9.3 Textbook
advertisement
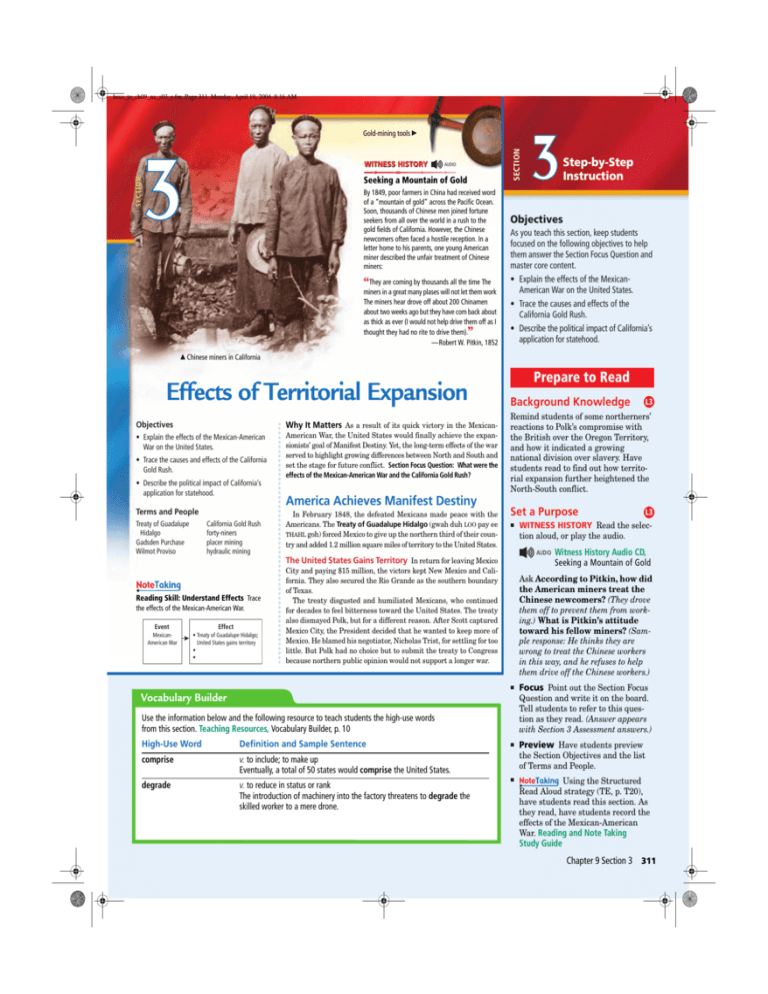
hsus_te_ch09_na_s03_s.fm Page 311 Monday, April 19, 2004 8:16 AM WITNESS HISTORY SECTION Gold-mining tools 䊳 AUDIO SECTION Seeking a Mountain of Gold By 1849, poor farmers in China had received word of a “mountain of gold” across the Pacific Ocean. Soon, thousands of Chinese men joined fortune seekers from all over the world in a rush to the gold fields of California. However, the Chinese newcomers often faced a hostile reception. In a letter home to his parents, one young American miner described the unfair treatment of Chinese miners: “They are coming by thousands all the time The miners in a great many plases will not let them work The miners hear drove off about 200 Chinamen about two weeks ago but they have com back about as thick as ever (I would not help drive them off as I thought they had no rite to drive them). —Robert W. Pitkin, 1852 ” 䊱 Step-by-Step Instruction Objectives As you teach this section, keep students focused on the following objectives to help them answer the Section Focus Question and master core content. • Explain the effects of the MexicanAmerican War on the United States. • Trace the causes and effects of the California Gold Rush. • Describe the political impact of California’s application for statehood. Chinese miners in California Effects of Territorial Expansion Objectives • Explain the effects of the Mexican-American War on the United States. • Trace the causes and effects of the California Gold Rush. • Describe the political impact of California’s application for statehood. Terms and People California Gold Rush forty-niners placer mining hydraulic mining Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo Gadsden Purchase Wilmot Proviso Why It Matters As a result of its quick victory in the MexicanAmerican War, the United States would finally achieve the expansionists’ goal of Manifest Destiny. Yet, the long-term effects of the war served to highlight growing differences between North and South and set the stage for future conflict. Section Focus Question: What were the effects of the Mexican-American War and the California Gold Rush? America Achieves Manifest Destiny In February 1848, the defeated Mexicans made peace with the Americans. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (gwah duh LOO pay ee THAHL goh) forced Mexico to give up the northern third of their country and added 1.2 million square miles of territory to the United States. Prepare to Read Background Knowledge Remind students of some northerners’ reactions to Polk’s compromise with the British over the Oregon Territory, and how it indicated a growing national division over slavery. Have students read to find out how territorial expansion further heightened the North-South conflict. Set a Purpose Reading Skill: Understand Effects Trace Event Effect MexicanAmerican War • Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo; United States gains territory • • L3 쐍 WITNESS HISTORY Read the selec- tion aloud, or play the audio. Witness History Audio CD, Seeking a Mountain of Gold The United States Gains Territory In return for leaving Mexico the effects of the Mexican-American War. L3 City and paying $15 million, the victors kept New Mexico and California. They also secured the Rio Grande as the southern boundary of Texas. The treaty disgusted and humiliated Mexicans, who continued for decades to feel bitterness toward the United States. The treaty also dismayed Polk, but for a different reason. After Scott captured Mexico City, the President decided that he wanted to keep more of Mexico. He blamed his negotiator, Nicholas Trist, for settling for too little. But Polk had no choice but to submit the treaty to Congress because northern public opinion would not support a longer war. Ask According to Pitkin, how did the American miners treat the Chinese newcomers? (They drove them off to prevent them from working.) What is Pitkin’s attitude toward his fellow miners? (Sample response: He thinks they are wrong to treat the Chinese workers in this way, and he refuses to help them drive off the Chinese workers.) 쐍 Focus Point out the Section Focus Question and write it on the board. Tell students to refer to this question as they read. (Answer appears with Section 3 Assessment answers.) Use the information below and the following resource to teach students the high-use words from this section. Teaching Resources, Vocabulary Builder, p. 10 High-Use Word Definition and Sample Sentence comprise v. to include; to make up Eventually, a total of 50 states would comprise the United States. degrade v. to reduce in status or rank The introduction of machinery into the factory threatens to degrade the skilled worker to a mere drone. 쐍 Preview Have students preview the Section Objectives and the list of Terms and People. 쐍 Using the Structured Read Aloud strategy (TE, p. T20), have students read this section. As they read, have students record the effects of the Mexican-American War. Reading and Note Taking Study Guide Chapter 9 Section 3 311 hsus_te_ch09_na_s03_s.fm Page 312 Monday, April 19, 2004 8:16 AM Ceded by Britain, (Convention of 1818) S the United States had achieved Manifest Destiny and stretched from the Atlantic to the Pacific. 1. Locate: (a) Oregon, (b) Texas, (c) Mexican Cession, (d) Gadsden Purchase the three key terms of this blue heading around a concept web with the center oval labeled “Expansion.” Then, have students add information to the satellite ovals relating each term to U.S. territorial expansion. 쐍 Teach Ask Why was Polk disap- pointed with the outcome of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo? (He wanted to keep more of Mexico.) Have students discuss how railroad needs drove westward expansion. What made the Wilmot Proviso so divisive? (It made slavery a prominent issue, splitting the two main political parties along NorthSouth lines, or proslavery and antislavery lines.) 2. Regions What territory did the United States acquire as the result of war? LOUISIANA PURCHASE (Purchased from France, 1803) ua da o, 1848lupe ) GADSD Vocabulary Builder comprise –(kuhm PRìZ) v. to include; to make up Independent Practice EN (Purcha PURCHASE s Mexico,ed from 1 85 3) 120° W 3. Connect Past and Present Is your own state on this map? If so, how and when was it acquired by the United States? ie Er L. TE S ED STA THE UN(I1T783) MEXIC (Treat AN CESSIO y of G N H id a lg Lake o Ontari L UNT gree Brita ment with RY in , 1 8 4 6) 쐍 Quick Activity Have students access Web Code ncp-0906 to use the Geography Interactive map and then answer the map skills questions in the text. Superior ES 쐍 Introduce: Key Terms Organize L. OREG ON C (A O L. Michigan Map Skills By 1853, eat th Gr842 ed wi Disputtain until 1 Bri n uro .H Instruct BRITISH TERRITORY 400 km AT 200 ST 0 E L 1 3 L3 Conic Projection 200 400 mi INA 0 N W ORIG Teach America Achieves Manifest Destiny For: Interactive map Web Code: ncp-0906 Growth of the United States to 1853 tic At l a n n Ocea TEXAS ANNEXATION (Annexed by Congress, 1845) Pa c i f i c Ocean 30° N 812) A ) FLORpID , 18 19 y S ai n (C eded b 1 (Annexed, (Annexed, 1810) MEXICO Present-day state boundaries co Gul f of Me x i 80° W 90° W 110° W In the Gadsden Purchase of 1853, the United States obtained from Mexico another 29,640 square miles in southern Arizona and New Mexico. The Americans bought this strip to facilitate a railroad across the continent. Along with the annexation of Texas, the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo and the Gadsden Purchase increased the area of the United States by about one third. Only the Louisiana Purchase had added more territory. The new lands comprised present-day New Mexico, California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, and half of Colorado. The Wilmot Proviso Divides Americans Even before the war ended, the prospect of gaining land from Mexico stirred fierce debate in the United States. In 1846, Whig congressman David Wilmot of Pennsylvania had proposed a law, known as the Wilmot Proviso, that would ban slavery in any lands won from Mexico. The proposal broke party unity and instead divided Congress largely along sectional lines. Most northern Democrats joined all northern Whigs to support the Wilmot Proviso. Southern Democrats joined southern Whigs in opposition. The Proviso passed in the House of Representatives, but it failed narrowly in the Senate. The Wilmot Proviso would reappear in every session of Congress for the next 15 years. Repeatedly, it passed in the House only to fail in the Senate. The Proviso brought the slavery issue to the forefront and weakened the two major parties, which had long tried to avoid discussing the issue in Congress. Thus, the lands won from Mexico increased tensions between North and South. 쐍 Have students fill in the Note Tak- ing chart for this section. 쐍 To help clarify the geography of U.S. territorial expansion, have students complete the Outline Map: Mexican Cession and the Gadsden Purchase worksheet. Teaching Resources, p. 17 Monitor Progress As students fill in their charts, circulate to make sure that they have correctly matched effects with events. For a completed version of the chart, see How did the Mexican-American War serve to heighten tensions over slavery? Note Taking Transparencies, B-49. Answers Map Skills 1. Review locations with students. 2. Texas, New Mexico, Arizona, California, Utah, Nevada, and parts of Wyoming and Colorado. 3. Students should accurately explain how and when their state joined the Union. The war gave the United States new territories—potential states—which could upset the balance of North-South power in Congress. 312 Manifest Destiny L1 Special Needs Students L2 English Language Learners To help students understand the effects of the MexicanAmerican War and the Gadsden Purchase, have them research one state created out of the territory won from Mexico. Then, ask them to use their findings to create a timeline to show at least five major events in the chosen state’s history from the year it was L2 Less Proficient Readers acquired to the present day. For example, students may note the year in which the chosen state joined the Union. Students may annotate their timelines with text, symbols, or pictures and include a title. Have students use their timelines to summarize the state’s history for a partner. hsus_te_ch09_na_s03_s.fm Page 313 Monday, April 19, 2004 8:16 AM The California Gold Rush The California Gold Rush To most Americans, the new lands in the West seemed too distant for rapid settlement. But in early 1848, workers at John Sutter’s sawmill found flecks of gold in the American River east of Sacramento, California. Instruct Forty-Niners Flock to California By summer, news of the gold strike caused a sensation in the eastern United States. In a mass migration known as the California Gold Rush, some 80,000 fortune seekers headed for California in search of easy riches. About half of these forty-niners traveled by land trails. Another half went by ship around South America or via a short land passage at the Isthmus of Panama. The ships landed their human cargo in San Francisco. The golden news also attracted miners from around the Pacific Rim. Many fortune seekers came from South America, especially Peru and Chile. Another 25,000 laborers migrated from China to California during the 1850s. From a mere 14,000 in 1847, California’s population of outside settlers surged to 225,000 in just five years. Miners Lead a Rough Life Forty-niners flocked to the gold fields with high hopes. One young man described the excitement of departing for California from Indiana: L3 쐍 Introduce: Key Terms Write the The Lure of California Gold The California gold fields attracted thousands of men and a smaller number of women (bottom). The poster (below, left) advertises ship passage to California. What does the guidebook (below, right) suggest about the appeal of the California Gold Rush? “ The diggings had been discovered but a twelvemonth before, and the glowing tales of their marvelous richness were on every tongue. Our enthusiasm was wrought up to the highest pitch, while the hardships and perils . . . were scarcely given a passing thought. —David Rohrer Leeper, “The Argonauts of ’49” ” At first, the miners used cheap metal pans, picks, and shovels to harvest gold flecks from the sand along the banks and bottoms of rivers and streams. This process was known as placer mining. A few miners got rich, but most worked hard for little gain. Because food and clothing were so expensive, shrewd traders made more money selling goods to the miners than the miners made by panning for gold. Conditions were hard in the crowded mining camps. Poor sanitation promoted diseases, especially cholera and dysentery, killing hundreds. In addition, life was cheap and law was scarce in the camps. Almost all of the inhabitants were men, who felt frustrated by their failure to find much gold and by their lack of family life. Competition and fights became common. One forty-niner noted, “It is surprising how indifferent people become to the sight of violence and bloodshed in this country.” In search of order, the miners carried out their own rough justice. Without official legal authority, they acted as judges, juries, and executioners. key terms California Gold Rush and forty-niners on the board and provide the definitions. Have students read to find out what life was like for forty-niners who joined the California Gold Rush. 쐍 Teach Display Color Transpar- ency: Mining for Gold. Using the Idea Wave strategy (TE, p. T20), discuss with students the conditions for miners in California during the Gold Rush. Ask What was early gold mining like? (At first, most gold was found by using placer mining, or panning or picking gold from rivers and streams.) What were conditions like for the miners? (Many died from diseases in the crowded, dirty camps or from violence because of the lack of law enforcement.) How did mining change over time? (Placer mining was replaced by more expensive and complicated, although efficient, methods such as hydraulic mining or hard-rock mining. Mining became a big business, bringing to an end the era of the independent miner.) Color Transparencies A-36 쐍 Analyzing the Visuals Refer students to the photograph on this page. Ask What type of mining are these miners doing? (placer mining) Independent Practice Methods of Mining Change Placer mining soon Refer students to the Infographic “San Francisco: Growth of a City” on the next page. Have students convert the information in the chart “Growth of San Francisco” to a bar or line graph. Then, have them answer the Thinking Critically questions. gave way to more efficient methods that required more money and equipment. One method was to dam and divert rivers to expose their beds. Another method, hydraulic mining, employed jets of water to erode gravel hills into long lines of sluices to catch the gold. Hydraulic mining damaged the environment by leveling hills and clogging rivers with sediment. Monitor Progress Blue Jeans Denim blue jeans were one of the more spectacular successes of the Gold Rush. In 1853, new U.S. citizen Levi Strauss left his family’s dry goods business in New York City to start his own company in the burgeoning port of San Francisco. To outfit miners and their families, Strauss sold imported dry goods such as clothing, umbrellas, and whole cloth. Strauss prospered, and Levi Strauss & Co. soon became a major business in the city. Then, in 1872, Strauss received a letter from a tailor named Jacob Davis. Davis had devised a unique way to make pants that could survive the toughest treatment and repeated washings. He used durable denim fabric and he reinforced the pieces that were most likely to rip apart with copper rivets. Because he did not have the money to apply for a patent, Davis invited Strauss to pay for and then share the patent, which Strauss did. The riveted “waist overalls,” as they were called, were a huge hit with miners, cowhands, and others who worked at rough jobs. Today, “Levis” are famous around the world as a symbol of American popular culture. As students complete their graphs and answer the questions, circulate to make sure that students understand how to convert the chart information to a graph format. Answer Caption that stories of the gold in California reached as far as France Chapter 9 Section 3 313 hsus_te_ch09_na_s03_s.fm Page 314 Monday, April 19, 2004 8:16 AM Effects of the Gold Rush L3 Instruct Vocabulary Builder degrade –(dee GRAYD) v. to reduce in status or rank 쐍 Introduce Remind students that when the forty-niners and other newcomers began to flock to California, many Mexicans, or Californios, and Native Americans already lived there. Ask students to predict the kinds of conflicts that might arise with the arrival of huge numbers of white settlers. Those with the most money turned to “hard rock mining,” searching in the mountains for veins of quartz that contained gold. Miners extracted gold by digging deep tunnels and shafts braced with posts and beams and drained by pumps. One California newspaper complained that the new type of large-scale mining operation “degrades the sturdy miner into a drudge . . . while [mine owners] reap the great profit of his endeavor.” The democratic age of placer mining was over. With few exceptions, wealthy investors rather than common miners owned the mines and enjoyed the profits. What problems did forty-niners face in the California gold fields? INFOGRAPHIC 쐍 Teach Ask How did white min- ers exclude Chinese and Mexican people from the gold fields? (They forced them to pay a heavy tax.) How were Native Americans in California treated? (Thousands were terrorized and killed.) Why do you think Californians wanted statehood so much? (Sample response: They may have believed lawlessness would be reduced if California were a state, and that statehood would help the economy grow.) For those traveling by ship, San Francisco was the gateway to the California gold fields. It was also a place where miners could come to buy supplies, exchange gold for cash, or relax. Through migration and trade, San Francisco quickly became the major American city on the Pacific coast in the 1800s. A Fast Trip West This 1851 advertisement promises a superfast trip from New York around the southern tip of South America to San Francisco—in as little as 97 days! 쐍 Quick Activity Have students read the HISTORY MAKERS feature about Mariano Vallejo. Ask How was Vallejo’s experience with white settlers typical and yet unique? (He lost much of his land through unjust court decisions, but he also served as a delegate to the California constitutional convention and as a state legislator.) Before and After What happened to San Francisco between 1848 (above) and 1850 (below)? One word explains the rapid building boom: GOLD! Street Scene This painting shows a busy street market in 1850 San Francisco. Independent Practice Have students write a summary statement for each red heading below the blue heading “Effects of the Gold Rush.” Thinking Critically Year Population Monitor Progress 1848 800 As students work on their summary statements, circulate to make sure that students are not paraphrasing, but summarizing, the information in one statement. 1849 25,000 1852 36,000 1860 57,000 overcrowding, loneliness, disease, and violence Thinking Critically 1. Sample response: general stores, saloons, restaurants, and shops owned and operated by tailors, photographers, jewelers, and goldsmiths 2. Possible responses: famine, epidemic, war, natural disaster; a boom in a new industry 314 Manifest Destiny 2. Draw Conclusions What other circumstances might cause rapid changes in a city’s population? For: To discover more about the growth of San Francisco Web Code: ncp-0910 SOURCE: CIA World Factbook Online L4 Advanced Readers Answers 1. Draw Inferences What kind of businesses do you think sprang up in San Francisco as a result of the Gold Rush? Growth of San Francisco L4 Gifted and Talented Students Ask students to do research to identify one company that was founded in California during the Gold Rush, such as Levi Strauss & Co. or Wells Fargo Bank, and write a report about it. Have students present the history of the company from its inception to the present day in an oral report that includes visuals such as posters and maps. Students should describe the company’s growth, include a description of the products or services it provided originally, and explain how those products or services have evolved in the last 150 years. Students should also include background information about the founders of the company, including their reasons for starting the company and how the company has participated in or affected the community in which it is located. hsus_te_ch09_na_s03_s.fm Page 315 Monday, April 19, 2004 8:16 AM Effects of the Gold Rush Newcomers from the eastern United States quickly asserted their dominance over California. To discourage the Chinese, they levied a heavy tax on foreign miners. Indians and Mexicans Face Discrimination White miners also terrorized and killed Native Americans by the thousands. Losing their land, many surviving Indians became workers on farms and ranches. Mob violence drove most Mexican Americans away from the gold fields. Those who stayed had to pay the foreign miners’ tax, though Mexicans had been in California long before the new American majority. Californios, or Mexican Californians, also lost most of their land. Contrary to the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, the courts ignored land titles created under Mexican law. Assess and Reteach Mariano Vallejo (1808–1890) Mariano Vallejo lived under Spanish, Mexican, and U.S. rule. The son of wealthy landowners, he became a general in the Mexican army. Critical of the Mexican government, Vallejo welcomed the arrival of U.S. settlers. Though he was briefly imprisoned during the Bear Flag revolt, he continued to support the American cause, serving as a delegate to the California constitutional convention and as a state legislator. But like many Californios, he lost most of his land to white settlers when the courts refused to recognize his family land grants. Vallejo lived his final years on a small fragment of his once large ranch. Assess Progress Assessment. 쐍 Administer the Section Quiz. Teaching Resources, p. 20 쐍 To further assess student under- standing, use Progress Monitoring Transparencies, 57. Reteach If students need more instruction, have them read the section summary. California Seeks Statehood The new Californians wanted quickly to organize a state and enter the union. In October 1849, their leaders held a convention and drew up a state constitution. The new constitution excluded African Americans, both slave and free. Most of the new Californians were northerners who did not want to compete with southern slaveholders who could use slave labor to seek gold. Nor did the miners want any free blacks to live in California. California’s application for statehood stirred discord between North and South. At the time, the Union was comprised of 15 free states and 15 slave states. Admission of a new free state would thus tip the delicate regional balance in the Senate. Over the next decade, debate over the spread of slavery into the lands won from Mexico would grow increasingly bitter. Thus, westward expansion became a major source of the division that ultimately led to the tragic Civil War. 33 Assessment Comprehension 1. Terms and People Write a sentence explaining how each of the following was connected with westward expansion. • Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo • Gadsden Purchase • Wilmot Proviso • California Gold Rush • forty-niners • placer mining • hydraulic mining Reading and Note Taking Study Guide L3 Adapted Reading and Note Taking Study Guide L1 L2 Spanish Reading and Note Taking Study Guide L2 Extend L4 Have students write a short story that takes place during the California Gold Rush. Stories may be in the first person or third person, and characters may be from any walk of life or work at any kind of job, as long as the story is realistic fiction and takes place between 1849 and 1855. After you have read the stories, ask volunteers to share their work with the class. What impact did the settlement of California have on Mexicans already living there? SECTION L3 쐍 Have students complete the Section Progress Monitoring Online For: Self-test with vocabulary practice Web Code: nca-0907 2. Reading Skill: Recognize Effects Use your chart to answer the Section Focus Question: What were the effects of the MexicanAmerican War and the California Gold Rush? Writing About History 3. Quick Write: Write an Editorial Write an editorial on the Wilmot Proviso that might have appeared in an 1846 newspaper. Define the issue and give reasons to support one position. Section 3 Assessment 1. Sentences should explain how each term is connected with westward expansion. 2. The war and the Gadsden Purchase together enlarged the United States by one third. Issues surrounding the new territory, however, led to increased tensions between the North and the South over slavery. The Gold Rush brought people from around the world rushing to California, and it also brought about the quick addition of California to the Union. Answer Critical Thinking 4. Apply Information How did the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo settle the chief issues that led to the MexicanAmerican War? 5. Draw Conclusions Who benefited most from the California Gold Rush? Who benefited least? 6. Evaluate Information What do you think was the most important longterm result of the Mexican-American War? Explain. 3. Editorials should express a clear point of view representative of the time period and include details supporting that point of view. 4. The treaty confirmed the annexation of Texas and gave the United States New Mexico, Arizona, Nevada, Utah, parts of Wyoming and Colorado, and California, which appeased expansionists. 5. Early miners and businesspeople whose companies provided goods and services to the miners benefited, as well as later investors in large mining companies. Mexicans faced a great deal of discrimination; Mexican miners were either taxed or forced away from the gold fields, and many people lost their land. Native Americans, Mexicans, and Chinese miners benefited least because they faced discrimination and, in the case of Native Americans, were often killed. 6. Sample response: the huge territorial gains that brought the United States vast natural resources, such as gold in California and later, oil in Texas For additional assessment, have students access Progress Monitoring Online at Web Code nca-0907. Chapter 9 Section 3 315






