1. A plane mirror reflecting a ray of incident light is rotated through
advertisement

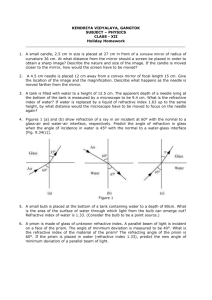
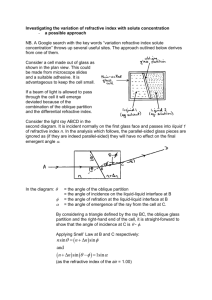
RAY OPTICS 1. A plane mirror reflecting a ray of incident light is rotated through an angle about an axis through the point of incidence in the plane of the mirror perpendicular to the plane of incidence, then, 2. 3. (a) the reflected ray does not rotate (c) the reflected ray rotates through an angle (d) the incident ray is fixed. 5. 6. (a) its velocity increases (b) its velocity decreases (c) its frequency decreases (d) its wavelength decreases The refractive index of a given piece of transparent quartz is the greatest for red light (b) violet light (c) green light (d) yellow light A well cut diamond appears bright because (a) it emits light (b) it is radioactive (c) of total reflection (d) it has high density Total internal reflection can occur when light passes (a) from denser to a rarer medium (c) from one medium to another of equal refractive index (d) from one medium to another of equal absorption coefficient (b) from rarer to a denser medium Critical angle of light passing from glass to air is minimum for (a) 7. the reflected ray rotates through an angle A monochromatic beam of light passes from a denser medium to a rarer medium. As a results (a) 4. (b) red (b) green (c) yellow (d) violet The critical angel for light going form medium X into medium Y is . The speed of light in medium X is v. The speed of light in medium Y is. 8. (a) v (1 – cos ) (b) v/sin (c) v/ cos (d) v cos The blue colour of sky is due to (a) 9. scattering (b) absorption (c) reflection (d) refraction A ray of light from a denser medium strikes a rare medium at angle of incidence i the reflected and refracted rays make an angle of 900 with each other. The angles of reflection and refraction are r and r’. The critical angle is. (a) 10. sin –1 (tan r) (b) sin–1 (tan i) (c) sin–1 (tan r) (d) tan–1 (tam i) A bird in air looks at a fish vertically below it and inside water h1 is the height of the bird above the surface of water and h2, the depth of the fish below the surface of water. If refractive index of water with respective to air be , then the distance of the fish as observed by the bird is (a) 11. h1 + h2 (b) h1 + h2 (c) h1 + h2 (d) h1 + h2 A light bulb is placed between two plane mirrors inclined at an angle of 600. The number of images formed are (a) 12. 6 (b) 2 (c) 5 (d) 4 A plane mirror is approaching you at 10 cm per second. You can see your image in it At what speed will your image approach you? (a) 10 cm/sec (b) 5 cm/sec (c) 20 cm/sec (d) 15 cm/sec 13. A glass slab of thickness 4 cm contains the same number of waves as 5 cm of water when both are traversed by the same monochromatic light. If the refractive index of water is 4/3, what is that of glass? (a) 14. 5/3 (b) 5/4 (c) 16/15 (d) 1.5 A fish is little away below the surface of a lake If the critical angle is 490, then the fish could see things above the water surface within an angular ring of 0 Ar water 0 49 where 15. (a) = 490 (b) = 900 (c) = 980 (d) = 24 1o 2 Fish A beam of monochromatic blue light of wavelength 4200 Å in air travels in water ( = 4/3) its wavelength in water will be. (a) 16. 2800 Å (b) 5600 Å (c) 3150 Å (d) 4000 Å A metal coin is at the bottom of a beaker filled with a liquid to a height of 6 cm. The R.I. of the liquid is 4/3. To an observer looking form above the surface of the liquid, the coil will appear raised up by (a) 17. 4.5 cm (b) 6.75 cm (c) 1.5 cm (d) 7.5 cm A convex mirror of focal length f produces an image (1/n) th of the size of the object. The distance of the object from the mirror is (a) 18. n, f (b) f/n (c) (n + 1)f (d) (n –1)f A double convex lens made of material of refractive index 1.5 and having a focal length of 10 cm is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 3.0. The lens will behave as 19. (a) converging lens of focal length 10 cm. (b) diverging lens of focal length 10 cm (c) converging lens of focal length 10/3 cm (d) converging lens of focal length 30 cm. A spherical mirror forms an erect image three times the linear size of the object. If the distance between the object and the image is 80 cm, the focal length of the mirror is. (a) 20. 15 cm (b) –15 cm (c) 30 cm (d) 40 cm In the figure given below there are two convex lenses L1 and L2 having focal lengths F1 and F2 respectively. The distance between L1 and L2 will be. 21. (a) F1 (b) F2 (c) F1 + F2 (d) F1 – F2 L1 L2 Two lenses having powers as + 2D and –4 D respectively are put together. Power of the combination would be: (a) –2 D (b) +2D (c) –4D (d) +4 D ACME STUDY POINT NEAR BOYS SCHOOL HAMIRPUR (H.P) CONTACT NUMBER – 01972- 203911 22. A convex lens of focal length 20 cm is cut into two equal parts so as to obtain two Plano convex lenses shown in figure The two parts are then put in contact as shown in figure What is the focal length of combination ? 23. (a) zero (b) 5 cm (c) 10 cm (d) 20 cm (a) (b) (c) A prism has a refractive angle of 600. When placed in the position of minimum deviation, it produces a deviation of 300 .Then the angle of incidence is. (a) 24. 300 (b) 450 (c) 150 (d) 600 The angle of the prism is 300. The rays incident of 600 at one refracting face suffer a deviation of 300. Then the angle of emergence is. (a) 25. 00 (b) 300 (c) 600 (d) 900 Angle of prism is A and its one surface is silvered Light rays falling at an angle of incidence 2A on first surface return back through the same path after suffering reflection at second silvered surface Refractive index of material is . (a) 26. 28. (b) 2 cos A (c) cos A/2 (d) tan A (c) diffraction (d) dispersion (b) coloured images Chromatic aberration in a lens is caused by (a) 27. 2 sin A reflection (b) interference An achromatic combination of lenses produces (a) images in block and white (c) images unaffected by variation of refractive index with wavelength (d) highly enlarged image. An achromatic convergent lens of focal length + 20 cm is made of two lenses (in contact) of materials having dispersive powers in the ratio of 1 : 2 and having focal lengths f1 and f2. Which of the following is true 29. (a) f1 = 10 cm ,f2 = – 20 cm (b) f1 = 20 cm ,f2 = 10 cm (c) f1 = – 10 cm , f2 = – 20 cm (d) f1 = 20 cm , f2 = – 10 cm (c) blue colour The angle of deviation for a prism is greatest for (a) 30. red colour (b) violet colour (d) green colour The current graph between the angle of deviation and angle of incidence for a prism is ACME STUDY POINT NEAR BOYS SCHOOL HAMIRPUR (H.P) CONTACT NUMBER – 01972- 203911 Answers Ray optics 1. (c,d) 2. (a) 3. (b) 4. (c) 5. (a) 6. (d) 7. (b) 8. (a) 9. (a,b) 10. (b) 11. (c) 12. (c) 13. (a) 14. (c) 15. (c) 16. (c) 17. (d) 18. (b) 19. (c) 20. (c) 21. (a) 22. (d) 23. (c) 24. (a) 25. (b) 26. (d) 27. (c) 28. (a) 29. (b) 30. (c) ACME STUDY POINT NEAR BOYS SCHOOL HAMIRPUR (H.P) CONTACT NUMBER – 01972- 203911