• Cognizant 20-20 Insights
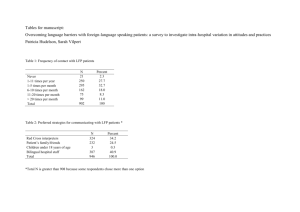
Crafting an End-to-End Pharma
GRC Strategy
Understanding the most appropriate regulatory compliance solution
extends beyond pure technological functionalities; it requires intimate
understanding of policies and procedures required to achieve meaningful
compliance with regulations, worldwide.
Executive Summary
The pharmaceuticals industry and related
businesses are mandated to comply with diverse
regulatory standards in different countries. This
includes the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) in the
U.S., and good manufacturing practice (GMP),
good laboratory practice (GLP), good pharmacy
practice, etc. in the U.S. and elsewhere. Hence,
spending on governance, risk management, and
compliance (GRC) tools is necessary.
This white paper details pharma-specific key
business processes and suitable GRC technologies available in the market.
GRC Market Dynamics
With steady year-over-year growth, GRC tools are
delivering increasing benefits to pharmaceuticals
companies seeking to streamline and automate
their compliance processes, worldwide. To properly leverage GRC, pharma companies must see
GRC as more than a tool or technology. Technology without proper direction is not going to help
most companies anyway. What they need is a
direction/approach toward compliance in addition
cognizant 20-20 insights | june 2013
to tools. This compliance strategy could comprise
processes, a roadmap, operating procedures, etc.
GRC Technology Investment Drivers
Corporate boards and senior executives of
pharma majors are seeking greater visibility and
insight into the effectiveness of controls and
compliance across their organizations to ensure
commitment to investors and to gain customer
confidence. Key factors influencing the recent
growth of GRC include:
• Business
transformation and SAP consolidation programs, primarily to protect investments in existing IT systems and tools.
Global
shared service centers and control
•
centers for better utilization of resources and
to ensure transparency in financial control
across organizations.
• Increased regulatory requirements, along with
the persistent pressure to reduce the cost of
compliance and assurance.
Demand
for integrated compliance tools
•
to address widespread needs of different
compliance groups within the organization
and to consolidate disparate indicators and
standards for judging compliance across the
organization.
•Pharma companies are under enormous
pressure since they need to assure clinical
trials and drug manufacturing quality standards to consumers/government, in addition
to finance-related assurance to stakeholders.
Pharma businesses expect – and are ready – to
invest in GRC solutions that address all of their
requirements. This eventually created a wave
of innovation among GRC vendors.
GRC Technology Overview
Today’s compliance departments need an integrated solution to address various stakeholder
requirements. Figure 1 highlights the different
modules. What follows is a detailed assessment of
the specific functionalities required.
Enterprise risk management:
•
•
•
•
Perform business risk assessments.
Prioritize risks and prepare mitigation plans.
Actively monitor changes in risk profile.
Report incidents.
Policies and control repository:
•Map
policy requirements to processes,
risks and controls.
• Maintain a repository of test scripts/data.
• Automatically report on results.
• Track exception and remediation plans.
Security and segregation of duties:
• Facilitate automated testing of system access
controls.
• Facilitate
automated testing of segregation
of duties.
Audit lifecycle management:
• Document independent audit activities.
•Provide quality assurance over compliance
•
•
activities.
Report results.
Track exceptions and remediation activities.
Investment in specific modules depends on budget
decisions from various units. As no single person
“owns” four module deployments, there should be
proper alignment among different stakeholders
to buy one solution for all of their requirements.
Hence, selection of a GRC vendor is a process
that should be orchestrated carefully to avoid
redundant solutions and to achieve cost savings.
(See GRC Tools and Vendor Consideration Process
further down on how to make this happen.)
All of the above mentioned regulations/framework can be centrally configured in GRC, as shown
in Figure 2, next page.
GRC Technology Vendor Overview
GRC vendors can be classified into three main
categories:
•
GRC integrated with ERP solutions: SAP and
Oracle are the only integrated GRC solutions
available. SAP’s GRC 10 is tightly integrated
Components of GRC
Enterprise
Risk
Management
Audit
GRC Central
Lifecycle
Management Repository
Security and
Segregation
of Duties
Figure 1
cognizant 20-20 insights
2
Policies and
Control
Repository
with SAP’s ERP solutions in terms of design
and architecture, which ensures more automated operations at a reduced cost and strong
systems performance.
• GRC-focused solutions: These solutions lack
ERP integration and process automation.
Hence, their performance and automation
pales in comparison with GRC solutions integrated with ERP.
• GRC niche solutions: This category includes
proven solutions from companies such as
Approva. For example, Approva’s Bizrights is
a leading product in the European market and
is positioned as a hybrid solution between
integrated and GRC-focused offerings in terms
of benefits.
What follows is a discussion of vendor
considerations and an assessment of SAP GRC
and Approva One (the latest version of Approva
Bizrights), two solutions with which we have vast
experience implementing for numerous pharma
companies.
GRC Tools and Vendor Consideration
Process
Figure 3, next page, depicts a typical pharma
company’s organizational hierarchy.
There are many questions to help understand
your organization’s GRC needs. We list some of
the more important ones below:
What is the value proposition you anticipate
from GRC?
• Do you need a single source risk and control
solution?
• It is nothing but a centralized repository of
risks and controls across all regulations.
Solution benefits:
• Easy communication to audit stakeholders.
• Reliable change control.
• Automated updates to control set.
•Systematic allocation of ownership and
accountability.
Cross-Functional GRC Capability
Global Compliance Platform
GRC Technology
1. Maintenance of central master
data structures:
• Multiple compliance frameworks.
• Business objectives.
• Organizational hierarchy.
• Risk and response catalog.
• Account groups and financial
assertions.
• Policies and procedures
(lifecycle management).
• Entity level controls catalog.
• Process and controls repository.
• Control objectives catalog.
2. Maintenance of “central”
evaluation templates:
• Assessment plans (survey library).
• Manual test plans.
• Automated test scripts.
Compliance Framework – COBIT
Compliance Framework – UK Bribery Act
Compliance Framework SoX
1. Assignment of relevant central
master data (ability to allow or
prevent local modifications).
2. Assignment of relevant control
evaluation templates (standardization
of testing/assessment procedures).
3. Compliance-specific reporting
platform and evidence repository.
4. Ability to allow or prevent “shared
evaluations” with other compliance
framework(s).
3. Cross-compliance planning and
reporting platform:
• Centralized planning and
monitoring of ongoing
compliance activities.
• Holistic view of compliance
activities across multiple
frameworks.
5. Compliance-specific roles and
authorization model.
Figure 2
cognizant 20-20 insights
Compliance Framework – Contract
3
•
•
Formalization of control framework.
Reduced controls.
Do you need a tool to address cross-functional
control and compliance framework requirements?
Your organization might require a tool to
manage diversified compliance requirements
such as financial control framework (FCF), IS
control framework and SOX control framework
under one single roof.
Solution benefits:
• Reduced reliance on off-line progress.
•Flexible visibility of control operation
and
remediation progress.
• Targeted remediation effort.
Solution benefits:
•
Reduced rework and duplication of compliance
data.
• Effective utilization of controls: Linkage of key
controls to multiple regulation risks.
•Linkage to organization policies and
procedures.
Would you like to automate the control
self-assessment cycle?
This means you can enter control validation
procedures and results within GRC. The entire
lifecycle of self-assessment, from self-assurance
to control effectiveness reporting, would then be
automated with the help of GRC.
Solution benefits:
•
•
•
•
Does your organization desire sophisticated
reporting and remediation trend analysis?
This is necessary for organizations that are not
happy with the reporting features of their current
compliance tool. GRC provides much improved
reporting on violations and helps predict
remediation trends.
Effective risk assessment and scoping.
Roll-forward capability.
Automatic communication.
Status reporting and escalation management.
Has your organization had to confront concerns voiced by the business that it is being
over-audited?
This means that synergy and alignment is required
among different compliance-relevant procedures
performed by multiple lines of defense.
Solution benefits:
•
Efficient effort and reduced duplication.
Does your organization require the complete
insight of continuous monitoring: data, control
and transactions?
This question concerns whether the business
needs thorough monitoring on transactions
being done through the ERP systems against
pre-configured rules. For example, monitoring to
be done on the purchase module will yield the
following insights:
•
•
•
Who performed more purchases?
Was it appropriately approved?
Were purchases realized into inventories?
Pharma Industry Organizatonal Hierarchy
Pharma PLC
Commercial
R&D
Finance
Operations
and IS
Global
Compliance
Regional
Audit Group
Group
Internal Audit
Figure 3
cognizant 20-20 insights
4
Solution benefits:
frame, the reasons they occur and a possible
means for mitigating this issue.
• Automated
testing of controls is performed
by GRC.
• Continuous monitoring of GRC offers “detective” controls. Detective controls are the rule
set/processes in place that detect violations
only after the control breach. For example, if
the organization decides that purchase requisitions worth more than $10,000 require three
levels of approval, then any purchase worth
more than $10,000 yet containing only two
levels of approval will be flagged as a violation.
This feature helps organizations discover how
many violations occur within a particular time
Is your organization looking for integrated
security and SOD along with GRC?
This means that automated user provisioning
to ERP is required after segregation of duties
analysis from GRC.
Solution benefits:
• Reduce SOD analysis effort.
• Automated user provisioning
reduces effort
from the security team and it improves reliance on complex SOD compliance.
Comparing Approva One vs. SAP GRC
Approva One seamlessly supports ERP products such as
SAP, Oracle, PeopleSoft and CGI.
It has rule templates ready for
the same. Any other third-party
CRM systems and HR systems
can also be included within
Approva One with additional
custom configuration effort.
SAP GRC 10 seamlessly supports only SAP products. Though there are
provisions given like non-SAP adapters for GRC or integration through
IDM, etc. these are not proven.
Approva One comes with two
modules: Authorization Insight
and Process Insight.
SAP GRC 10 comes with modules for access control and process control,
but as an integrated solution (in contrast with predecessor releases) also
has a risk management module.
Authorization Insight:
Responsible for rule book
design, exception management,
mitigation controls, continuous
monitoring and risk analysis.
Access Control:
Access control simplifies the remediation and mitigation process with
the help of process control components. It allows central management
of firefighter IDs, streamlines the temporary super-user access log review
by adding workflow capabilities and has business role concepts.
Process Insight:
Responsible for audit lifecycle
management like SOX framework design, design effectiveness review, internal audit
planning and testing of
controls, etc.
Process Control:
This helps to define and set up automated monitoring of controls and
workflow alerts including transactional record and configuration changes at
SAP ERP. SAP Business Objects GRC 10 version provides capabilities around
content lifecycle management that allows the import and export of risks
and controls together by enhancing the integration with AC and PC into
a single enterprise risk management platform that provides summarized
views representing the different organizational risks and related automated,
manual and security controls from a business process perspective.
Risk Management:
SAP GRC 10 has a separate module called risk management, in contrast
to Approva. This deals with risk assessment and risk prioritization. SAP
risk management enables an enterprise-wide risk management process as
mandated by certain legal requirements and recommended by best-practice
management frameworks. SAP risk management uses the various work centers of the GRC, in which you can carry out all risk management activities.
The process control component of GRC 10 complements risk management.
SAP bifurcated the risk management aspect of GRC into a separate module
to give better visibility to executive management who actually require a
bird’s eye view of enterprise risks and its mitigation controls.
Figure 4
cognizant 20-20 insights
5
Other questions to resolve include:
» IT infrastructure.
» Controls maturity.
» Lines of defense model.
• Do
you know the ratings/pros and cons of
various compliance tools in the market?
» Before you start researching GRC solutions,
ensure that you read recent analysis from
Forrester and Gartner – the two top market
research companies.
•What
needs to be considered before constituting the program to identify a suitable
GRC vendor?
» Key users of compliance are in finance. But
be sure to include other key stakeholders/
representatives in the GRC program, according to their weight in compliance needs.
» Primarily target your organization’s ERP
environment. But be sure to include all
tools that fall within the compliance ring.
»
Elicit
needs
for
different
control
repositories.
» Get inputs from local, regional integrated
assurance teams on current compliance
manual processes or tools.
» Perform an overall assessment of current
compliance tools and processes.
In a nutshell, GRC vendor selection always
starts with:
•An
in-depth self-assessment of your
compliance requirements.
• An assessment of the underlying business
environment, covering:
Approva One Bizrights and SAP Business Objects
GRC-10 are good packages to consider among
many strong GRC solutions on the market.
In its latest release, Approva One offers
innovations such as a provision to follow up on
SOD remediation and a user interface for end-toend mitigation processes. Approva continues to
concentrate on its core strengths (i.e., it is easy
to operate, flexible, supports a wide range of
financial systems and has lower procurement and
operating costs).
SAP Business Objects GRC-10 has been nicely
upgraded. From a technical perspective, SAP GRC
has moved from the Java programming language
to ABAP. This core change allows centralized
support across all its components. The SAP
GRC solution’s new platform improves change
management processes by leveraging existing
transport systems, background job scheduling,
archiving and other standard SAP features. SAP
Roadmap for GRC promises continuous innovations by releasing updated GRC functionalities
and patches, which bodes well for its customer
base. On the other hand, Approva, as noted
earlier, has also improved the capabilities of its
Approva One offering, with additional updates
expected. Hence, these two products are worthy
of consideration for pharma GRC requirements.
References
• Gartner’s French Caldwell, Tom Scholtz, John Hagerty, "Magic Quadrant for Enterprise Governance,
Risk and Compliance Platforms," July 13 2011, pp. 9-14, http://fm.sap.com/data/UPLOAD/files/
Gartner_Magic_Quadrant_for_EGRC_(July_2011)%5B1%5D.pdf.
•Forrester’s
Chris McClean with Stephanie Balaouras and Nicholas M. Hayes, "Enterprise
Governance, Risk, and Compliance Platforms, Q4 2011," Dec 2 2011, pp. 9-10, http://www.protiviti.co.in/
en-US/Documents/About-Us/The-Forrester-Wave-Enterprise-Governance-Risk-and-CompliancePlatforms-Q4-2011.pdf.
About the Author
Karthikeyan Muniappan is a Senior SAP Consultant in Cognizant’s Enterprise Application Systems
Practice and is a member of its SAP basis Sub-practice. He won an innovation award in 2011 from
Cognizant and SAP India for his contribution to SOX/SOD compliance and the relevant toolset. Karthik
has a master of engineering degree from Anna University in computer science and engineering. He can
be reached at Karthikeyan.Muniappan@cognizant.com.
cognizant 20-20 insights
6
About Cognizant
Cognizant (NASDAQ: CTSH) is a leading provider of information technology, consulting, and business process
outsourcing services, dedicated to helping the world’s leading companies build stronger businesses. Headquartered
in Teaneck, New Jersey (U.S.), Cognizant combines a passion for client satisfaction, technology innovation, deep
industry and business process expertise, and a global, collaborative workforce that embodies the future of work.
With over 50 delivery centers worldwide and approximately 162,700 employees as of March 31, 2013, Cognizant is a
member of the NASDAQ-100, the S&P 500, the Forbes Global 2000, and the Fortune 500 and is ranked among the
top performing and fastest growing companies in the world.
Visit us online at www.cognizant.com for more information.
World Headquarters
European Headquarters
India Operations Headquarters
500 Frank W. Burr Blvd.
Teaneck, NJ 07666 USA
Phone: +1 201 801 0233
Fax: +1 201 801 0243
Toll Free: +1 888 937 3277
Email: inquiry@cognizant.com
1 Kingdom Street
Paddington Central
London W2 6BD
Phone: +44 (0) 207 297 7600
Fax: +44 (0) 207 121 0102
Email: infouk@cognizant.com
#5/535, Old Mahabalipuram Road
Okkiyam Pettai, Thoraipakkam
Chennai, 600 096 India
Phone: +91 (0) 44 4209 6000
Fax: +91 (0) 44 4209 6060
Email: inquiryindia@cognizant.com
­­© Copyright 2013, Cognizant. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, transmitted in any form or by any
means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the express written permission from Cognizant. The information contained herein is
subject to change without notice. All other trademarks mentioned herein are the property of their respective owners.