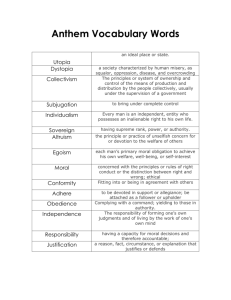
Review Sheet for the Ethics Final Exam The following is a good list
advertisement

Review Sheet for the Ethics Final Exam The following is a good list to guide your review of important terms, concepts and topics relating to the moral theories and moral issues that we covered in the first half of this semester. You will want to make sure to be able to apply and connect our seven moral theories to the moral issues. By connect, we mean that you should be able to formulate a basic argument either for and/or against a particular position on a moral issue using a particular moral theory. This ability to connect will be informed from your foundation in the moral theories and your readings of various articles in the text. Each problem on the midterm is generally worth 1 or 2 points including (but not limited to) True/False, Listing, Fill in the Blank, Multiple Choice, Multiple Select Matching and one essay question worth 10 points. The entire exam is worth 100 pts. Moral Theories General Terms (pp. 2-6) Intrinsic value Extrinsic value Moral Theory Theoretical aim Practical aim Value-based moral theories Duty-based moral theories “deontological” Consequentialism Important ideas on page 7 Utilitarianism (Jeremy Bentham & John Stuart Mill) – Principle of Utility (welfare) Hedonistic Utilitarianism (pleasure and pain) Perfectionist Consequentialism (human perfection in knowledge and achievement) Act Consequentialism Rule Consequentialism (two levels of evaluation, p. 9, acceptance value) Natural Law Theory Idea that certain actions are “natural” while others are “unnatural” St. Thomas Aquinas (objective true moral principles grounded in human nature) Four basic intrinsic goods p. 12 Core basis for determining moral actions Doctrine of Double Effect Intrinsic permissibility Necessity Nonintentionality Proportionality Kantian Moral Theory Golden Rule Immanuel Kant Hypothetical Imperatives Categorical Imperatives Humanity Formulation (respect, treats persons as ends and not merely as means) Universal Law Formulation (maxim) Application of UL with two tests p. 19 Realm of Ends Rights-Based Moral Theory Basic idea of a right Rights Holders and Rights Addressee Content of a Right Strength of a Right Rights Infringement Rights Violations Negative Right Positive Right Moral, Human and Legal Rights Basic Rights J.L. Mackie Application of Rights-Based Moral Theory (moral judgment, rights-focused approaches) Virtue Ethics Plato and Aristotle Virtuous Agent Virtues and Vices (p. 26) Application of Virtue Ethics Ethics of Prima Facie Duty W.D. Ross Robert Audi Four basic intrinsic goods (p. 27) Ten basic prima facie duties (value-based, duties of special obligation) Dual hybrid nature of Prima Facie (both consequential and deontological) No super principle discussion (p. 28) Social Contract Theory Thomas Hobbes, Jean-Jacques Rousseau, Gauthier, Scanlon and John Rawls Hypothetical agents Original position Mutual agreement under a “veil of ignorance” Principle of Greatest Equal Liberty Difference Principle Application to the distribution of wealth Justice as fairness and rightness as fairness Contractualism Moral Issues Chapter 9: Ethical Treatment of Animals Direct Moral Standing Indirect Moral Standing Ethical Agents Ethical Patients Speciesism/Anthropocentrism Bentham’s statement on the interests of animals (387-388) Moral Progress Sentience: Capacity to feel pain Vegetarianism Chapter 10: Abortion Zygote Embryo Fetus Viability Sentience “marks” of direct moral standing Reasons to seek abortion: therapeutic, eugenic, humanitarian, socioeconomic, personal Pro-choice, pro-life Conservative, liberal, moderate 1973 Roe v. Wade: guaranteed legality of abortion through first two trimesters 1992: Planned Parenthood v. Casey: established viability instead of trimesters 2003: Partial-Birth Abortion Ban Good Samaritan, Bad Samaritan, Minimally Decent Samaritan, Splendid/Very Good Samaritan (Thomsen 443-444) Chapter 11: Cloning and Genetic Enhancement Stem Cells Therapeutic cloning Reproductive cloning Genetic Enhancement Eugenics SCNT (Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer) IVF (in vitro fertilization) Chapter 12: The Death Penalty Legal Punishment Definition Retributive Theory of Punishment Principle of Proportionality Retentionists Negative consequences of death penalty Abolitionists Chapter 13: War, Terrorism and Torture War, Cold War & Hot War Preemptive & Preventative War Terrorism Torture Terrorist Torture Interrogational Torture 1984 UN Convention against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatments or Punishments Moral Nihilism Antiwar Pacifism Jus ad Bellum Legitimate authority Just cause Last resort Prospect of success Political proportionality Chapter 13: War, Terrorism and Torture (continued…) Jus in Bello Military necessity Discrimination Military proportionality Applying the Doctrine of Double Effect (Intrinsic proportionality, necessity, nonintentionality, proportionality) Self-Defense Rights approach Kantian Theory approach Epistemology Ticking Time Bomb Scenario Chapter 14: World Hunger and Poverty Kantian duty to beneficence 1.4 billion of the world’s population lives in extreme poverty, 2008 Questions in response to the duty of beneficence: Scope, Content, and Strength Thomas Robert Malthus and the Neo-Malthusians Garrett Hardin’s view Peter Singer’s view Ethics of Prima Facie duty when duties conflict Lifeboat ethics analogy Chapter 15: The Environment, Consumption and Climate Change Direct Moral Standing ANWR debate Four approaches to the question of Direct Moral Standing Anthropocentrism Sentientism Biocentrism Ecocentrism (ecosystem) Four approaches as they relate to being inclusive of nonhuman beings (living and nonliving) Atomism Holism Ecoholism Environmental ethic Tom Regan’s characterization (two parts) IPCC report projections for the 21st Century Four Categories of Concern 1. Agriculture, Forestry and Ecosystems 2. Water Resources 3. Human Health 4. Industry, Settlement and Society Examples of the impact of climate change