The Atom & Periodic Table The Atom & Periodic Table
advertisement
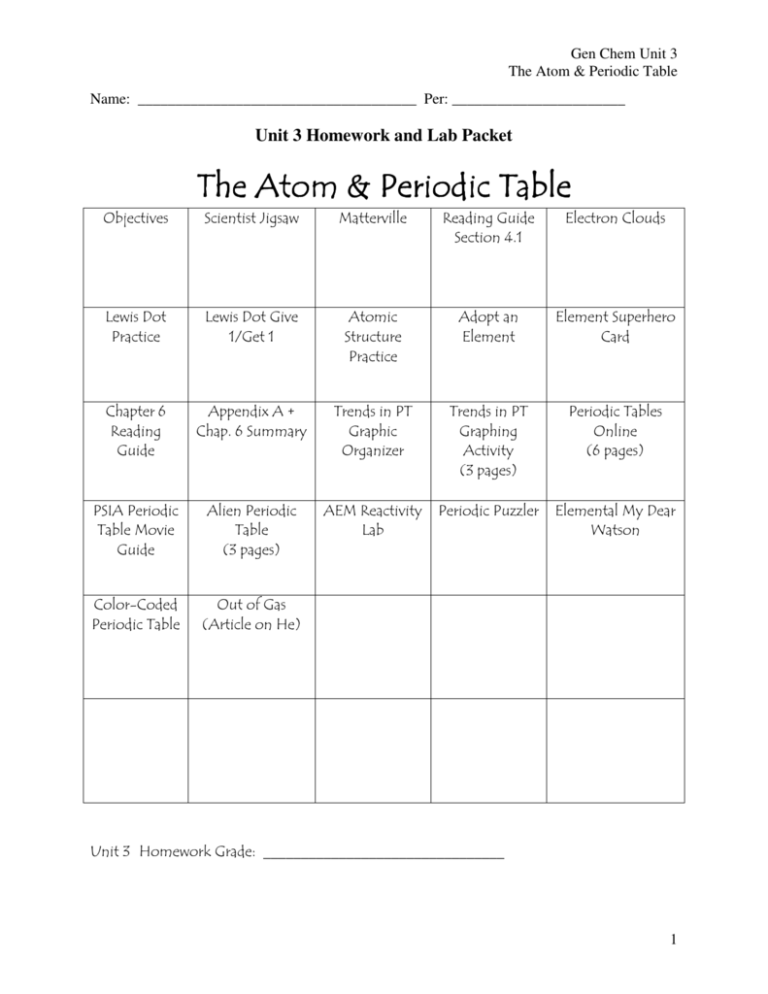
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom & Periodic Table
Name: _____________________________________ Per: _______________________
Unit 3 Homework and Lab Packet
"
#
!
$
%
# ' (
$
%
!
& !
'
"
'' ) *
# '(
+
0
"
'
,
"
#
'
+
.' /
+
,
,
$
.'
#
2#
. 4
('
"
/
+%
1
/
3
-
5
'
6
4/
788888888888888888888888888888888
1
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom & Periodic Table
Unit 3 Overall Goals:
Understand and apply knowledge of the structure of atoms.
Understand and apply knowledge of the structure and properties of matter.
After completing this unit, you should be able to understand and explain the following.
1. Know the development of the atomic models and the scientists responsible for them.
2. Identify atoms and ions by mass number, atomic number, charge, number of electrons,
protons, and neutrons.
3. Define isotope.
4. Define periodicity and be able to explain how it relates to the periodic table.
5. Understand the principles used to structure the periodic table.
6. Know the name of the scientist who is accredited with creating the periodic table.
7. Understand and know the common names and terms related to the periodic table of elements
(ex: family, group, period, metalloid, etc).
8. Know the terms and properties related to metals, non-metals, and metalloids.
9. Understand the energy levels of electrons for the first eighteen elements.
10. Know the term valence electrons and determine the number of valence electrons by using
the periodic table.
11. Be able to write the Lewis dot structure for the elements based on their location on the
periodic table.
12. Know the trends of atomic radius, ionization energy, atomic mass, reactivity and number of
valence electrons.
13. Know the major families on the periodic table and the trends they follow.
2
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom & Periodic Table
Scientist
Description of research
Drawing of their model
John Dalton (p. 101-102; 128-129)
JJ Thompson (p.104-105; 128-129)
Ernest Rutherford (p.106-108; 128-129)
Neils Bohr (p.128-129)
Erwin Schroedinger (from notes)
3
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
The Atoms Family
4
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
5
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Reading Guide
Section 4.1 (p. 100-103)
1. What is an atom?
2. What did Democritus believe about the structure of an atom?
3. John Dalton was one of the first scientists to list ideas about the atom. List his four ideas
below in your own words.
A.
B.
C.
D.
4. What instrument can be used to observe individual atoms?
5. According to Dalton’s theory, is it possible to convert atoms of one element into atoms of
another? Briefly explain.
6. EXRA CREDIT: Read the “Inquiry Activity” on page 100. Conduct the simple experiment
at home. Be sure to record your observations and answer the “Think About It” questions.
6
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Electron Clouds
Use the information provided for each element to complete the diagram. Draw the electrons in
their proper shells, and place the correct numbers in the nucleus to indicate the number of
protons and the number of neutrons.
1. Sulfur:
atomic number 16
mass number 32
4. Sodium:
P
N
2. Beryllium: atomic number 4
mass number 9
P
N
5. Potassium: atomic number 19
mass number 39
P
N
3. Nitrogen: atomic number 7
mass number 14
P
N
atomic number 11
mass number 23
P
N
6. Argon:
atomic number 18
mass number 40
P
N
7
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Lewis Dot Structure Practice
Fill in the following section of the periodic table with the symbols of the first 18 elements. Then,
add the electron dots to complete the Lewis dot structures.
1A
2A
3A
4A
5A
6A
7A
8A
1. What generalization can be made about the Lewis dot structures in a group (column) of
elements?
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
2. Define valence electrons.
________________________________________________________________________
3. Why do the noble gases not react?
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
4. Hydrogen can be considered an alkali metal (Group 1A) or a halogen (Group 7A). Why?
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
8
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Lewis Dot Give One/Get One
Directions: In the “Give one” column below, draw a Lewis Dot structure for ONE of the
atoms listed. Then, meet with your partner, and teach them your atom. Your partner
will then teach you their atom. You should write this in your “Get one” column.
Elements
Give One
Get one
Lithium, Sodium, or
Potassium
Beryllium, Magnesium, or
Calcium
Boron, Aluminum, or
Galium
Carbon, Silicon, or Tin
Nitrogen, Phosphorus, or
Bismuth
Oxygen, Sulfur, or
Selenium
Fluorine, Chlorine, or
Bromine
Helium, Neon, or Krypton
9
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Atomic Structure Practice
There are three subatomic particles. Protons, neutrons, and electrons.
1. Which of these have substantial mass? _____________________________________
2. Which of these have electromagnetic charge? ________________________________
For this page, ASSUME CHARGE IS ZERO.
Name
Symbol
Atomic #
Mass #
Protons
Neutrons
Electrons
Charge
Lithium-7
Lithium-9
Phosphorus31
Oxygen-16
Boron-11
Sodium-23
Nitrogen-14
Aluminum27
Argon-40
Argon-39
Argon-38
Magnesium24
Sulfur-33
Phosphorus34
Carbon-14
Beryllium-9
Ba
136
22
41
26
50
44
Al
32
14
15
30
90
235
144
143
10
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
For this page, do NOT assume the charge is zero.
Name
Symbol
Atomic #
Mass #
Protons
Neutron
Electrons
Lead-207
Calcium40
+4
18
O2-
18
-2
Silver-109
46
Sn+4
68
37
Al+3
17
21
24
24
+1
21
26
60
15
Bromine81
Bromine82
Barium138
18
19
107
16
+1
18
-1
0
56
+2
32
21
18
-3
18
+3
Iron-55
+3
Iron-54
24
Ag+
109
27
57
24
80
V5+
Tellurium127
Charge
120
+1
49
-2
52
42
+6
11
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Adopt-an-Element
Requirements: In this activity, you will be conducting research on your specific element. You
will then use this information to create an advertisement for that element.
1. Complete an “Adopt-an-Element” information sheet.
You may use a variety of reference sources. Possible ideas are encyclopedias (book or
web-based), textbooks, the Internet, etc. Information sheets must be NEAT and CONTAIN ALL
THE INFORMATION. You need to include a list of your sources that you used (at least 2 are
required).
2. Create an advertisement for your element.
The advertisement must include the element’s name, symbol, atomic number, atomic
mass, cost, a unique use for the element, and an advertising slogan that describes one or more of
its important uses or qualities. Advertisements must be neat, colorful, and contain all the
information listed above. You may add pictures that relate to your advertisement theme.
Be sure to include:
•
Element’s symbol
33
74.9
• Element’s name
• Atomic number
•
Atomic mass
As
• Ad slogan
Arsenic
• Cost
• Unique use
Arsenic’s a sure fire way
• Your name
to deal with a nasty rat.
It works better than
You may add pictures or drawings
A mean old cat!
that illustrate the various
uses for your element.
Use = rat poisoning
Cost = $3.20 for 1 gram
Your add must follow the same
format as this example!!
John Smith
A list of periodic table sites is available on:
THE SCIENCE SPOT
http://sciencespot.net/
Go to KID ZONE, then choose CHEMISTRY LINKS
12
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Adopt-an-Element
Information Sheet
Element Name ______________________________________
Symbol ______________________
Atomic Number __________________
# of Protons _________
Atomic Mass __________________
# of Neutrons _________
# of Electrons _________
Melting Point _________oC Boiling Point _________oC Normal phase __________
Cost = ____________________ for ______________________
Classification: _____ nonmetal
_____ metal
_____ metalloid
My element belongs to the ______________________ family.
Origin of name ___________________________________________________________
Discovered by ______________________________________________ in ___________
Interesting Info: (important uses, interesting facts, common compounds, etc)
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Sources: (at least 2)
1.
2.
13
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Element Trading Cards Project
All of the known elements are arranged on the Periodic Table. Ninety-three occur naturally on Earth. Scientists
using advanced techniques and equipment (like particle accelerators) have synthesized the rest of the elements. As a
student of chemistry, it is important for you to have a good working knowledge of the elements.
Objectives:
1. Research one element and record its basic properties.
2. Create an “element trading card” which will incorporate these properties, along with a
picture of their element.
3. Be prepared to present your trading card to the class, have a sample of something
containing your element, and discuss some of the uses of your element.
Elemental Trading Card Guidelines
1. The card should be created on card stock. The dimensions should be exactly 5.7 cm by
8.6 cm.
2. The front of the card must have the element’s name and symbol and a visual image of the
element. (The graphics/visuals on the card should be of high quality and creativity. You
may use graphics, etc., from the web if you reference the source.)
3. The back of the card should include the element’s “statistics”:
a. What is the name of your element; what is the origin of the name?
b. What symbol represents your element and for what reason has this symbol been
chosen (if not obvious)?
c. Where on Earth do you find your element?
d. Briefly describe the history of your element'
s discovery? (When was the first
documented evidence recorded of it? By whom and where was its discovery
documented?)
e. What physical properties define your element? (Physical state (solid, liquid, gas),
melting point, boiling point, and physical description such as color, odor, etc.).
f. What are the (interesting) chemical properties of your element? (Is it flammable,
combustible, corrosive, etc.)
g. What is the importance of your element? How do people use it?
Research time will be provided on Tuesday, Sept. 13, or Wednesday, Sept. 14.
There are only 18 laptops, so students will use this time to research their elements or be
prepared to research on their own. Here are some websites that will be useful, which
would make a great HOTLIST!
http://www.webelements.com/webelements/scholar/index.html
http://www.chemsoc.org/viselements/pages/pertable_fla.htm
http://chem4kids.com/elements/table.html
http://www-tech.mit.edu/Chemicool/
http://chemicalelements.com
14
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
On presentation date, students should bring and describe an object containing or composed of
their element and answer the following questions:
1.
2.
Why were elements discovered at particular times in history?
What societal factors contributed to/permitted the discoveries of each element?
Upon listening to presentations, students should identify elements that were discovered in the
same time period as their own element and make a list.
Element Trading Card Rubric (30 pts)—turn in with trading card
Organization (3 pts)
•
card contains name, date, period
/1
•
card is 5.7 by 8.6 cm (2 ¼ by 3 3/8 inches) and makes efficient use of all space
(front and back), is aesthetically pleasing, neat, and shows effort.
/2
•
Includes element name and element symbol
/2
•
Includes at least one image of your element (preferably of your element in natural
state; -2 if the electron structure of atom.)
/2
Includes 7 clearly designated and easy-to-follow content sections (a-g on
information sheet).
What is the ORIGIN of the name of the element? What SYMBOL represents your
element and for what reason has this symbol been chosen? WHERE on Earth is
your element commonly found? (In what U.S. states and/or other countries is it
commonly found?)
Describe the HISTORY of your element'
s discovery. (When was the first
documented evidence recorded of it? By whom and where was its discovery
documented?)
What CHARACTERISTICS (physical and chemical properties) define your
element? (Includes the phase (s, l, g), melting point, boiling point, and physical
description (color, odor, etc.), and if it is flammable, combustible, corrosive, etc.)
What is the IMPORTANCE of your element? How do people use it? What are
some examples of uses?
/2
•
Includes an attached bibliography in AMA format. (See science website for details;
- 3 pts for partial or no sources cited.)
/2
•
List of elements that were discovered in the same time period as your own element
/2
Front of card (4 pts)
Back of card (12 pts)—may earn neg. points for incompleteness in any of these sections.
•
•
•
•
•
/3
/2
/3
/2
Attached to card (4 pts)
Presentation (7 pts)
•
Speaks clearly; looks at audience
/2
•
Answers both questions above
/2
•
Provides and explains sample of element
/3
TOTAL
/30
15
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Reading Guide: Chapter 6 (p. 154-178; Appendix A)
1. What does periodicity mean?
PERIODIC(ity)______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
2. How did Mendeleev group the elements them in his version of the periodic table?
____________________________________________________________________
3. How were columns arranged according to Mendeleev?
____________________________________________________________________
4. How were rows arranged according to Mendeleev?
____________________________________________________________________
5. The Modern Periodic table has one similarity to Mendeleev’s. What is it?
____________________________________________________________________
6. How can elements with a higher atomic mass come before ones with a smaller one?
____________________________________________________________________
7. Define:
a. Period
b. Group (family)
c. Noble Gas
8. Place a check next to each of the properties of most metals.
___reflect light
___conduct heat
___conduct electricity
___brittle
___hard (solid)
___gases
___high melting point
___malleable
9. Where are the transition metals found on the periodic table?
_____________________________________________________________________
10. Why is it useful to combine different metals together to make alloys?
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
16
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
11. Place a check next to each of the properties of most non-metals.
___poor conductor
___dull
___solids
___gases
___brittle
___malleable
___electrons are held tightly by the nucleus
12. What two elements make up most of Earth’s atmosphere? ________________________
AND ______________________
13. What is special about silicon?
14. What metal is used to make wire? ________________________
15. What are the two ingredients used to make steel?
____________________ AND ___________________
16. Why metal is used to prevent rusting? ________________________
17. What is the only non-metal which is a liquid at room temperature?
______________________________
18. What element is used in lasers? ____________________
19. What two elements are used to make halogen lamps?
_________________ AND ________________
17
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Appendix A and Chapter 6 (Summary)
18
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Questions:
1. Who created the first periodic table of elements?
2. How many elements were known at the time of the first periodic table?
3. How many elements are known today (see the periodic table on the other side)?
4. What properties did Mendeleev use to categorize his elements?
5. What two problems did Mendeleev run into while categorizing his elements?
6. What two properties are used to categorize elements on the modern periodic table?
19
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Trends in Periodic Table Graphic Organizer
20
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Trend
Definition
Going down
a group
Going left to
right across a
period
NM
NM
Atomic radius
Reactivity
Ionization
Energy
M
Reason for Trend
M
Draw the above trends onto the periodic table on page 21. Use a different
color for each trend.
Red= Atomic radius
Blue= Reactivity
Orange= Ionization Energy
21
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Trends in the Periodic Table Graphing Activity
The arrangement of elements in the periodic table reveals many important trends, or
patterns, in the properties of elements. Many of the trends shown by the table are periodic. That
is, they repeat within the table. For example, a periodic trend may involve low values at the top
of a group, high values at the bottom, and low, values once again at the top of the next group.
Recall that the atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons in the
nucleus. The atomic mass is the average number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an
element. Atomic radius is the distance from the center of an atom to the outermost electrons of
the atom. The first ionization energy of an element is the energy needed to remove the most
loosely help electron of an atom of the element.
Directions: You will be making three graphs in this assignment
1. Using the periodic table that follows, make a graph of ATOMIC MASS vs. ATOMIC
NUMBER using the atomic number of 3 to 20 only. Use a different color for each period of the
periodic table. When all the points are plotted, draw a smooth curve for each period with a
different color. DO NOT CONNECT THE DIFFERENT PERIODS.
2. Prepare a graph of ATOMIC RADIUS vs. ATOMIC NUMBER, using the atoms of 3 through
20 only. Use a different color for each period of the periodic table. When all the points are
plotted, draw a smooth curve for each period with a different color. DO NOT CONNECT THE
DIFFERENT PERIODS.
3. Prepare a graph of FIRST IONIZATION ENERGY vs. ATOMIC NUMBER, using the atomic
numbers of 3 to 20 only. Use a different color for each period of the periodic table. When all
the points are plotted, draw a smooth curve for each period with a different color. DO NOT
CONNECT THE DIFFERENT PERIODS.
22
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
23
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Graphing Trends in Periodic Table Questions: Use your graphs to answer the following
questions.
1. What happens to atomic mass when going across each period?
2. What happens to atomic mass when going down a group?
3. What happens to atomic radius when going across each period?
4. What happens to atomic radius when going down a group?
5. What patterns do you notice on Atomic Radius vs. Atomic Number graph?
6. What happens to first ionization energy when going across each period?
7. What happens to the first ionization energy when going down a family?
8. What pattern do you notice on the First Ionization Energy vs. Atomic Number graph?
24
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Periodic Tables Online
Part 1:
•
•
•
•
•
Go to http://sciencespot.net
Click on Kid Zone
Click on Matter & Atoms in the Chemistry section
Click on CHEMystery link
Click on the Periodic Table of Elements link on the left hand side of the page
1. Using a blue, orange, purple, green, and red colored pencil, color code and label the following
categories to match the periodic table online:
- Representative metals
- Transition metals
- Inner transition metals
- Metalloids
- Nonmetals
25
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Part 2:
•
•
•
•
Go to http://sciencespot.net
Click on Kid Zone
Click on Periodic Table Sites in the Chemistry section
Click on Chemical Elements.com link
Use the menu on the left-hand side of the screen to answer the following questions.
1. Where are the metalloids found on the periodic table?
________________________________________________________________________
2. Which elements are metalloids? List their symbols
_____
_____
_____
_____
_____
_____
_____
3. What are two uses for metalloids?
________________________________________________________________________
4. Where are the noble gases found on the periodic table?
________________________________________________________________________
5. Which elements are classified as noble gases? List their symbols.
_____
_____
_____
_____
_____
_____
6. Which elements are classified as nonmetals? List their symbols.
_____
_____
_____
_____
_____
_____
_____
7. What does the term “halogen” mean?
_______________________________________________________________________
8. Which elements are classified as halogens? List their symbols.
_____
_____
_____
_____
_____
9. Where do you find the transition metals on the periodic table?
________________________________________________________________________
10. What is unique about the location of the valence electrons in the transition metals?
________________________________________________________________________
26
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Part 3:
• Go to www.chem4kids.com
• Use this website as a review of the atom and the periodic table.
• Your assigned element is the element that has the same atomic number as your birthday
(day of the month)
o Ex: my birthday is November 20, so my element is Calcium (atomic #=20)
Prior Knowledge Questions
1. What is an element?
________________________________________________________________________
2. On the periodic table, what are the rows called? ______________________________
What do they all have in common? ___________________________________________
3. What are the columns called? ____________________________________________
What so they all have in common? ___________________________________________
4. What is an atom? ______________________________________________________
5. What is a nucleus? _____________________________________________________
6. Define ATOMIC NUMBER: ____________________________________________
7. Define ATOMIC MASS: _______________________________________________
MY ELEMENT IS (from Part 3 instructions): _________________________________
1. Write a brief description of your element.
2. Who found your element and when?
27
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
In the upper left hand corner of the ELEMENT PAGE, there is a menu with the choices:
“Say it” “Shell Info” or “Bond With It”
Use these choices and this menu to answer the following questions
3. What is your element’s atomic number?
4. How many electrons do you have when it has a neutral charge?
5. How many protons do you have?
6. What is your average atomic mass?
7. List three ways that your element is used.
8. Draw the Bohr diagram of your element with all of its shells. Make sure to label the electrons
and nucleus.
Part 4
Directions: go to the website http://www.colorado.edu/physics/2000/applets/a2.html
a. Make sure that you are on David’s Whizzy Periodic Table.
b. Once there, click on Hydrogen (H).
c. Choose the Nuclear View
You will be completing the follow chart as you search this website.
28
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Color
Particle
Name
Charge
Red
Black
Yellow &
Pink
1. What does the red particle represent? Fill in the red particle row in the chart above.
2. What charge does the red particle have? ___________________________
3. How many are there in Hydrogen? ________________________________
Now click on the Shell View.
1. What does the pink particle represent? Fill in the pink particle row in the chart
above.
2. What charge does it have? _______________________________________
3. How many are there? ___________________________________________
Now choose Neon, and choose the Nucleus View.
4. What do the black particles represent? Fill in the black particle row in the chart
above.
5. How many red particle are there in Neon? ___________________________
6. What is Neon’s atomic number? ___________________________________
Now choose Shell View.
7. How many pink and yellow particles are there in Neon? _________________
8. How many pink particles are in the first shell of Neon? __________________
9. How many yellow particles are in the second shell of Neon? _____________
10. How much Neon would $100.00 get you? ___________________________
29
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
11. What is Neon used for? _________________________________________
Now choose Beryllium, and choose the Nucleus View.
12. How many black particles are there in Beryllium? _____________________
13. How many red particles are there in Beryllium? ______________________
Now chose the Shell View.
14. How many pink and yellow particles are there in Beryllium? _____________
15. What is Beryllium’s atomic number? _______________________________
16. How many protons does Beryllium have in its nucleus? ________________
17. How many electrons does Beryllium have in its shell? _________________
18. How many electrons are in the first energy level in Beryllium? __________
19. How many electrons are in the second energy level in Beryllium? ________
20. How much Beryllium could you buy with $100? ______________________
21. What is Beryllium used to make? _________________________________
30
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Periodic Table Movie
Physical Science in Action
During the video.
1. The ___________ __________ is a map of the atoms and elements.
2. The first electron shell of an atom can only hold ___ electrons. The second electron shell can
only hold ___ electrons. An atom can bond with another atom only if its outer electron shell
IS NOT ________.
3. Dimitri Mendeleev studied and grouped elements by their _____________. This allowed
him to develop the periodic table.
4. Draw and label the square on the periodic table for the element sulfur. Include the element
name, symbol, atomic weight, and atomic number:
5. Atomic number is the number of ___________ in an atom of the element. Atomic
Mass/Weight is the number of ___________ plus the number of ____________ in the atom
of the element.
6. Not every atom of an element has the same number of ____________. The a___________
mass is the average mass of the atom of a particular element.
7. The periodic table has ____ rows called periods. Each element in the same ___________ has
the same number of electron shells/orbits.
8. The periodic table has ______ columns called groups/families. Each element in the same
group has the same number of electron(s) in its __________ shell/orbit. In addition, the
elements in each group share similar ________________.
9. Alkali, Alkaline Earth, Transition, Other, and Rare Earth are the classifications of
____________.
10. Metalloids have properties of both __________ and _______________.
11. Metals ______________ heat and electricity easily. Nonmetals do not ______________ heat
and electricity.
31
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
12. Halogens and Nobel Gases are __________________.
13. Nobel gases have ____ electrons in their outer shell and are very stable; they do not react
chemically.
After the video.
Without looking at the periodic table, list all the elements of which you can remember. Write
each element’s name and symbol.
32
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Alien Periodic Table
Introduction:
Imagine that scientists have made radio contact with life on a distant planet. The planet is
composed of many of the same elements as are found on Earth. However, the inhabitants of the
planet have different names and symbols for the elements. The radio transmission gave data on
the known chemical and physical properties of 30 elements that belong to Groups 1, 2, 13, 14,
15, 16, 17, and 18. You need to place the elements into a blank periodic table based on these
properties.
Problem: Where do the alien elements fit in the periodic table?
Procedure:
1. Listed below are data on the chemical and physical properties of the 30 elements. Write the
elements in their proper position in the blank periodic table.
2. Once you have determined the proper position for each element, then write the symbol in the
correct place.
The noble gases are bombal (Bo), wobble (Wo), jeptum (J), and logon (L). Among these
gases, wobble has the greatest atomic mass and bombal the least. Logon is lighter than
jeptum.
The most reactive group of metals are xtalt (X), byyou (By), chow (Ch), and quackzil
(Q). Of these metals, chow has the lowest atomic mass. Quackzil is in the same period
as wobble.
Apstrom (A), vulcania (V), and kratt (Kt) are nonmetals whose atoms typically gain or
share one electron. Vulcania is in the same period as quackzil and wobble.
The metalloids are ernst (E), highho (Hi), terriblum (T), and sississ (Ss). Sississ is the
metalloid with the greatest atomic mass. Ernst is the metalloid with the lowest atomic
mass. Highho and terriblum are in Group 14. Terriblum has more protons than highho.
Yazzer (Yz) touches the zigzag line, but it'
s a metal, not a metalloid.
The lightest element of all is called pfsst (Pf). The heaviest element in the group of 30 is
eldorado (El). The most chemically active nonmetal is apstrom. Kratt reacts with byyou
to form table salt.
The element doggone (D) has only 4 protons in its atom.
Floxxit (Fx) is important in the chemistry of life. It forms compounds of long chains of
atoms. Rhaatrap (R) and doadeer (Do) are metals in the fourth period, but rhaatrap is less
reactive than doadeer.
Magnificon (M), goldy (G), and sississ are all members of Group 15. Goldy has fewer
total electrons than magnificon.
33
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
Urrp (Up), oz (Oz), and nuutye (Nu) all gain 2 electrons when they react. Nuutye is
found as a diatomic molecule and has the same properties as a gas found here in Earth'
s
atmosphere. Oz has a lower atomic number than urrp.
The element anatom (An) has atoms with a total of 49 electrons. Zapper (Z) and pie (Pi)
lose two electrons when they react. Zapper is used in flashbulbs.
Analysis Questions:
1. List the name of each alien element and the Earth element that it represents. Do this for all
30 elements used in this activity. (write small)
2. Were you able to place some elements within the periodic table with just a single clue?
Explain your answer using two examples from the activity.
3. Why did you need two or more clues to place other elements? Explain your answer using one
specific example from the activity.
4. Why could you use clues about atomic mass to place elements, even though the periodic
table is based on atomic number?
34
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom and Periodic Table
1
2
Alien Periodic Table
13
14
15
16
17
18
35
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom & Periodic Table
Alkaline Earth Metals Reactivity Lab
Materials:
Spot (well plate)
calcium nitrate
potassium carbonate
potassium chromate
strontium nitrate
potassium sulfate
magnesium nitrate
barium nitrate
Caution: The chemicals used in this lab can cause severe damage to your eyes very quickly. Do
not let you goggles off your face for a moment. Some of the chemicals have very corrosive
odors. Do not smell any of these chemicals directly.
Precipitate: Solid that forms when two liquids are mixed.
MORE PRECIPITATES = MORE REACTIVE
Procedure:
1. Prepare the following table in your lab book. Do NOT include the arrows.
Table 1: Reactivity of Alkaline Earth Metals
Alkaline Earth
Potassium
Potassium Sulfate
3 drops
Metal
Carbonate
3 drops
Magnesium Nitrate
(write formula)
3 drops
Calcium Nitrate
(write formula)
3 drops
Strontium Nitrate
(write formula)
3 drops
Barium Nitrate
(write formula)
3 drops
Potassium
Chromate
3 drops
2. Get a well plate
-set it up just like the above table
-the plate should contain 3 columns and 4 rows
3. With chalk, label you lab table to that the well plate is labeled EXACTLY like your table.
4. Add the appropriate number of drops to each well, according to the table above.
36
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom & Periodic Table
5. In each box of your data table record:
• Reaction or no reaction
• Color reaction
• Strong precipitate or Weak precipitate
Questions
1. List the Alkaline Earth Metals tested today in order of their chemical reactivity (most reactive
to least reactive).
2. How does the order listed above compare to the trusty periodic table?
3. Group 1A in the Periodic Table is known as the Alkali Metals. Based on this experiment,
predict the reactivity of all the elements in Group 1A of the periodic table. List them from most
reactive to least reactive.
Conclusion:
1. purpose achieved? Proof with data
2. What affected your data? Errors or mistakes
37
Gen Chem Unit 3
The Atom & Periodic Table
Periodic Puzzler
Can you place these elements in their proper positions on the Periodic Table without knowing
their identity? Instead of the usual chemical symbol, a code letter represents each element.
Some clues to the element’s identity are listed below. The elements fall into these families or
groups:
JKQ
WNVG
IAL
EPFZ
YBR
ODS
CXU
THM
Place each code letter in its proper space in the table below, and then indicate the actual chemical
symbol that corresponds to each letter.
Elements
V
E
U
D
J
T
R
A
R
O
S
F
Y
I
C
V
H
G
N
J
Q
E
Z
U
is an inert gas.
is an alkali metal.
is a halogen.
is an element with 5 valence electrons.
is an alkaline earth metal.
is found in period 4.
is found in group 13.
has six protons in its nucleus.
has an atomic number one less than A.
has an atomic number one more than A.
has 18 more protons than D.
has only one proton.
has atoms that are heavier than the atoms
of B.
has the largest atomic number in its
group.
has atoms that are heavier that U, but
lighter than X.
has one more proton than U.
has the smallest atomic number in its
group.
has two protons.
is in the third period.
is in the second period.
has an atomic mass greater than J but
less than K
has an atomic number less than Z but
greater than P.
has more protons than other elements in
its group.
is in the second period.
38
Gen Chem 1 Unit 3
Atom + Periodic Table
1
2
13
14
15
16
17
18
Groups and Families
Use your periodic table to obtain the name and symbol of the element being described.
CHARACTERISTIC
NAME
SYMBOL
1. Alkali metal in the fourth period.
2. Inner transition metal in period 7 that
starts with the letter "E."
3. Halogen in the third period.
4. Member of the oxygen family that is a
metal.
5. Second period metalloid.
6. First transition metal in period four.
7. Nonmetal in period six.
8. Noble gas in period five.
9. Only halogen that is naturally a liquid.
39
Gen Chem 1 Unit 3
Atom + Periodic Table
Elemental, My Dear Watson
The famous detective Sherlock Holmes used all kinds of clues to solve the mysteries. Like any
good detective, he knew the value of fingerprints, because no two people have the same
fingerprints. In a way, atomic numbers are like fingerprints, because no two elements have
the same atomic number. In this activity you will be a chemical detective who tracks down
elements by deducing their atomic numbers. You will need to use your periodic table to
complete this activity.
1.
The atomic number of element X is six less than the atomic number of Y.
Element Y is one of the elements that make up water. What are elements X and Y?
Element X =
2.
Element Y =
To find element Z, start at the beginning of Period 2 on the Periodic Table.
Move to the right until you come to an element whose atomic number is six more than
the atomic number of the first element in the period. What is element Z?
Element Z =
3.
Element D loses two electrons in a chemical reaction.
Now it has the same number of electrons as neon. What is element D?
Element D =
4.
If the atomic numbers of calcium and beryllium are added together, you will find this
element. What is the element?
Element =
5.
This metal has an atomic number that some people this is unlucky.
What is the element and the atomic number?
Element =
6.
Atomic Number =
Add together the atomic number of the first three noble gases, and you’ll have the atomic
number of this element. What is the element and the atomic number?
Element =
Atomic Number =
40
Gen Chem 1 Unit 3
Atom + Periodic Table
7.
The atomic number of element J is greater than the atomic number of platinum but less
than the atomic number of lead. Its atomic number is divisible by four. What is element J?
Element =
8.
Element Q has an atomic number less than that of calcium.
Element Q has an atomic number three times that of the first nonmetal in the carbon
family. What is element Q? And what is the atomic number?
Atomic Number =
Element =
9.
Element R can be found in the halogen family.
When element R gains one electron it has the same number of electrons as a noble gas.
This noble gas has eighteen protons. What is element R?
Element R =
10.
I am element that needs to lose two electrons to become stable.
I also can be used to make your teeth strong and last a long time.
What element am I? And what is my atomic number? And what family do I belong to?
Atomic Number = _______
Element =
Family =
11.
Element O has an atomic mass less than two hundred.
When musicians hit it big they receive this type of record.
And of course it is my favorite precious metal. What is element O? And what is the
atomic number?
Element =
12.
Atomic Number =
Element B is found in the atmosphere.
This element is needed for plants, both day and night.
And element B has an atomic number half that of silicon. What is element B?
Element =
41
Gen Chem 1 Unit 3
Atom + Periodic Table
Color-Coded Periodic Table Activity
Directions: Be sure to follow all instructions carefully and completely! Use your textbook and
any other resources to help you complete the periodic table.
6. Draw a RED diagonal line through the elements that exist as a gas at room temperature.
7. Draw a BLUE diagonal line through the elements that exist as a liquid at room temperature.
8. Draw HEAVY BLACK LINE down the staircase that separates the metals from the
nonmetals.
9. Draw a DIAGONAL BLACK LINE from the upper left to the lower right through Astatine (85).
10. Lightly shade all the metalloids orange, including the lower portion of Astatine (85).
11. Use the following colors to identify the various sections of the periodic table.
a. Alkali Metals = green
b. Alkaline Earth Metals = brown
c. Halogens = pink
d. Noble Gases = yellow
e. Transition Metals = purple
f. Lanthanide Series = red do in the lower right corner
g. Actinide Series = blue dot in the lower right corner
12. Make a color key in the large open region showing all the colored groups assigned in # 11.
13. Answer the following question below (these should be review):
a. Define the following vocabulary words: period, group, atomic number, atomic mass,
and isotope.
b. What are the characteristics that make an element a metal, nonmetal, and or
metalloid?
c. List all of the information that can be found in every box on the periodic table.
d. Make a list of reasons for why you would need to use the periodic table.
42
Gen Chem 1 Unit 3
Atom + Periodic Table
43
Gen Chem 1 Unit 3
Atom + Periodic Table
44
Gen Chem 1 Unit 3
Atom + Periodic Table
1. Make a Data Table Showing the recent rise in the price of helium
2. Why is the price of helium rising?
3. How do they get helium? Name two ways.
4. What does the word dwindling mean in the passage?
5. Name 4 uses for helium
6. What does the word inert mean in the passage?
45