Sociological Theories: Emphasis on Social Structure
advertisement

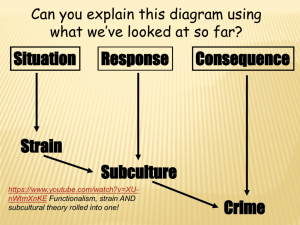
Sociological Theories: Emphasis on Social Structure Chapter 6 Early Theorist Cartographic School – 1820 to 1880 Founders – Quetelet and Guerry First social scientist to use objective mathematical techniques to study the influence of: Age, sex, season, climate, heterogeneity, education, poverty and drink- On the propensity to commit crime. Cartographic School Quetelet & Guerry concluded: …that crime must be a regular feature of social life. …that crime must be rooted in social arrangements, and.. …if those arrangements could be identified, crime could be eliminated. Early Theorist Emile Durkheim – 1858-1917 Publication of Suicide in 1897 Individual behavior vs socialcultural forces within society. (Social solidarity) Egoistic suicide Altruistic suicide Anomic suicide Emile Durkheim Crime is functional for society – How? Anomie.. …is the breakdown of social norms or the dissociation of the individual from the collective conscience (general sense of morality of the times.) Emile Durkheim Anomie is the cause of crime… Lack of regulation…the collective conscience is unable to regulate human desires. Lack of integration…individualism is promoted to such a degree that people become selfish (egoistic), no longer care about the welfare of other human beings. Congruence Theory Congruence theory…maintain that the social system is in a state of harmony when it provides realistic means for achieving the prescribed successgoals. …delinquency and criminality occur because access to legitimate means for achieving success-goals is limited, the social system is said to be unbalanced. Congruence Theory Basic Assumptions: Normally, there is conjunction between the goals and means so that society is fairly well integrated. Individuals, generally, are productive conformists who, through learning and socialization, internalize the socially prescribed goals and means. Congruence Theory Basic Assumptions: Cont’d Most criminality and delinquency is the result of strain or the imbalance of the person’s cognitive system. The reaction to certain forms of deviant behavior depends upon how much of a threat to the established order society views the behavior. Social Disorganization Theory Tonnies- Transition of societies Communal Society/Gemeinschaft Associational Society/Gessellschaft Ferdinand Tonnies Communal/Gemeinschaft There is a minimal division of labor and no specialization of roles. The family in the most important unit in the society. Most social relationships are personal and tend to be long-lasting. Behavior is regulated mainly by custom and tradition. Ferdinand Tonnies Associational/Gessellschaft There is a high division of labor and specialization. Family influence is replaced by other major social institutions. Social relationships are impersonal and short-lived. Social behavior is governed by law rather than custom. Social Disorganization Theory Clifford Shaw and Henry McKayThe Ecology of Crime…crime is a product of the decaying transitional neighborhoodDiagram the Concentric Zone Model – Causes of Social Disorganization Successive changes in the composition of the population. Disintegration of the existing culture. Diffusion of cultural standards. Industrialization of the area. Social Disorganization Results in: Dissolution of neighborhood culture and organization. Breakup of conventional neighborhood traditions and institutions. The effectiveness of the neighborhood as a unit of control and a medium for the transmission of the moral standards of society is reduced. (Consequences) Social Disorganization New Means of Social Control: Family Schools Church …with the dissolution of these institutions, social is primarily left up to the…? Police Anomie/Strain Theory Robert K. Merton-(Durkheim) …every society includes cultural goals and institutional means (norms) about how to reach those goals. “Aberrant behavior may be regarded sociologically as a symptom of dissociation between culturally prescribed aspirations and socially structured avenues of realizing these aspirations.” #5 of Assumptions Anomie/Strain Theory #10…reactional patterns of environmental circumstances presented to the individuals are: (Adaptations to anomie) Conformity Innovation Ritualism Retreatism Rebellion Subculture Theories Subculture_ …is a group of people within a society that have a style of living that includes features of the dominant culture and cultural elements not found in the dominant culture. Such as? Subculture Theories Walter B. MillerLower-class subculture & delinquency – Focal Concerns: Trouble Toughness Smartness Excitement Subculture Theories Lower-class subculture – Focal Concerns: Fate Autonomy Subculture Theories Richard Cloward & Lloyd Ohlin: Differential Opportunity TheoryNeighborhoods characterized by Criminal Subculture. Neighborhoods characterized by Conflict Subculture. Neighborhoods characterized by Retreatist Subculture.