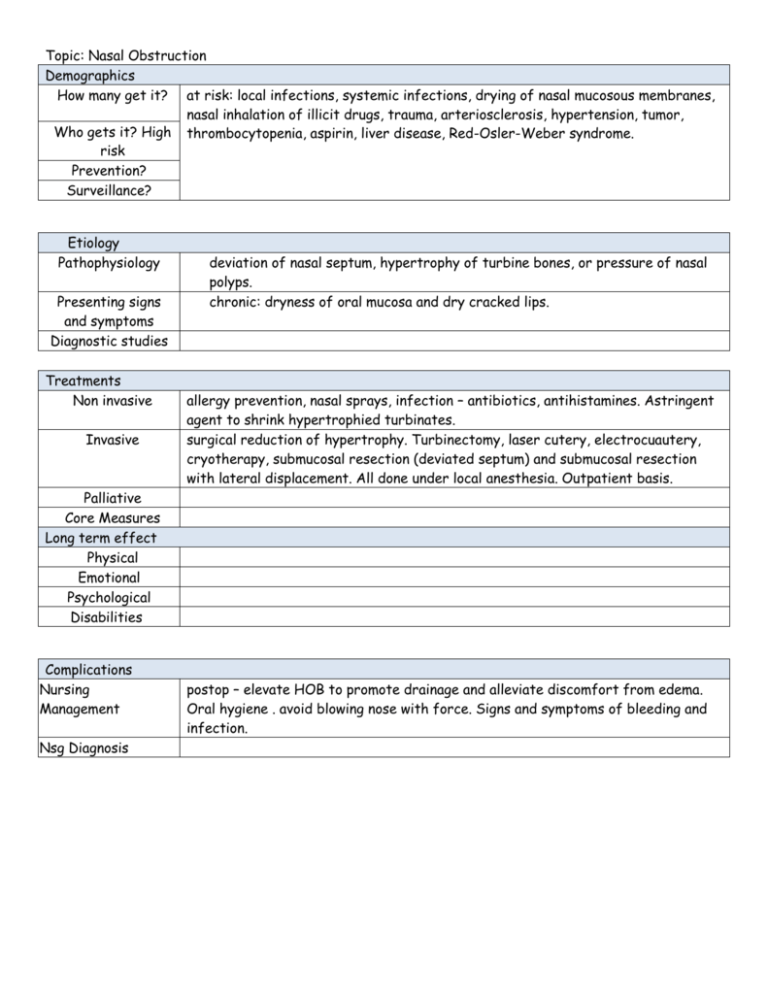
Topic: Nasal Obstruction Demographics How many get it? at risk: local infections, systemic infections, drying of nasal mucosous membranes, nasal inhalation of illicit drugs, trauma, arteriosclerosis, hypertension, tumor, Who gets it? High thrombocytopenia, aspirin, liver disease, Red-Osler-Weber syndrome. risk Prevention? Surveillance? Etiology Pathophysiology Presenting signs and symptoms Diagnostic studies Treatments Non invasive Invasive deviation of nasal septum, hypertrophy of turbine bones, or pressure of nasal polyps. chronic: dryness of oral mucosa and dry cracked lips. allergy prevention, nasal sprays, infection – antibiotics, antihistamines. Astringent agent to shrink hypertrophied turbinates. surgical reduction of hypertrophy. Turbinectomy, laser cutery, electrocuautery, cryotherapy, submucosal resection (deviated septum) and submucosal resection with lateral displacement. All done under local anesthesia. Outpatient basis. Palliative Core Measures Long term effect Physical Emotional Psychological Disabilities Complications Nursing Management Nsg Diagnosis postop – elevate HOB to promote drainage and alleviate discomfort from edema. Oral hygiene . avoid blowing nose with force. Signs and symptoms of bleeding and infection.