PHONEMES smallest unit of sound MORPHEMES smallest unit of
advertisement

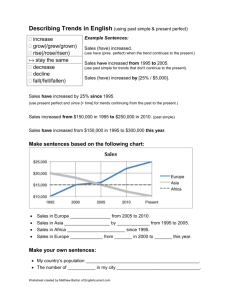
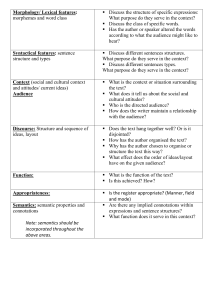
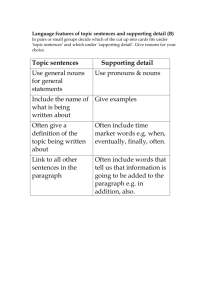
smallest unit of sound PHONEMES smallest unit of language that has meaning MORPHEMES 2 or more words PHRASES & SENTENCES meaning in language; meanings change over generarions. SEMANTICS rules of grammar SYNTAX 2 mons; first vocalizations, whimpers, gurgles COOING & CRYING 4-6 mons.; repetition of syllables; universal, cross-cultural sounds initially, but later babble in native language. BABBLING 12 mons.; one word can mean an entire phrase ONE WORD STAGE uses word only in one context; narrow set of objects UNDEREXTENSION overuse of word; wider set of objects OVEREXTENSION 18-20 mons. 2 word sentences TWO WORD STAGE (telegraphic speech) 2 yrs. Increases rapidly SEMANTICS & SYNTAX 4-5 yrs.; misuse of tense because they haven't acquired fine grammar skills by this age. OVERREGULARIZATION We have an innate, built-in learning mechanism LAD (language acquisition device) NOAM CHOMSKY (language theory) critical period - language must be acquired before a certain age to develop language fully. language is learned through conditioning; reinforce sounds/words. Criticism – can't learn an infinite number of sentences. SKINNER (language theory) rapid, comes w/o thought ASSOCIATIVE THINKING slower, need time to process & use knowledge COGNITIVE THINKING mental frameworks; prototype guidelines SCHEMAS drawing conclusions from the specific to general INDUCTIVE REASONING drawing conclusions from general to specific DEDUCTIVE REASONING guessing at random TRIAL & ERROR starting at the end & going back to the beginning WORKING BACKWARD applying rules that guarantee a solution ALGORITHMS rule of thumb strategies or shortcuts HEURISTICS chart that represents all possible combinations MATRIX putting problem aside for a period of time INCUBATION sudden realization of solution INSIGHT the function we assign to objects tends to remain fixed or stable, creating an inability to solve the problem; we see them only in terms of their customary functions. FUNCTIONAL FIXEDNESS inability to see from new perspective FIXATION tendency to persist w/old patterns for problem solving MENTAL SET tendency to confirm rather than refute; search for info. That confirms our preconceptions CONFIRMATION BIAS different correct answers to the same problem; higher level thinking DIVERGENT THINKING one correct answer CONVERGENT THINKING judging the probability of an event by how easily examples of the event come to mind; leads to bad decision making AVAILABILITY HEURISTIC when the sample you are judging matches your prototype; usually leads to the correct choice REPRESENTATIVENESS HEURISTIC