Refraction Revision
advertisement

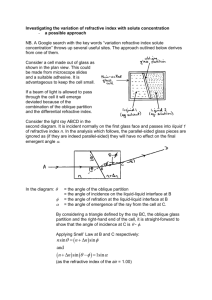
Refraction Revision Laws of Refraction • The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the surface at the point of incidence all lie in one plane. • For any two given pair of media, the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant. • The above law is called Snell's law after the scientist Willebrod Snellius who first formulated it Thus Where m is the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium. We know that the phenomenon of refraction is taking place because the speed of light changes when it is travelling from one optical medium to another. Thus we can define refractive index in terms of the speed of light in the two media. The refractive index of glass with respect to air is given by the relation. In general, if a ray of light is passing from medium 1 to medium 2, then If the medium 1 is air or vacuum, the refractive index of medium 2 is referred to as the absolute refractive index. The refractive index of a medium depends on the following factors: • the nature of the medium • the colour or wavelength of the incident light Material Absolute refractive index Flint glass 1.650 Diamond 2.417 Ruby 1.760 Pyrex® 1.470 Water 1.330 Air 1.0008 Ice 1.310 Critical angle Questions 1. A ray of light in glass makes an angle of incidence of 50° with a glass-water boundary. What angle of refraction does the light make in the water? 2. What is the critical angle for this glass-water boundary? 3. You are given kerosene, turpentine and water. In which of these does light travel fastest? Given that (nk = 1.44, nt = 1.47 and nw = 1.33) 4 The speed of light in diamond is 1.24 x 108 m/s. What is its refractive index? 5 The refractive index of ice is 1.31. What is the speed of light in ice? 6 A ray of light passes the boundary between air and a transparent material. The angle of refraction is 20°, and the angle of incidence is 10°. What is the speed of light in this material? Why is it impossible for this material to exist? 7 What is the critical angle of a beam of light leaving a transparent material with a refractive index of 2? Answers: 1 59.8° 2 62.5° 3 As refractive index of water is the least out of the given three media. Hence, light travels fastest in water. 5 The speed of light in diamond is 1.24 x 108 m/s. What is its refractive index? Assuming the speed of light in the reference medium is 3 x 108: 6 The refractive index of ice is 1.31. What is the speed of light in ice? 7 A ray of light passes the boundary between air and a transparent material. The angle of reflection is 20°, and the angle of incidence is 10°. What is the speed of light in this material? Why is it impossible for this material to exist? This is greater than the speed of light in a vacuum (3 x 108), and so is impossible. 8 What is the critical angle of a beam of light leaving a transparent material with a refractive index of 2? C = 30°