Blood Counts – What do the numbers mean?
advertisement

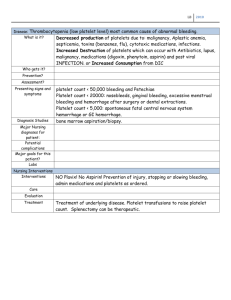
Blood Counts – What do the numbers mean? Many people have blood tests to check for For some people who are having illness or to see how the body is responding chemotherapy or radiation treatments, to a treatment, such as radiation or values may be lower than normal. Your chemotherapy. If you have had blood work doctor or nurse can explain what an done, you may have received a report with acceptable value is for you during your a lot of numbers and terms that you may not treatment. understand. This handout explains what the numbers mean for your complete blood There will be different numbers for each count. part of the CBC. Parts of the CBC will refer to the red cells. Other parts will give A complete blood count is often called a information about the white cells and CBC. This test lets your doctor know about platelets. different kinds of blood cells you have in your body. Your blood has three main types Types of Blood Cells of cells that will be measured in a CBC: Red blood cells cause the red color in your Red blood cells or erythrocytes blood. The red blood cells carry oxygen White blood cells, also called from your lungs to your organs and tissues. leukocytes, Platelets or thrombocytes The blood cells are made in the bone marrow in the center of your breastbone, hipbones, shinbones, backbones, and other bones. If you have anything that is affecting your bone marrow, it can affect your blood counts. They also carry carbon dioxide from the tissues back to your lungs so it can be exhaled. White blood cells protect your body from infections. The white cells engulf the site of infection and digest the germs. There are 5 types of white cells, and each has a job to do: the white cells and act as the first line of A sample of your blood will be taken by defense against infection. finger stick or by a needle from a vein. The blood is put on a slide by a technician and be looked at to see what types are there and whether they are normal. Normal values for a CBC Normal values will vary between men and women. There are also differences between adults and children. Eosinophils – these respond to allergic reactions stained or colored to make it easier to see the cells under a microscope. The cells will Neutrophils - make up more than half of Basophils – work in allergic responses and carry histamine. Monocytes – the second line of defense in infections, these eat up the germs to get rid of them. Lymphocytes – these white blood cells If your white cell counts are too high, you are part of your body’s immune system may have: and attack and destroy invading germs. an infection inflammatory disease, such as gout or Platelets are another type of blood cell. These stop bleeding caused by injuries by causing your blood to clot. What happens if the red cells are too high or too low? If red cell counts are too high, you may have polycythemia. Symptoms may include: thickening of your blood and excess arthritis an allergic response some types of cancer, or other disease Treatment depends on the cause of the high count. White cell counts can also be too low. This is called leukopenia. This may be caused by infection, severe stress, or some vitamin clotting deficiency. A low white cell count may be trouble thinking from radiation or chemotherapy treatments. headaches feeling irritable Treatment for polycythemia depends on what is causing your body to produce more red cells. If the white count is very low for a long time, it will be hard for you to fight infections. You will need to take extra caution to reduce your chances of getting infections by: theaters, and churches. If your red cell count is too low, you have anemia. This would mean that your blood cannot carry enough oxygen to your tissues. Avoiding crowded places like stores, Being with people who have colds or other illnesses. Some of the signs of anemia are: What happens if the platelets are too high or too low? Feeling tired Pale skin color Weakness Shortness of breath excessive bleeding, infection, cancer, some Pounding heart anemias, or surgery. Most of the time the An increase in the platelets is called thrombocytosis. Some of the causes are platelets will return to normal levels once Anemia can occur because of a poor diet, you have recovered from the injury or blood loss, or diseases that destroy your red illness that led to the platelet change. There blood cells. Treatment depends on the cause are some conditions that may need more of the anemia. If your red cell count is too treatment if the platelets stay high. low, your doctor may order a blood transfusion to help you feel better. Thrombocytopenia is the term for too few platelets. Platelet numbers can be low from bone marrow diseases, such as leukemia. A low platelet count may also happen with an enlarged spleen, or a low level of vitamin B12. likely to bruise or bleed. You may need to Is there anything I can do to improve my blood levels? take some extra precautions to reduce the Changes to your blood counts may be Low platelet numbers can make you more chances of your bleeding. Talk to your doctor or nurse about this. If your platelet level is very low, your doctor may order a platelet transfusion to decrease your risk for bleeding. expected with certain treatments. Most counts will return to normal once the cause of the change is treated. In some cases your doctor may suggest vitamins, iron, or diet changes to improve your blood counts. If you have questions about your blood counts, talk to your doctor or nurse. Rev 4/08, 8/11, 11/14 © Mount Carmel 2014