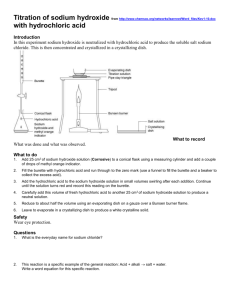
BENZOCAINE Benzocainum BENZOIC ACID Acidum benzoicum
advertisement

Benzocaine EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 5.0 Appearance of solution. Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y6 (2.2.2, Method II). Acidity or alkalinity. To 25 ml of solution S add 0.1 ml of phenolphthalein solution R. The solution is colourless. Add 0.3 ml of 0.01 M sodium hydroxide. The solution is pink. Add 0.1 ml of methyl red solution R and 0.5 ml of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid. The solution is orange-red. Volatile bases and salts of volatile bases (2.4.1). 0.20 g complies with limit test B for ammonium (50 ppm). Prepare the standard using 0.1 ml of ammonium standard solution (100 ppm NH4) R. Replace heavy magnesium oxide by 2.0 ml of strong sodium hydroxide solution R. Loss on drying (2.2.32). Not more than 5.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 100 °C to 105 °C for 4 h. Sulphated ash (2.4.14). Not more than 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g. Second identification : A, C, D. A. Melting point (2.2.14) : 89 °C to 92 °C. B. Examine by infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24), comparing with the spectrum obtained with benzocaine CRS. C. To about 50 mg in a test-tube add 0.2 ml of a 500 g/l solution of chromium trioxide R. Cover the mouth of the tube with a piece of filter paper moistened with a freshly prepared mixture of equal volumes of a 50 g/l solution of sodium nitroprusside R and a 200 g/l solution of piperazine hydrate R. Boil gently for at least 30 s. A blue colour develops on the filter paper. D. Dissolve about 50 mg in alcohol R and dilute to 100 ml with the same solvent. 2 ml of the solution gives the reaction of primary aromatic amines (2.3.1). STORAGE Store protected from light. STORAGE Store protected from light. TESTS Appearance of solution. Dissolve 1.0 g in alcohol R and dilute to 20 ml with the same solvent. The solution is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II). ASSAY Dissolve 2.000 g in water R and dilute to 100.0 ml with Acidity or alkalinity. Dissolve 0.5 g in 10 ml of alcohol R the same solvent. Transfer 25.0 ml of the solution to a previously neutralised to 0.05 ml of phenolphthalein separating funnel, add 10 ml of a 4 g/l solution of sodium solution R. Add 10 ml of carbon dioxide-free water R. The hydroxide R, 10.0 ml of a freshly prepared 50 g/l solution solution remains colourless and not more than 0.5 ml of of potassium iodide R and 25 ml of methylene chloride R. 0.01 M sodium hydroxide is required to change the colour Shake vigorously, allow to separate and discard the lower of the indicator. layer. Shake the upper layer with three quantities, each of Loss on drying (2.2.32). Not more than 0.5 per cent, 10 ml, of methylene chloride R and discard the lower layers. determined on 1.00 g by drying in vacuo. To the upper layer add 40 ml of hydrochloric acid R, allow to cool and titrate with 0.05 M potassium iodate until the deep Sulphated ash (2.4.14). Not more than 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g. brown colour is almost discharged. Add 4 ml of methylene chloride R and continue the titration, shaking vigorously, ASSAY until the lower layer is no longer brown. Carry out a blank Dissolve 0.400 g in a mixture of 25 ml of hydrochloric titration using a mixture of 10.0 ml of a freshly prepared 50 g/l solution of potassium iodide R, 20 ml of water R and acid R and 50 ml of water R. Carry out the determination of primary aromatic amino-nitrogen (2.5.8). 40 ml of hydrochloric acid R. 1 ml of 0.1 M sodium nitrite is equivalent to 16.52 mg 1 ml of 0.05 M potassium iodate is equivalent to 44.81 mg of C9H11NO2. of C27H42ClNO2. 01/2005:0011 01/2005:0066 BENZOCAINE BENZOIC ACID Benzocainum C9H11NO2 Acidum benzoicum Mr 165.2 DEFINITION Benzocaine contains not less than 99.0 per cent and not more than the equivalent of 101.0 per cent of ethyl 4-aminobenzoate, calculated with reference to the dried substance. C7 H 6 O 2 Mr 122.1 DEFINITION Benzoic acid contains not less than 99.0 per cent and not more than the equivalent of 100.5 per cent of benzenecarboxylic acid. CHARACTERS A white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals, very slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol. CHARACTERS A white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals, odourless or with a very slight characteristic odour, slightly soluble in water, soluble in boiling water, freely soluble in alcohol and in fatty oils. IDENTIFICATION First identification : A, B. IDENTIFICATION A. Melting point (2.2.14) : 121 °C to 124 °C. 1072 See the information section on general monographs (cover pages)