The Five Themes of Geography Resource.indd
advertisement
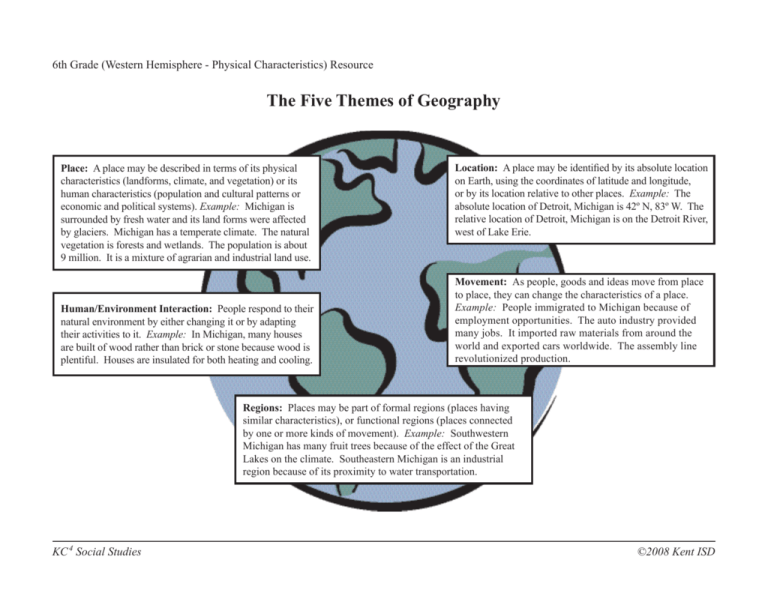
6th Grade (Western Hemisphere - Physical Characteristics) Resource The Five Themes of Geography Place: A place may be described in terms of its physical characteristics (landforms, climate, and vegetation) or its human characteristics (population and cultural patterns or economic and political systems). Example: Michigan is surrounded by fresh water and its land forms were affected by glaciers. Michigan has a temperate climate. The natural vegetation is forests and wetlands. The population is about 9 million. It is a mixture of agrarian and industrial land use. Human/Environment Interaction: People respond to their natural environment by either changing it or by adapting their activities to it. Example: In Michigan, many houses are built of wood rather than brick or stone because wood is plentiful. Houses are insulated for both heating and cooling. Location: A place may be identified by its absolute location on Earth, using the coordinates of latitude and longitude, or by its location relative to other places. Example: The absolute location of Detroit, Michigan is 42º N, 83º W. The relative location of Detroit, Michigan is on the Detroit River, west of Lake Erie. Movement: As people, goods and ideas move from place to place, they can change the characteristics of a place. Example: People immigrated to Michigan because of employment opportunities. The auto industry provided many jobs. It imported raw materials from around the world and exported cars worldwide. The assembly line revolutionized production. Regions: Places may be part of formal regions (places having similar characteristics), or functional regions (places connected by one or more kinds of movement). Example: Southwestern Michigan has many fruit trees because of the effect of the Great Lakes on the climate. Southeastern Michigan is an industrial region because of its proximity to water transportation. KC 4 Social Studies ©2008 Kent ISD











