Lab 12eye_ earF10
advertisement

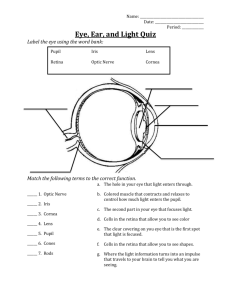
Lab 12 Special Senses: Vision Special Senses: Hearing and Equilibrium Exercise 24 Exercise 25 Vision Some of the activities below can be done at home. Activity 1:Identifying Accessory Eye Structures Activity 2: Identifying Internal Structures of the Eye Dissection: The Cow Eye Activity 5: Demonstrating the Blind Spot Activity 6: Determining Near Point Accommodation Activity 7: Testing Visual Acuity There is a white line on the lab floor 20 feet from the chart. Activity 8: Testing for Astigmatism Activity 9: Testing for Color Blindness Activity 10: Testing for Binocular Vision Demonstrating Afterimages Negative afterimage (www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Negative_afterimage) An afterimage in which the lightness relationship is reversed; if chromatic, it appears in complementary color, for example a green image that is looked at for a while when gaze is turned to a white sheet of paper it would have a red afterimage. Afterimages usually last from about a few seconds to a minute. most nerve cells quickly readjust. Use the picture of the American flag at the front of the lab. Stare at the image for one minute and then look at the white area below the flag until an image appears. It can take several seconds. Hearing Activity 1: Identifying the Structures of the Ear Activity 4: Conducting Laboratory Tests on Hearing Acuity Test Sound Localization Weber Test Microscopic Anatomy of the Cochlea - from Figures in Lab Manual Viewing the slide is optional. Name____________________________ Lab Section ________________ Pre-lab Activity - Turn in at the beginning of the lab. 1. The mucous membrane that lines the eyelids and covers the surface of the eye is the ___________________. Inflammation of this membrane is called ___________________ . 2. What are the three basic layers of the eyeball? ___________________, ______________________, and ___________________. 3. The transparent part of the outer layer of the eyeball is called the ____________ . 4. The hole in the center of the iris is called the _____________ . 5. Put the following terms in the correct order for the pathway of light into the eyeball. ______ Cornea ______ Retina ______ Lens aqueous humor ______ Vitreous humor ______ Pupil 6. Photoreceptors for color vision are called __________________ and are located in the ___________________ . 7. The optic nerves become the optic tracts after the __________________________. 8. The axons of the ganglion cells of the retina form the _______________________. 9. Define optic disc. 10. Define fovea. 11. The three parts of the ear are the ? ___________________, ______________________, and ___________________. 12. What is the name of the organ of hearing? 13. Other than hearing, what is another role for the inner ear. 14. Trace the pathway of sound waves into the ear. ______ Auditory canal ______ Perilymph of scala vestibuli ______ Incus ______ Stapes ______ Malleus ______ Tympanic membrane ______ Oval window Name____________________________ Lab Section ________________ Data and Review Sheets - Special Senses Data Sheet 1. Record the results of the Snellen Test for Visual Acuity Right eye unaided ________ Right eye with correction _________ Left eye unaided ________ Left eye with correction _________ Why is it important to check each eye separately? 2. Record the results of the test for Near Point of Accommodation Right eye ________ Left eye ________ Is your near point within normal range? 3. a. Describe what happened when you stared at the flag figure and then looked at a white background. b. What is this called? Cow Eye Dissection Questions 1. What is the name of the place where the retina attached to the eyeball? 2. What is the relationship between the location of the optic disc and the optic nerve? 3. Compare the shape of the cow pupil to the pupil of the human eye. 4. What is tapetum lucidum? What is its role? Is it present in the human eye? 5. In what two ways are the cornea and lens affected by the preservative? 2 points. __________________________________ and ______________________________ 6. What is the normal condition of the lens and cornea in an unpreserved eye? 2 points. __________________________________ and ______________________________ Review Sheet 1. What does 20/20 vision mean? 2. What does 20/40 vision mean? 3. What does 20/15 vision mean? 4. a. What is astigmatism? b. What is the test for astigmatism? 5. a. What is another name for the part of the retina called the blind spot? b. Why is vision lost when light passes over this area? c. What receptors are responsible for color vision? d. What receptors are responsible for vision in shades of gray? 6. a. Where are the extrinsic or external eye muscles attached to the eyeball? b. Which branch of the nervous system controls these muscles? Somatic motor Autonomic (circle one) c. Where are the internal muscles of the eye located? (2 places) _______________________ _______________________ d. Which branch of the nervous system controls these muscles? Somatic motor Autonomic (circle one) 7. Use the figure in the lab manual to trace an impulse from the retina to the visual cortex. Axons of ganglion cells of the retina ⇒ _____________________ ⇒ _____________________ ⇒_____________________⇒ synapse in the thalamus ⇒_____________________ ⇒visual cortex A N B C D M E L F G H I J K 8. Match the letters on the figure with the terms below: ____ Aqueous humor ____ Optic nerve ____ Choroid ____ Pupil ____ Ciliary body ____ Retina ____ Cornea ____ Sclera ____ Iris ____ Scleral venous sinus ____ Lens ____ Suspensory ligaments ____ Optic disc ____ Vitreous body The Ear F A G B H C I D J E K L 9. Label on the figure: ____ Auditory tube ____ Middle ear cavity ____ Cochlea ____ Semicircular canals ____ External auditory canal ____ Stapes ____ Incus ____ Tympanic membrane ____ Inner ear ____ Vestibule ____ Malleus ____ Vestibulocochlear nerve 10. What is the role of the hair cells of the cochlea in hearing sounds of different pitches, and why should you wear ear plugs at loud concerts? 11. Label: Print the labels in the margins. basilar membrane outer hair cells cochlear nerve tectorial membrane inner hair cells 12. Label: Print the letters at the end of the correct leader lines. A basilar membrane B cochlear nerve C stapes D oval window 13. Record threshold of audibility. Right ear _______ cm. Left ear ________ cm. 14. Sound localization. Can sound be localized equally well from all positions? _____________ If not, at which positions was sound less easily located?