Cell structure What do all cells have in common? Cell structure What
advertisement
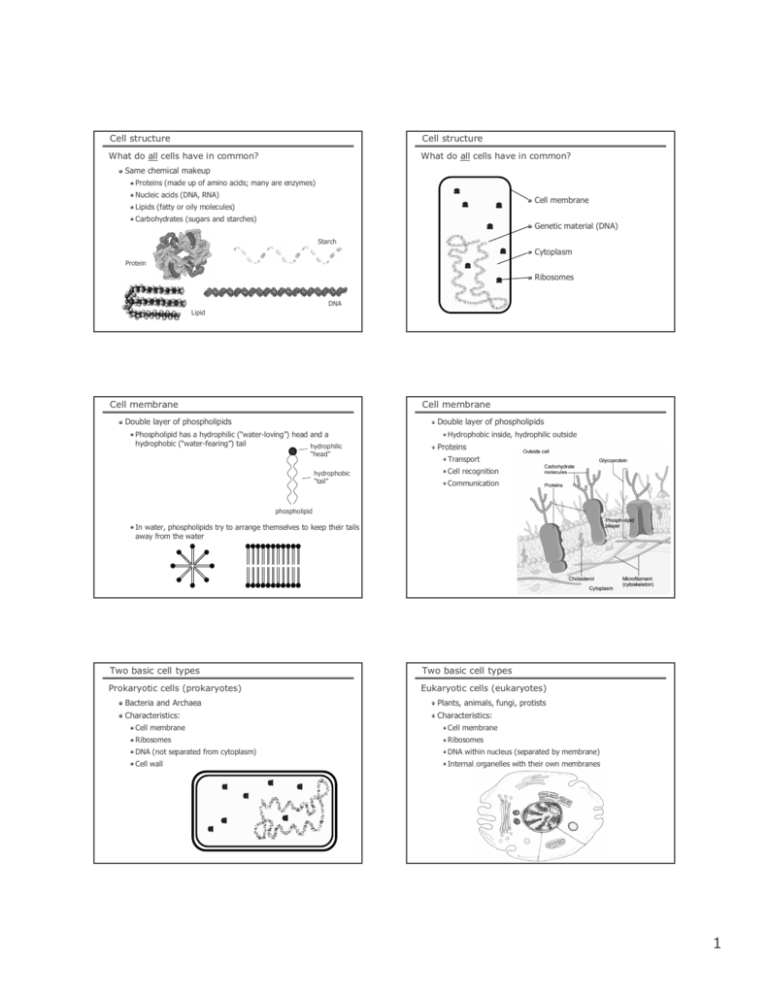
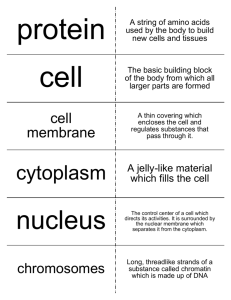
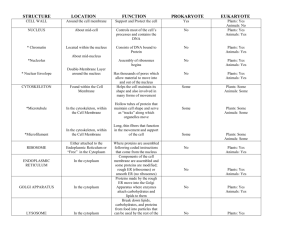
Cell structure Cell structure What do all cells have in common? What do all cells have in common? Same chemical makeup Proteins (made up of amino acids; many are enzymes) Nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) Cell membrane Lipids (fatty or oily molecules) Carbohydrates (sugars and starches) Genetic material (DNA) Starch Cytoplasm Protein Ribosomes DNA Lipid Cell membrane Cell membrane Double layer of phospholipids Double layer of phospholipids Phospholipid has a hydrophilic (“water-loving”) head and a hydrophobic (“water-fearing”) tail hydrophilic “head” hydrophobic “tail” Hydrophobic inside, hydrophilic outside Proteins Transport Cell recognition Communication phospholipid In water, phospholipids try to arrange themselves to keep their tails away from the water Two basic cell types Two basic cell types Prokaryotic cells (prokaryotes) Eukaryotic cells (eukaryotes) Bacteria and Archaea Plants, animals, fungi, protists Characteristics: Characteristics: Cell membrane Cell membrane Ribosomes Ribosomes DNA (not separated from cytoplasm) DNA within nucleus (separated by membrane) Cell wall Internal organelles with their own membranes 1 Animal Cell Structure Animal Cell Structure Nucleus Endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus Houses DNA Surrounded by nuclear envelope Chromatin: unspooled DNA when cell is not dividing Networks of membranesurrounded sacs ER Folding and processing of secreted proteins Synthesis of membrane components Golgi Vesicles transport proteins Animal Cell Structure Animal Cell Structure Ribosomes Mitochondria Made of proteins and RNA (no membrane) Assemble proteins (using instructions from genes) Convert food molecules (such as sugars and fats) to usable energy (ATP) Free in cytoplasm or attached to ER Contain own genetic material Originated as symbiotic bacteria Passed from mother to child Animal Cell Structure Animal Cell Structure Lysosomes and peroxisomes Cytoskeleton Sacs of digestive enzymes Network of protein filaments Breakdown ingested materials or worn-out components Involved in: Cell division Shape Movement Attachment 2