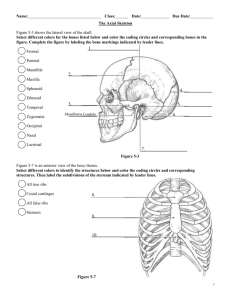
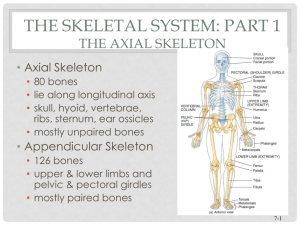
Topic 7: The Axial Skeleton Divisions of the Skeleton:
advertisement

1/9/2013 Topic 7: The Axial Skeleton What makes up the axial skeleton? Ribs and Sternum Vertebrae What is the morphology of these structures? What sorts of specializations have evolved? How do they develop? What are their forms and how have they evolved? Vertebral column What are the evolutionary trends in the regionalization and complexity of the vertebral column? What are the functions of the vertebral column? What specializations have evolved? Endochondral Divisions of the Skeleton: _____________ Sternum _____________ Unpaired fins Dermal Gastralia Liem et al. Fig. 8-15, 8-18; Dean 1895 1 1/9/2013 Sternum & Ribs What are the functions of a rib cage? False Ribs True Ribs Floating Ribs Sternum & Ribs Ribs reduced to absent in amphibians Lack a rib cage ______________ single element Associated with pectoral girdle Well-developed in amniotes Full rib cage Differentiate ___________ & _______________ Sternum articulates with ribs ________________ protect abdomen in some Liem et al. Fig. 8-7 2 1/9/2013 Gastralia Turtle Shell Crocodylia Plesiosauria Protection of abdomen _________ – top _________ – bottom Overlaid by keratinized scutes Primarily dermal Ribs & vertebrae fuse to overlying plates What might be the costs and benefits of such a shell? © ucmp.berkeley.edu; plesiosauria.com Turtle Shell - Development Liem et al. Fig. 8-15; © Nova Scotia Museum Bird _______________ Rib cage is external to the ________________ Costal scerotomal cells move laterally, not ventrally Myotomal cells and girdle sclerotome move ventrally Bony posterior projection of ribs Overlaps one rib caudally Locks ribs together to increase ___________ efficiency Some crocs have cartilaginous uncinate processes Liem et al. Fig. 8-17; © www.livescience.org Liem et al. Fig. 8-16 Vertebrae ______________ Variable in morphology Form a vertebral column Vertebral Development Wolpert, 1998 What kind of homology do they demonstrate? Paraxial Mesoderm Segmentation Somites Dissociation Sclerotomes Dermatomes Myotomes Somite Resegmentation Vertebrae Paraxial mesoderm © R Anderson © KA Stevens Dermis of Skin Trunk Muscles See Liem et al. Table 4-1 1 1/9/2013 Vertebral Development: Determination of Vertebral Number ________________________ Model Opposing Retinoic Acid and FGF/Wnt gradients set up a posteriorly-moving determination front Expression of Lunatic Fringe is cyclic and anterior to posterior Each time Lunatic Fringe expression hits the determination front a new somite boundary is formed Gomez & Pourquie 2009; Gomez et al. 2008 Vertebral Development: Determination of _________________ _____________ Evolution One Hox gene duplicated Hox cluster was duplicated twice Cluster of 13 paralogues 4 paralogous clusters, or 52 Hox genes Some Hox genes have been lost by mutation Fishes have 44 Hox genes Amniotes have 39 Hox genes Liem et al. 2001, Fig 4-41 1 1/9/2013 Vertebral Development: Determination of Vertebral Identity e.g., Chicken HoxC expression Somite _____________ Sclerotome condensation _________________ Anterior Vertebral Development Hox gene expression is ______ Combination of Hox genes expressed determines vertebral identity Posterior HoxC11 HoxC10 HoxC9 HoxC8 HoxC6 HoxC5 HoxC4 Modified from Burke et al. 1995 Chal & Pourquie 2009, Fig 3-6; © PJB Vertebral Morphology Categorize where they are concave _______________ Amphicoelous _______________ Opisthocoelous _______________ Vertebral Morphology Petromyzontiformes Who has acoelous vertebrae? Chondrichthyes How about amphicoelous? _____________ “Exposed” notochord _____________ Encapsulated notochord Neural arch & canal Hemal arch & canal Kardong Fig. 8-4 Liem et al. Fig. 7-5A, 8-1A Vertebral Morphology Vertebral Morphology _______________ Bone, amphicoelous vertebrae Undifferentiated vertebrae Enclosed, continuous notochord ____________ vertebrae Increased robustness Closer articulation Increased elaboration • Opisthocoelous – many amphibians, some ‘reptiles’ • Procoelous – many ‘reptiles’ • Zygapophyses • Transverse processes • Neural & hemal spines Salmon Liem et al. Fig. 8-2A , 8-8B; A Morton Photo: M Taylor 1 1/9/2013 Vertebral Morphology Vertebral Morphology Bird vertebrae are more differentiated _____________ & differentiated Intervertebral disks Many processes – What are they for? Cervical Mammals Heterocoelous Saddle-shaped articulation _________________ along two axes, twisting Lumbar Fused to pelvis and sacral vertebrae ____________________ Eliminate ____________ © R Jayasena; Liem et al. Fig. 8-17B Vertebral Regionalization & Complexity Vertebral Morphology What is meant by vertebral regionalization? What trends have we seen in complexity of vertebrae? What are the (competing) functions of the vertebral column? Fish vertebrae are relatively undifferentiated Other vertebrates have increasingly differentiated vertebrae Fish: Trunk, ___________ Amphibians & “Reptiles”: ______________________ ______________________ © indyspinemed.com, Univ. Maryland; De Iullis & Pulera Fig. 7.8 ___________, trunk, sacral, caudal Mammals: Cervical, _____________, lumbar, sacral, caudal © indyspinemed.com Vertebral Column Function Stability & Support Vertebral Column Function Control torsion Control bending Reduction in number of vertebrae What are some examples of this? Kardong, Fig. 8-39 Movement & flexibility ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ Kardong, Fig. 8-34, 8-38; KA Stevens Bounding locomotion in mammals Lateral undulation in sprawlers Movement allowed in some planes, not others How might flexibility be increased? Vertebrate Life 24-2; © KP Bergmann 2 1/9/2013 Human ___________________ Human spinal lordosis Humans have greater lordosis than other apes Females have greater lordosis than males What does this tell us? Spinal loading Balanced COM ♂ ♀ ♂♀ Pregnancy shifts COM _______________ Lordosis is increased in response ♂♀ ♂♀ Whitcome et al. 2007 ♂♀ Whitcome et al. 2007 3