An Introduction to Functions - Precalculus Section 1.1
advertisement

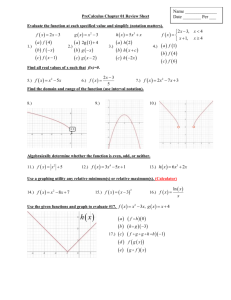
SECTION 1.1 An Introduction to Functions Chapter 1 A Review of Functions Section 1.1: An Introduction to Functions Definition of a Function and Evaluating a Function Domain and Range of a Function Definition of a Function and Evaluating a Function Definition: MATH 1330 Precalculus 1 CHAPTER 1 A Review of Functions Defining a Function by an Equation in the Variables x and y: Example: Solution: The Function Notation: 2 University of Houston Department of Mathematics SECTION 1.1 An Introduction to Functions Evaluating a Function: Example: Solution: MATH 1330 Precalculus 3 CHAPTER 1 A Review of Functions Example: Solution: 4 University of Houston Department of Mathematics SECTION 1.1 An Introduction to Functions Difference Quotients: Example: Solution: Additional Example 1: Solution: MATH 1330 Precalculus 5 CHAPTER 1 A Review of Functions Additional Example 2: Solution: Additional Example 3: 6 University of Houston Department of Mathematics SECTION 1.1 An Introduction to Functions Solution: Additional Example 4: Solution: MATH 1330 Precalculus 7 CHAPTER 1 A Review of Functions Additional Example 5: Solution: 8 University of Houston Department of Mathematics SECTION 1.1 An Introduction to Functions Additional Example 6: Solution: MATH 1330 Precalculus 9 CHAPTER 1 A Review of Functions Additional Example 7: Solution: Domain and Range of a Function Review of Interval Notation: 10 University of Houston Department of Mathematics SECTION 1.1 An Introduction to Functions Finding the Domain of a Function: Example: Solution: MATH 1330 Precalculus 11 CHAPTER 1 A Review of Functions Example: Solution: Finding the Range of a Function: 12 University of Houston Department of Mathematics SECTION 1.1 An Introduction to Functions Example: Solution: Additional Example 1: Solution: MATH 1330 Precalculus 13 CHAPTER 1 A Review of Functions Additional Example 2: Solution: Additional Example 3: Solution: 14 University of Houston Department of Mathematics SECTION 1.1 An Introduction to Functions Additional Example 4: Solution: Additional Example 5: Solution: MATH 1330 Precalculus 15 CHAPTER 1 A Review of Functions 16 University of Houston Department of Mathematics SECTION 1.1 An Introduction to Functions MATH 1330 Precalculus 17 CHAPTER 1 A Review of Functions Additional Example 6: Solution: Additional Example 7: Solution: 18 University of Houston Department of Mathematics SECTION 1.1 An Introduction to Functions MATH 1330 Precalculus 19 Exercise Set 1.1: An Introduction to Functions For each of the examples below, determine whether the mapping makes sense within the context of the given situation, and then state whether or not the mapping represents a function. 1. Erik conducts a science experiment and maps the temperature outside his kitchen window at various times during the morning. 57 9 62 10 7. Divide by 7, then add 4 8. Multiply by 2, then square 9. Take the square root, then subtract 6 10. Add 4, square, then subtract 2 65 o Time 2. Express each of the following rules in function notation. (For example, “Subtract 3, then square” would be written as f ( x ) ( x 3)2 .) Temp. ( F) Dr. Kim counts the number of people in attendance at various times during his lecture this afternoon. 1 85 2 Find the domain of each of the following functions. Then express your answer in interval notation. 11. f ( x) 5 x3 12. f ( x) x6 x 1 87 3 13. g ( x) Time # of People State whether or not each of the following mappings represents a function. If a mapping is a function, then identify its domain and range. 14. f ( x) 15. f ( x) 3. 7 9 -3 A 0 5 4 16. g ( x) x4 x2 9 3x 1 x2 4 x2 6 x 5 x 2 11x 28 3x 15 x 8 x 20 2 B 17. f (t ) t 4. -6 8 4 -7 A B 9 18. h( x) 3 x 19. g ( x) 5 x 20. h(t ) 4 t 5. 9 -2 -6 21. f ( x) x 5 1 A 6. B 0 8 20 23. F ( x) 3 2x x4 24. G ( x) x3 x7 2 4 A 22. g ( x) x 7 B University of Houston Department of Mathematics Exercise Set 1.1: An Introduction to Functions 25. f ( x) 3 x 5 35. (a) f (t ) t (b) g (t ) 9 t 26. g ( x) 3 x2 x 6 27. h(t ) 3 t 2 7t 8 t 5 28. f ( x) 5 2x 9 4x 7 29. f (t ) t 2 10t 24 (c) h(t ) 9 t 36. (a) f ( x) x (b) g ( x) x 1 (c) h( x) x 1 37. (a) f ( x) x 2 3 (b) g ( x) x 2 3 4 30. g (t ) t 2 5t 14 Find the domain and range of each of the following functions. Express answers in interval notation. 31. (a) f ( x) x (b) g ( x) x 6 (c) h( x) 2 x 2 3 5 38. (a) f (t ) t 2 6 (b) g (t ) t 2 6 7 (c) h(t ) 13 t 2 6 8 (c) h( x) x 6 (d) p( x) x 6 3 32. (a) f (t ) 3 t 39. g (t ) 2 x 7 5 40. h(t ) 6 t 1 (b) g (t ) 3 t (c) h(t ) 3 t (d) p(t ) 3 t 7 33. (a) 42. g ( x) 4 8 3x 2 f ( x) x 2 4 (b) g ( x) 4 x 2 (c) h( x) x 2 4 (d) p ( x) x 2 4 (e) q ( x) 4 x 2 (f) r ( x) x 2 4 34. (a) 41. f ( x) 3 5x 6 4 Find the domain and range of each of the following functions. Express answers in interval notation. (Hint: When finding the range, first solve for x.) 3 x2 x5 (b) g ( x) x2 43. (a) f ( x) f (t ) 25 t 2 (b) g (t ) t 2 25 (c) h(t ) 25 t 2 (d) p(t ) 25 t 2 4 x3 5x 2 (b) g ( x) x 3 44. (a) f ( x) (e) q (t ) t 2 25 (f) r (t ) 25 t 2 MATH 1330 Precalculus 21 Exercise Set 1.1: An Introduction to Functions 3x 2 , if x 0 53. If f ( x) 4, if 0 x 2 , find: x 5, if x 2 Evaluate the following. 45. If f ( x) 5x 4 , find: f (3), f 12 , f (a), f (a 3), f (a) 3, f (a) f (3) f (0), f (6), f 2, f (1), f (4), f 32 46. If f ( x) 3x 1 , find: f (5), f (8), f 74 , f (t ) 2, f (t 2), f (t ) f (2) 47. If g ( x) x 2 3x 4 , find: 4 x 7, if x 1 54. If f ( x) x 2 6, if - 1 x 3 , find: 7, if x 3 f (0), f (4), f 1, f (3), f (6), f 53 , g ( x 5), g , g (3a), 3g (a) g (0), g 1 4 1 a 48. If h(t ) t 2 2t 5 , find: h(1), h 32 , h(c 6), h( x), h(2x), 2h( x) Determine whether each of the following equations defines y as a function of x. (Do not graph.) 55. 3x 5 y 8 49. If f ( x) 2 x , find: x3 f (7), f (0), f 53 , 56. x 3 y 2 f (t ), f (t 2 3) 57. x 2 y 3 58. 3x 4 2 xy 5 x x2 x , find: 50. If f ( x) x4 59. 7 x y 4 5 f (2), f (5), f 74 , f (3 p), f ( p3 ) 2 61. x3 y 2 y 6 2 x 5, if x 4 , find: 3 x 2 , if x 4 51. If f ( x) f (6), f (2), f 3, f (0), f (4), f 9 2 x 2 4 x, if x 2 52. If f ( x) , find: 7 2 x, if x 2 f (5), f (3), f 0, f (1), f (2), f 10 3 22 60. 3x 2 y 2 16 62. x 3y 5 63. x3 5 y 64. y 3 7 x 65. y 2 x 66. x 3y 4 University of Houston Department of Mathematics Exercise Set 1.1: An Introduction to Functions For each of the following problems: (a) Find f ( x h) . (b) Find the difference quotient (Assume that h 0 .) f ( x h) f ( x ) . h 67. f ( x) 7 x 4 68. f ( x) 5 3x 69. f ( x) x 2 5 x 2 70. f ( x) x 2 3x 8 71. f ( x) 8 72. f ( x) 6 73. f x 1 x 74. f x 1 x3 MATH 1330 Precalculus 23