5.2 St.1e Flashcard List
advertisement

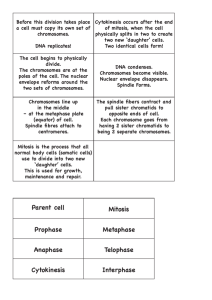
Name: _________________________________ Date:__________________ Period: ___ Chapter 5.2 Flashcard List Ch. 5.2 Quiz Date: _____________________ Standard 1e: Students know cells divide to increase their numbers through a process of mitosis, ! ! which results in two daughter cells with identical sets of chromosomes. What this means: Cells split to make more cells through a process that includes mitosis. ! through this process, a single cell becomes two cells that have the ! ! same genetic material (DNA). Word/concept Definition/example cell cycle the regular sequence of growth and development that healthy cells go through; there are 3 stages in the cell cycle interphase the first stage of the cell cycle; the stage that lasts the longest; the time when the cell is growing to its mature size, copying the DNA, so that each chromosome contains two chromatids, and preparing for cell division (making other organelles and more cytoplasm); mitosis the second stage of the cell cycle; the division of the nucleus; mitosis has 4 phases; mitosis results in the formation of two identical nuclei with identical sets of chromosomes, but the cell has not yet divided into two new cells prophase the first phase of mitosis; the chromatids condense to form chromosomes, the nuclear membrane starts to break down metaphase the second phase of mitosis; the nuclear membrane is gone, the chromosome pairs line up around the middle of the cell picture/diagram Word/concept Definition/example anaphase the third phase of mitosis; the chromosomes or chromatids separate from each other and move toward opposite sides of the cell telophase the 4th and last phase of mitosis; chromosomes are at opposite sides of the elongated cell, a new nucleus forms around each new identical set of chromosomes picture/diagram At the end of mitosis--this is still just one cell, but two nuclei --> cytokinesis the third (last) stage of the cell cycle; the cytoplasm and organelles are divided into two new cells along with the two new nuclei; cytokinesis results in two identical new daughter cells identical to the original parent cell. As soon as cytokinesis ends, each new daughter cell goes immediately into a new interphase period. parent cell the original body cell that will undergo cell division to create two new identical cells daughter cell one of two identical new cells that result from the division of a single parent cell two newly formed daughter cells ---------------> identical to each other, AND identical to the original parent cell chromosomes the structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells that is made up of DNA and protein; condensed chromatin; the genetic material, the hereditary material chromatin long strands of DNA and proteins that contains the genetic material (when condensed it is called chromosomes) the two new cells have formed-- now interphase begins again immediately Word/concept Definition/example picture/diagram centrioles a bundle of long tubelike structures made of microtubules; helps the cell divide during mitosis centromere a region on a chromosome that joins two sister chromatids; the part of the chromosome that is most constricted, where the spindle fibers will attach during cell division gamete/sex cell a sperm cell or an egg cell; gametes have half the number of chromosomes (the haploid number) of a regular body cell egg cell -------> sperm cells-----> body cell a regular cell in the body that is not a sperm cell or an egg cell (like a skin, or muscle cell for example); also called somatic cells; they have the full number of chromosomes (the diploid number) haploid the word used to describe the number of chromosomes found in gametes (egg or sperm cells); haploid is half the number of chromosomes in somatic or body cells-in humans the haploid number of chromosomes is 23 diploid the word used to describe the number of chromosomes found in somatic or body cells; diploid is the full number of chromosomes (twice as many as the haploid number) In humans the diploid number of chromosomes is 46