Topic 1 Overview of Jamaica and the Caribbean
advertisement
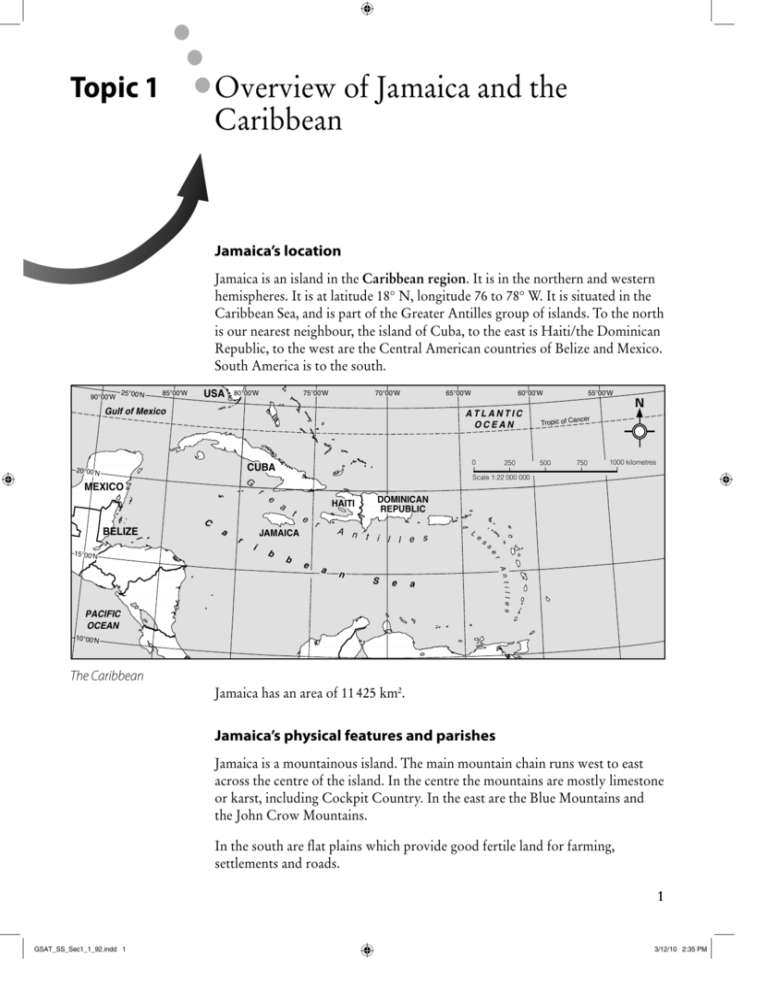
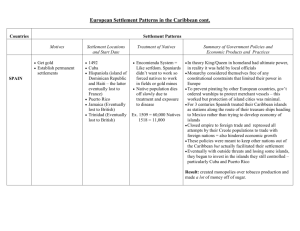
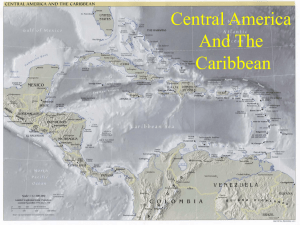
Overview of Jamaica and the Caribbean Topic 1 Jamaica’s location Jamaica is an island in the Caribbean region. It is in the northern and western hemispheres. It is at latitude 18° N, longitude 76 to 78° W. It is situated in the Caribbean Sea, and is part of the Greater Antilles group of islands. To the north is our nearest neighbour, the island of Cuba, to the east is Haiti/the Dominican Republic, to the west are the Central American countries of Belize and Mexico. South America is to the south. 90°00'W 25°00'N 85°00'W USA 80°00'W 75°00'W 70°00'W 65°00'W ATLANTIC OCEAN 0 CUBA 20°00'N r e HAITI a t C 500 750 1000 kilometres e r A n t i l l e s JAMAICA e e b L s i DOMINICAN REPUBLIC s b r 15°00'N r 250 ncer Tropic of Ca Scale 1:22 000 000 G MEXICO a 55°00'W N Gulf of Mexico BELIZE 60°00'W a n S e a PACIFIC OCEAN t i l l e s A n e 10°00'N The Caribbean Jamaica has an area of 11 425 km2. Jamaica’s physical features and parishes Jamaica is a mountainous island. The main mountain chain runs west to east across the centre of the island. In the centre the mountains are mostly limestone or karst, including Cockpit Country. In the east are the Blue Mountains and the John Crow Mountains. In the south are flat plains which provide good fertile land for farming, settlements and roads. 1 GSAT_SS_Sec1_1_92.indd 1 3/12/10 2:35 PM The main rivers are the Rio Grande, Rio Cobre, Rio Minho, Rio Negro, Great River, Cabarita. The rivers begin in the mountains and then flow either to the north or south coast. The Plantain Garden River is the only one which flows from west to east. 78°00'W 77°00'W 77°30'W 76°30'W N 18°30'N G iver Cabar R at re ita River Cockpit Country o Ri M ou obre nt Liguanea Plain ain s lain tain G arden River P Rio Minho St Jago Plains ns ai 18°00'N nt ou M ow Cr e hn nd Jo Gra Rio The Blu e Ri o C N egro Vere Plains 0 CARIBBEAN SEA 20 40 kilometres Scale 1:1 300 000 Jamaica’s physical features The uses of rivers Rivers provide a number of important resources, including: ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ water for drinking, washing, and other domestic uses water for irrigating crops water for industrial uses hydro-electric power tourist attractions – waterfalls, rafting, boat rides N Lucea Montego Bay Falmouth St Ann’s Bay Port Maria HANOVER ST JAMES CORNWALL TRELAWNY ST ANN ST MARY WESTMORELAND Black River ST ELIZABETH Mandeville ER Jamaica’s countries, parishes and parish capitals Port Antonio MIDDLESEX HEST MANC Savannala-Mar ST CATHERINE CLARENDON May Pen Spanish Town PORTLAND ST ANDREW SURREY Half WayTree ST THOMAS Kingston Morant Bay 0 20 40 kilometres Scale 1:1 700 000 2 GSAT_SS_Sec1_1_92.indd 2 3/12/10 2:35 PM Parishes: location, size, relief and rivers Parish Clarendon Hanover Kingston Manchester Portland St Andrew Location/county South Middlesex North-west Cornwall South-west Surrey South-west Middlesex Size (km2) 1196 450 22 Relief Mocho Mts Dolphin Head Liguanea Plain 830 Don Figuerero Mts, May Day Mts North Surrey 814 South-west Surrey North-west St Ann Middlesex St Catherine South-east Middlesex St Elizabeth South-east Cornwall St James North Cornwall St Mary North-east Middlesex St Thomas South-east Surrey Trelawny North-east Cornwall Westmoreland South-west Cornwall Rivers Milk, Rio Minho Cabarita Hope 431 Blue Mts: High Peak (2082 m), Middle Peak (2256 m), John Crow Mts Blue Mts, Red Hills, Liguanea Plain 1213 Dry Harbour Mts (Albion 839 m) Roaring 1192 1212 595 611 743 875 807 Bull Head Mts, St Jago Plains, Hellshire Hills Nassau Mts, Santa Cruz Mts, Pedro Plains Cockpit Country Blue Mts, Mt Telegraph (1301 m) Macca Sucker (1330 m) Cockpit Country (Cockpit 746 m) George’s Plain Rio Cobre Rio Negro Great, Montego White, Rio Nuevo Plantain Garden, Yallahs, Morant Martha Brae Cabarita Rio Grande Hope The Caribbean’s location The Caribbean region is located in the area of the Caribbean Sea, between the Atlantic Ocean and the mainland of Central America. The Caribbean is in the northern and western hemispheres. It lies north of the Equator and mostly south of the Tropic of Cancer. It covers an area from latitude 4° N to 27° N, and from longitude 48° W to 90° W about 4020 km in size. To the north is the United States, to the west are Central America and the Pacific Ocean, to the south is South America and to the east is the Atlantic Ocean. The Caribbean’s physical features and countries The Caribbean region is made up of islands and also some countries which are part of mainland Central and South America, such as Belize, in Central America, and Guyana and Venezuela, in South America. The Caribbean has a chain of islands, The West Indies stretching from the Bahamas and Cuba south and east to Trinidad and Tobago. These are in three main groups: the Bahamas, the Greater Antilles and the Lesser Antilles. The Greater Antilles include Cuba, Dominica, Hispaniola (Haiti and the Dominican Republic) and Peurto Rico. The Lesser Antilles group is divided into the Leeward Islands, the Windward Islands, the Netherlands Antilles and includes Barbados and Trinidad and Tobago. The Caribbean islands, and even some of the mainland countries, are mostly made of limestone, from coral. This is a region where the Earth’s plates meet, so there are some volcanic islands, such as Montserrat and St Lucia. Some countries are very flat and low-lying, such as the Cayman Islands and 3 GSAT_SS_Sec1_1_92.indd 3 3/12/10 2:35 PM 25°00'N 85°00'W USA 80°00'W 75°00'W 70°00'W 65°00'W Gulf of Mexico BAHAMAS Tropic of Cancer 0 CUBA 20°00'N G MEXICO Cayman Islands (UK) r e HAITI r Neth. Puerto Antilles Rico (USA) A n t i l l e s e a n r se b e a PACIFIC OCEAN A n t i l l e s S Neth. Antilles 10°00'N Montserrat (UK) s b d ar s ew d e lan e DOMINICAN REPUBLIC Is t JAMAICA i 1000 kilometres 750 e HONDURAS r 500 L 15°00'N a ATLANTIC OCEAN Scale 1:20 000 000 C BELIZE 55°00'W N L a 250 60°00'W ST LUCIA Wi n Isl dward and s 90°00'W BARBADOS TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO VENEZUELA GUYANA The Caribbean Barbados. Other countries, such as Jamaica, the Dominican Republic and Trinidad, and mainland countries such as Guyana, Honduras and Venezuela, are mountainous. The mainland countries and the larger, more mountainous islands have many rivers, but some countries, such as the Cayman Islands, lack rivers and have difficulty supplying enough water for domestic use. Here are some examples of the range of Caribbean physical features: ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ Mainland countries of Central and South America: Belize and Guyana are Caribbean because of their common historical, eonomic and cultural backgrounds. Island nations: Jamaica, Cuba, Trinidad and Tobago Volcanic islands: Montserrat (active), St Lucia (dormant) Coral islands: the Bahamas Limestone islands: Jamaica, Cayman Islands Mountain ranges: Blue Mountains ( Jamaica), Sierra Maestra (Cuba), Northern Range (Trinidad), Pakaraima Mts (Guyana) Mountainous islands: Dominica, St Kitts and Nevis, St Lucia, Montserrat, Guadeloupe Flat, low-lying islands: Barbados, Cayman Islands, Bahamas Rivers: Essequibo (Guyana), Belize River (Belize) 4 GSAT_SS_Sec1_1_92.indd 4 3/12/10 2:35 PM Caribbean countries can also be grouped by language and colonial history: ■ ■ ■ ■ English, eg Jamaica, Trinidad, Barbados, Belize Spanish, eg Cuba, Guatemala, Mexico French, eg Haiti, St Martin, Martinique, Guadeloupe Dutch, eg Netherlands Antilles, Curacao, St Maarten Caribbean countries and their capitals Country Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Aruba Bahamas Barbados British Virgin Islands Cayman Islands Cuba Curacao Capital The Valley St John’s Oranjestad Nassau Bridgetown Road Town George Town Havana Willemstad Dominica Dominican Republic Grenada Roseau Santo Domingo St George’s Country Guadeloupe Haiti Jamaica Martinique Montserrat Puerto Rico St Kitts and Nevis St Lucia St Vincent and the Grenadines Trinidad and Tobago Turks and Caicos Islands US Virgin Islands Capital Basse-Terre Port-au-Prince Kingston Fort de France Plymouth San Juan Basseterre Castries Kingstown Port of Spain Cockburn Town Charlotte Amalie Exercise 1 1 What is the name of the area of water that surrounds Jamaica? A the Atlantic Ocean B the Caribbean Sea C the Mediterranean Sea D the Pacific Ocean 2 Jamaica is part of a group of islands known as the A Bahamas B Netherlands Antilles C Greater Antilles D Lesser Antilles 3 George’s, Pedro and the Liguanea are all A coastal plains B mountain ranges C mountain peaks D waterfalls . . 5 GSAT_SS_Sec1_1_92.indd 5 3/12/10 2:35 PM 4 In which area of Jamaica is the Blue Mountain range? A the east B the north C the south D the west 5 What are the three Jamaican counties called? A Cornwall, Middlesex and Kingston B Cornwall, Middlesex and Surrey C Middlesex, St Ann and Manchester D Surrey, Manchester and St Ann 6 Which parish is indicated on the map by ‘X’? A Clarendon B St Ann C St Catherine D Trelawny 7 The Caribbean region lies between which lines of latitude? A 4° N and 27° N B 14° N and 37° N C 40° N and 67° N D 48° N and 100° N 8 Which of these countries has a coastline on the Gulf of Mexico? A Cuba B Dominica C St Lucia D Trinidad and Tobago 9 The Bahamas are A volcanic islands B mountainous islands C low-lying coral islands D on the mainland 10 In which of the following islands is French the official language? A Cuba B Martinique C St Lucia D Trinidad and Tobago x . 6 GSAT_SS_Sec1_1_92.indd 6 3/12/10 2:35 PM