Date
Name
Honors Chemistry
P
R
S
Unit 2 Test Study Guide
Objectives:
2.1 Recognize discoveries from Dalton (atomic theory), Thomson (the electron), Rutherford (the nucleus), and
Bohr (planetary model of atom) and understand how these discoveries lead to the modern theory.
2.2 Describe Rutherford's "gold foil" experiment that led to the discovery of the nuclear atom. Identify the
major components (protons, neutrons, and electrons) of the nuclear atom and explain how they interact.
2.4 Write the electron configurations for the first twenty elements of the periodic table.
2.5 Identify the three main types of radioactive decay (alpha, beta, and gamma) and compare their properties
(composition, mass, charge, and penetrating power).
2.6 Describe the process of radioactive decay by using nuclear equations and explain the concept of half-life for
an isotope, for example, C-14 is a powerful tool in determining the age of objects.
2.7 Compare and contrast nuclear fission and nuclear fusion.
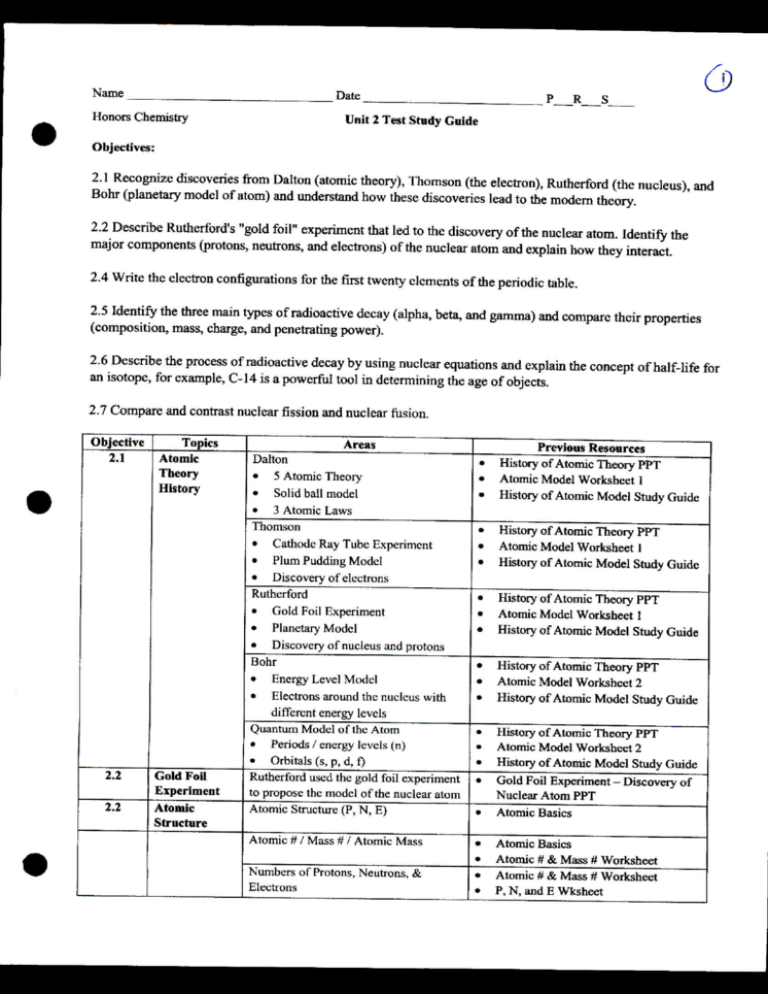
Objective
2.1
2.2
2.2
Topics
Atomic
Theory
History
Gold Foil
Experiment
Atomic
Structure
Areas
Dalton
•
• 5 Atomic Theory
•
•
• Solid ball model
• 3 Atomic Laws
Thomson
•
• Cathode Ray Tube Experiment
*
•
• Plum Pudding Model
• Discovery of electrons
Rutherford
•
• Gold Foil Experiment
•
•
• Planetary Model
• Discovery of nucleus and protons
Bohr
•
• Energy Level Model
•
•
• Electrons around the nucleus with
different energy levels
Quantum Model of the Atom
•
• Periods / energy levels (n)
•
•
• Orbitals (s, p, d, f)
Rutherford used the gold foil experiment •
to propose the model of the nuclear atom
Atomic Structure (P, N, E)
•
Previous Resources
History of Atomic Theory PPT
Atomic Model Worksheet 1
History of Atomic Model Study Guide
Atomic # / Mass # / Atomic Mass
Atomic Basics
Atomic # & Mass # Worksheet
Atomic # & Mass # Worksheet
P, N, and E Wksheet
Numbers of Protons, Neutrons, &
Electrons
•
•
*
•
History of Atomic Theory PPT
Atomic Model Worksheet 1
History of Atomic Model Study Guide
History of Atomic Theory PPT
Atomic Model Worksheet 1
History of Atomic Model Study Guide
History of Atomic Theory PPT
Atomic Model Worksheet 2
History of Atomic Model Study Guide
History of Atomic Theory PPT
Atomic Model Worksheet 2
History of Atomic Model Study Guide
Gold Foil Experiment - Discovery of
Nuclear Atom PPT
Atomic Basics
Bohr's Diagram vs Lewis Structure
•
•
Charges / Valence E
Atomic Symbols & Names
Atoms vs Ions vs Isotopes
2.4
Electron
Configuration
Full Electron Configuration
Shorthand Electron Configuration
Valence Electrons
Maximum Electrons
Orbitals #, Orbitals Shapes, # electrons
maximum held, locations in the table
Orbital Notation (3 rules / principles)
2.5
Radioactivity
Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Positron
(Symbols, Composition, Mass, Charge,
Penetrating Power)
2.6
Nuclear
Equations
•
•
Half-Life
2.7
Nuclear
Fission &
Fusion
4 types of Radioactive Decay
Equations
Identify and Balance
• Half-life (t«)
• # of half- life (n)
• Original Amount (Ao)
• Amt Remaining (At)
• Total time / age (tT)
• Fraction remaining At/Ao - ( l/2)n
• Triangle formula
Compare and Contrast
•
•
•
*
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Bohr Diagram and Lewis Structure
Wksheet
Bohr Model & Lewis Structure
Practice
Atomic Structure Study Guide
Atomic Structure Study Guide
Atoms and Ions Worksheet
Isotopes & Ions Worksheet
Isotope Extra Practice
Atomic Structure Study Guide
Electron Configuration Wksheet 1 , 2,
3
Electron Configuration Study Guide
Electron Configuration Wksheet 1 , 2, 3
Electron Configuration Study Guide
Electron Configuration Wksheet 2
Electron Configuration Study Guide
Electron Configuration Wksheet 2
Electron Configuration Study Guide
Electron Configuration Wksheet 2
Electron Configuration Study Guide
•
•
•
•
•
Orbital Notation Diagram
Orbital Notation Practice
Electron Configuration Study Guide
Radioactive Decay PPT
Radioactive Decay: Alpha, Beta, and
Gamma Worksheet
•
•
•
•
•
Types of Radioactive Decay 1
Nuclear Decay Worksheet
Types of Radioactive Decay 2
Nuclear Decay Study Guide
Half-Life Practice Worksheet 1
•
•
Nuclear Fission and Fusion PPT
Nuclear Fission and Fusion Multiple
Choice 1 & 2
Nuclear Fission and Fusion Worksheet
•
Worksheet 8: Historical development of atoms
Set A: Historical atomic models
Topic 3: The atomic structure
Objective: To test your knowledge of historical atomic models
Draw and briefly describe each historical model of the atom. (. Tr\
s (\Afr\
l.£o/'<4 sphere model
2. Plum-pudding model
•J
4.
5.
)
model
6. State two conclusions of the Gold foil experiment.
7. State conclusions of the Cathode ray experiment.
Copyright©2010 E3 Scholastic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
77
17
Bohr Diagram & Lewis Structure Worksheet
Element
Atomic | Atomic
Mass
Carbon
12.02
AAass*
E
12
6
0
Hydrogen
Lithium
Magnesium J
24
")2
11
Boron
p
0,6
12
12
n
(l)
Bohr Model
Lewis
Dot
Element
Atomic
#
Lewis
Atomic
Mass
Mass*
j
Bohr Model
4.
Helium
Oxygen
8
16
Fluorine
19
Nitrogen
14
Silicon
14
28
8
8
10
14
14
Dot
Atoms vs Ions vs Isotopes
Properties
Example
Atoms
Symbol
Name
/Haws*.
C 0 C&a&jl)
V
4-
Ions
r X-
f
£3
77)BL?
Isotopes
£
Atoms vs Ions vs Isotopes Practice
Name:
Atom / Ion /
Isotope
Date:
Element Name
Symbol
Atomic #
P
Mass*
P
N
6
8
6
6
127
52
E
S
Valence
E
Charge
6
54
47
46
17
37
20
20
19
18
13
R
27
10
-1
9
3
1
Write the unabbreviated electron configurations, abbreviated electron configuration |Noble Gas Notation], and orbital notation for the followings:
1Cement/Ion
H
Hydrogen Atom
Cl
Chloride Ion
Na + ^
Li
Ca
I
Ar
Ca 2+
F
Be3^
S
Ne
He
N3-
c
o2
p
B3+
Ar
Mg2+
Unabbreviated Electron Configurations Abbreviated Electron
Configurations
Orbital Notation
PARTB
IDENTIFY THE ELEMENT DESCRJJ»E*D BELOW:
1. WHICH ELEMEN^CONTAINS A FULL SEJXfflD ENERGY LEVEL?
2. WHICH EkE'MENT CONTAINS THffEE UNPAIRED ELECTRON* ITS THIRD ENERGY LEVEL?
3. WHICH ELEMENT CONTAINS FIVE ELECTRONS IbWfS 3D ORBITAL?
PART C - RULES OF ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS
Which of the following "rules" is being violated in each electron configuration below? Explain your
answer for each. Hand's Rule, Paul! Exclusion Principle, Aufbau Principle
7. 11
1s
8. li
2s
2p
li lilili
1s
2s
9. li
1s
li
2s
10 li
11
2s
1s
2p
lil_l
3s
3p
lilili 11 lilil
2p
3s
3p
lilili li lilili lilililili
2p
3s
3p
3d
tac-'-ty & Electron Configuration - Ch. 4
CHEM
fc)
Determine what elements are denoted by the following electron configurations:
.1)
1s22s22p63s23p4
_
2)
.2)
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104P65s1
, 3)
[Kr] 5s24d105p3
4)
[Xe] 6s24f145d6
5)
[Rn] 7s25f11
Is22sz2p63s1
7.)
Is22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d6
S-)
[Kr]
[Xe]
[Rn] 7s25fH6d4
Determine which of the following electror^configurations are not valid:
I-f
1I)
Is22s22p63s23p64s24d104p65s1
12)
Is22s22p63s3
13)
[Rn] 7s25f96d2
[Ar] 5s24d105p5
S)
[Xe] Ss^f10
16)
1 S22s22p63s23p64s24d104p5 ,
17)
Is^s^Ss^d5 _____
18)
[Ra] 7j
19)
[Kr] 5s24d105p5.
20)
[Xe]
Orbitals Questions
1. If each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons, how many electrons can each of the
following hold?
a) 2s
b)5p
c)4f
d)3d
e)4d
2. List the orbitals names and their shapes:
3. How many orbitals can there in an energy level?
4. a) Which is the lowest energy level that can have a s orbital? _
b) Which is the lowest energy level that can have a p orbital?,
c) Which is the lowest energy level that can have a d orbital?
d) Which is the lowest energy level that can have a f orbital?.
5. a) How many maximum electrons in the 5th energy level?
b) How many maximum electrons in the 6th energy level?
c) How many maximum electrons in the 7th energy level?
6. What is the term to describe the energy level?
7. If we use apartment to describe the electron configuration:
a) energy level = floor =
b) sublevels = north, south = (s-block. d-block.
c) orbitals = rooms - (s-orbital,
d) electrons = people = (electrons)
8. How many energy levels totally in the period table?
9. Why d-orbitals are not counted as valence electrons?
. and
., and