Plant Nutrition I. Photosynthesis
advertisement

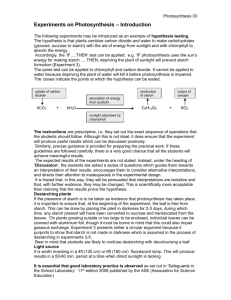
Plant Nutrition I. Photosynthesis Like all living organisms, plants and algae need food too. They require the food energy for growth, respiration and reproduction. Plants are able to make their own food; they don’t need to consume it. They do this through a process called photosynthesis. This process takes place in the green parts of plants (i.e. the leaves) in the presence of light. II. The process of photosynthesis The cells in the leaves of plants contain many small green parts called chloroplasts. These chloroplasts contain a green substance called chlorophyll. During photosynthesis, the chlorophyll in the chloroplasts absorbs light energy. This energy is then used to convert carbon dioxide from the air, plus water from the soil into a simple sugar called glucose. This chemical reaction produces oxygen as a by-­‐product. The oxygen is released into the air for us to breathe in. Diagram cited from: http://www.thinglink.com/ Diagram cited by: http://www.hobart.k12.in.us/ 1 Some of the glucose that is produced during photosynthesis is used immediately, however, the majority is converted into insoluble starch and stored. In the classroom, we can use iodine solution (yellowy-­‐brown liquid) to determine if photosynthesis has taken place in a plant. When iodine solution reacts with starch, it turns blue. III. Plant cells, tissues and organs Plants are made up of organs, just as we are. The organs in a plant are stems, roots and leaves. These organs are made up of tissues. The tissues (groups of similar cells working together) in a leaf are: 1. Mesophyll tissue – where most of the photosynthesis in a plant occurs. 2. Xylem and Phloem – they transport the water, minerals and sucrose around the plant. 3. Epidermal tissue – this is like the skin of the plant, it covers the whole plant. Diagram cited from: http://www.quia.com/ 2 IV. Leaf adaptations -­‐ They are broad, giving them a large surface area for light to fall on -­‐ They contain chlorophyll within the chloroplasts for absorbing light energy -­‐ They have veins which transport plenty of water into the cells of the leaves -­‐ They contain air spaces which allows carbon dioxide to diffuse into the cells and oxygen to diffuse out These adaptations in the leaves allow plants to photosynthesise as much as possible, whenever there is light available. Algae are aquatic so adapt to photosynthesising in water. They absorb dissolved carbon dioxide from the water around them. V. The rate of photosynthesis The rate of photosynthesis is affected by the intensity of light, the amount of CO2 and the temperature (and also obviously water). Any of these three highlighted factors can be the limiting factor. This means they can stop photosynthesis from happening any faster. Which factor is limiting at a particular time depends on the environmental conditions. At nighttime, light is the limiting factor. In winter, temperature is the limiting factor. When it is warm enough and bright enough, CO2 is usually the limiting factor. 3 Diagram cited from: http://users.rcn.com/ VI. Ideal conditions for farming Outdoors, plants are always affected by the factors discussed above. These are out of our control. However, nowadays, farmers, gardeners and big companies are able to artificially create the ideal environment for plants to grow using greenhouses. Big commercial greenhouses are used and they take advantage of what we know about limiting factors. In these, the temperature, levels of carbon dioxide and light can be controlled and varied in order to get the fastest possible rates of photosynthesis. Greenhouses trap the suns heat, but also, in winter, heaters can be used to keep the temperature at an optimum level. Artificial light can be used after the sun goes down to keep photosynthesis going. Carbon dioxide levels can be increased using a paraffin heater. Plants can even be grown straight out of water, with all the added mineral ions (i.e. nitrate ions for necessary for protein synthesis) and no soil so that there is nothing slowing down their growth rate. (This is called hydroponics). Keeping plants enclosed makes it easier to keep them free from pests and diseases and fertilisers can be added to the soil for optimum mineral levels for healthy growth. If the conditions are kept just right, plants will grow much faster and a decent crop can be 4 harvested much more frequently. Diagram cited from: http://www.praxair.com/ VII. How plants use glucose 1. FOR RESPIRATION Plants manufacture glucose in their leaves. They then use some of it for respiration. This releases energy, which then enables the plant to convert the rest of the glucose into various other useful substances, which they can use to build new cells and grow. They also need minerals from the soil to assist with this. 2. MAKING CELL WALLS Glucose is converted into cellulose for making strong cell walls. 3. MAKING PROTEINS Glucose is combined with nitrate ions to make amino acids, and then proteins. 4. STORED IN SEEDS Glucose is turned into lipids (fats and oils) for storing in seeds. E.g. sunflower seeds contain a lot of oil, which we then turn into sunflower oil to cook with. Seeds also store starch. 5 5. STORED AS STARCH Glucose is turned into starch and stored in roots, stems and leaves. This is so that the plant can access it for use when photosynthesis isn’t happening (e.g. in winter). Starch is insoluble, which makes it much better for storing than glucose. A cell high in glucose will draw a lot of water in by osmosis and swell up. Potatoes and parsnips store a lot of starch underground over winter so that a new plant can grow from it the following spring. 6 MCQ C Carbon dioxide + A ! B + Oxygen 1. What is A in the above equation? a) Glucose b) Water c) Sunlight d) Chlorophyll 2. What is B in the above equation? a) Glucose b) Water c) Sunlight d) Chlorophyll 3. What is C in the above equation? a) Glucose b) Water c) Sunlight d) Chlorophyll 4. What substance do plants make for storage in seeds? a) Glucose b) Energy c) Starch d) Lipids (fats, oils) 7 5. What mineral ions need to be present in the soil to aid the production of proteins in the plant? a) Potassium b) Magnesium c) Zinc d) Nitrates 6. The substance that plants make for storage in the roots, stems and leaves of the plant is? a) Glucose b) Water c) Starch d) Lipids (fats, oils) 7. Tomatoes in a greenhouse grow faster if the carbon dioxide concentration is increased. This shows that: a) Carbon dioxide concentration must have been a limiting factor b) Light intensity must have been a limiting factor c) Temperature must have been a limiting factor d) Lack of water must have been a limiting factor 8. Fats, oils and starch are how plants store their glucose more long term. Why is it beneficial to the plant to store glucose in these ways? a) Because fats, oils and starch are insoluble b) Because fats, oils and starch are solid at room temperature c) Because fats, oils and starch are readily accessible to the plant d) Because fats, oils and starch are good forms of energy for humans 9. What colour does starch go in the presence of iodine? a) Black b) Yellow c) Purple 8 d) Blue 10. Which of the following is true of growing crops in a greenhouse? a) Temperature, light and carbon dioxide levels can be controlled easily b) Its easier to prevent pests and diseases from entering c) With optimum control measures you can harvest a decent crop much more frequently d) All of the above 9