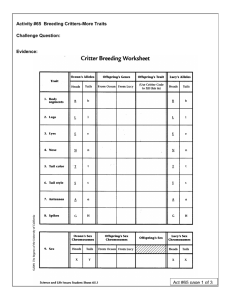
Mendel's Second Experiment: Dihybrid Cross • wanted to see how
advertisement

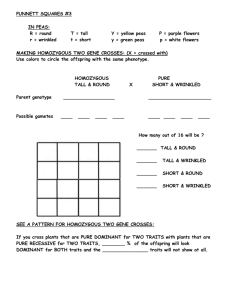
Mendel's Second Experiment: Dihybrid Cross • wanted to see how multiple traits are inherited • to determine if inheritance of one trait affected inheritance of another Experimental Setup 1) obtain parent plants that were purebred for two traits (seed shape, color) • selectively bred plants until all offspring had round, yellow seeds • selectively bred plants until all offspring had wrinkled, green seeds 2) performed the Dihybrid Cross • crossed a purebred round, yellow with a purebred wrinkled, green • observed traits in the offspring, the F1 generation • allowed the F1 plants to self pollinate • observed traits in the offspring F2 generation Why "dihybrid"? di = 2 traits involved hybrid = indicates offspring result of cross b/w purebreds 1 To create a Punnett Square for a Dihybrid Cross • list possible gametes from one parent along top, other along side • # possible gametes = 2 x # traits (here 2x2) • fill in square and determine phenotypes and ratios 2 Results F1 Generation • all had round, yellow seeds F2 Generation • phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1 To explain these results, he proposed: Law of Independent Assortment ­ the inheritance of alleles for one trait does not affect the inheritance of alleles for another trait. Different pairs of alleles are passed to the offspring independently of one another. ex. Determine the results from a cross between a plant that is homozygous yellow for seed color, heterozygous round for seed shape and a plant that is has wrinkled green seeds. Try #1 p540, #1 p544 3 p540 #1 answer p810 Good for extra practice! In people, curly hair is dominant over straight hair and the ability to curl the tongue is dominant over not being able to curl the tongue. A man with curly hair who has the ability to curl his tongue and a woman with curly hair who cannot curl her tongue have children. What are the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of their offspring? p544 #1 A dihybrid cross is made of two pea plants. Purple flowers are dominant (P) and white flowers are recessive (p). Tall plants (T) are dominant and short plants recessive. Both parents are heterozygous for both traits. Prepare a Punnett square to determine the phenotypic ratios of the offspring. What Mendelian law does this ratio demonstrate? Answer: 9 : 3 : 3: 1 Demonstrates the Law of Independent Assortment 4 To determine genotype for an individual based on two traits • perform a test cross between the individual who is expressing dominant allele for both traits with an individual who is recessive for both alleles • if individual is homozygous dominant for both traits ­ all F1 will show dominant trait • if individual is heterozygous dominant for both traits ­ 25% of F1 will show recessive trait (1:1:1:1) • if individual is heterozygous for one trait and homozygous recessive for the other ­ all F1 offspring will have the homozygous recessive trait; half will be recessive in the other trait while half will be dominant in the other trait (1:1) 5 ex. if unknown male was heterozygous for both traits Suppose you were trying to find out what genotype a certain pea plant is so you would know for future crosses. It has purple flowers and wrinkled seeds. Use a Test Cross to show the possible ratio of phenotypes in the offspring. If in an actual cross between this unknown plant and a plant with white flowers and wrinkled seeds, 3 of the 7 offspring produced had white flowers and wrinkled seeds, what was the genotype of the unknown parent plant? 6