HOLE'S HA&P | C - Dynamic Science
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
METABOLISM
Chapter 4 Notes
H
OLE
’
S
HA&P | C
HAPTER
F
OUR
O BJECTIVES 4.1-4.5( PART ) ONLY
1.
Define metabolism .
2.
Explain why protein synthesis is important.
3.
Compare and contrast anabolism and catabolism.
4.
Define dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis .
5.
Describe how enzymes control metabolic reactions.
6.
List the basic steps of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
7.
Define active site .
8.
Define rate-limiting enzyme and indicate why it is important in a metabolic pathway.
9.
Explain how ATP stores chemical energy and makes it available to a cell.
10.
State the importance of the oxidation of glucose.
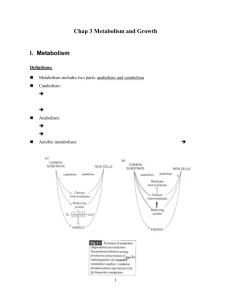
4.1-4.2
M ETABOLISM
Definition
Metabolic Processes
Dehydration
Synthesis
METABOLISM | HA&P Notes Chapter 4 page 1
Anabolism
Hydrolysis
Catabolism
4.3
C ONTROL OF M ETABOLIC R EACTIONS
Enzymes
METABOLISM | HA&P Notes Chapter 4 page 2
METABOLISM | HA&P Notes Chapter 4 page 3
Induced Fit
Enzyme Action
Substrate
Active Site
METABOLISM | HA&P Notes Chapter 4 page 4
Product
Metabolic
Pathways
Regulation
Cofactors/
Coenzymes
METABOLISM | HA&P Notes Chapter 4 page 5
Factors Affecting
Enzymes
4.4
E NERGY FOR M ETABOLIC R EACTIONS
Energy
Laws of Thermodynamics
METABOLISM | HA&P Notes Chapter 4 page 6
Cellular Respiration
Exergonic
Endergonic
METABOLISM | HA&P Notes Chapter 4 page 7
Coupled Reactions
Aerobic / Anaerobic
ATP
METABOLISM | HA&P Notes Chapter 4 page 8
METABOLISM | HA&P Notes Chapter 4 page 9
Questions:
1.
Define each of the following terms.
Anabolism
Catabolism
Metabolism
2.
Answer A nabolism or C atabolism:
______ Cellular respiration
______
______
“Downhill” reaction
______
Store/consume energy
Build complex molecules
______ Photosynthesis
______
______
“Uphill” reaction
______
Release Energy
Break down complex molecules
3.
Fill in the blanks regarding ANABOLISM
Monomer
Monosaccharide
Glycerol & 3 Fatty Acids
Nucleotides
Amino Acids
Polymer formed after anabolism
4.
According to the first law of thermodynamics, if the total energy before a reaction is 500kcal… the total energy after would be what?
METABOLISM | HA&P Notes Chapter 4 page 10
5.
According to the second law of thermodynamics, if the total energy before a reaction is 500kcal… the total useful & available energy after would be: a.
Less than 500kcal b.
500kcal c.
More than 500kcal
6.
How do enzymes control the rate of a chemical reaction?
7.
How does an enzyme “recognize” its substrate?
8.
How can a rate-limiting enzyme be an example of negative feedback control of a metabolic pathway?
9.
What is the role of a cofactor?
10.
What factors can denature an enzyme?
11.
What is energy?
12.
Define cellular respiration (include the formula for the reaction).
METABOLISM | HA&P Notes Chapter 4 page 11
13.
How does cellular oxidation differ from “burning”?
14.
When ATP is produced, energy is required. Where does that energy come from?
15.
When ATP is used, energy is released. How is that energy used?
16.
Label the following image: note where the energy is stored…
17.
Why does aerobic respiration make more energy in the form of ATP?
18.
Fill out this diagram (Fig 4.14)
METABOLISM | HA&P Notes Chapter 4 page 12