Temperature & Specific Heat Worksheet - Chemistry
advertisement

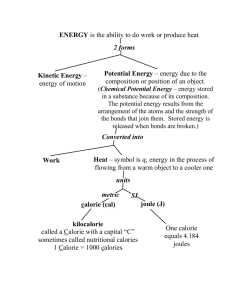
Name ______________________________________ Pd _____ Date ___________________ Chemistry Temperature & Specific Heat Worksheet Temperature Conversions 1. Complete the table below: Celsius Kelvin Fahrenheit Celsius Kelvin Fahrenheit 37.0°C 224 K -­‐27°C 875 K 114°F 200 K 65.3°F 0°C 62°C 0 K 72°F 0°F 25°C 100°C -­‐25°F 100 K 145°C 100°F 2. Your friend from France came to visit you in January. When she was packing for the trip she went on weather.com and found that the average temperature in Annville is 31°. Why did she pack shorts, sleeveless tops and no coat? 3. You have a friend who is using a recipe for flan from a Mexican cookbook. You notice that he set your oven temperature at 175°F. What would you advise him to do? 4. What the one characteristic of the Kelvin scale that is not a characteristic of either the Celsius or Fahrenheit temperature scales? Units of Energy Conversions Use conversion factors and dimensional analysis to answer these problems. 1 calorie = 4.184 joules. 5. A person uses 550 kcal of energy to run a race. Convert the energy used for the race to the following energy units: a. Calories b. Joules c. Kilojoules 6. Convert each of the following energy units: a. 3500 cal to kcal b. 415 J to cal c. 28 cal to kJ 7. Convert each of the following energy units: a. 8.1 kcal to cal b. 325 J to kJ c. 2.50 kcal to J 8. A burning match releases 1100 J of energy. Convert the energy released by 20 matches to the following energy units: a. Kilojoules b. Calories 9. It takes 4184 J of energy to raise the temperature of 1.000 kg of water 1.000 °C. a. How many joules does it take to raise the temperature of 1.50 kg of water 1.00 °C? b. How many calories does it take to raise the temperature of 1.0 kg of water 15.5 °C? Specific Heat Calculations 10. Water has a specific heat of 4.184 J/g·∙°C. a. How much energy must be added to 1450 g of water to raise the temperature from 5.5 °C to 29.0 °C? b. How much energy is removed from 10.55 kg of water to lower the temperature from 22.5°C to 3.0°C? c. Adding 550 calories of energy raised the temperature of water from 10.0 °C to 13.25 °C. What was the mass of the water? 11. Iron has a specific heat of 0.45 J/g·∙°C. a. How much energy must be added to 376 g of iron to raise the temperature from 25.5 °C to 429.0°C? b. Removing 9550 kcal of energy lowered the temperature of iron from 100.0 °C to 73.25 °C. What was the mass of the iron? c. 19770 J of energy was added to 5.80 kg of iron. If the iron was originally at 25.0°C what was the final temperature of the iron? 12. Steam has a specific heat of 1.90 J/g·∙°C. a. How much energy must be added to 125 kg of steam to raise the temperature from 105.5 °C to 129.0°C? b. How much energy must be removed from 1520 g of steam to lower the temperature from 202.5°C to 100.0 °C? c. 109 kJ of energy was added to 2.50 kg of steam. If the steam was originally at 100.0°C what was the final temperature of the steam? 13. What is the specific heat of a substance if 525 calories of energy increases the temperature of 10.0 g of the substance 5.75°C? 14. What is the specific heat of a substance if removing 95.0 J of energy decreases the temperature of 5.0 g of the substance from 23.5°C to 18.1°C?