Anonymous Candidate Code: BIO 121 Final Exam (Session 1)
advertisement

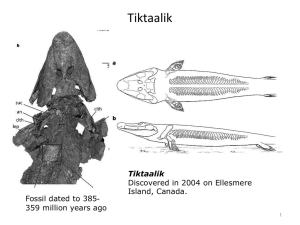
Anonymous Candidate Code: Joseph Fourier University 2014-2015 BIO 121 Final Exam (Session 1) --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Exam conditions: - 2H, - no document allowed, - no calculator allowed, - no cell phone allowed. The exam subject is composed of two parts: Part A: answer in the provided squares below. Part B consists in multiple choice questions: tick the correct or the wrong answer(s) as requested. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- PART A (You should be answering to these questions in 60 minutes or less) Drepanocytosis (sickle-cell anemia) is a genetic disease largely spread all over the world. It is caused by a mutation on chromosome 11 resulting in a mutation of the globin part of hemoglobin. Comparison of the nucleotide sequence of the mutated allele (allele S) to that of the normal allele revealed a point mutation, as described in the following table: Partial DNA sequence of a wild-type (healthy) individual Partial DNA sequence of a mutated (sick) individual GAG GTG 1 Use the “square/triangle/circle’ code to schematize below the various parts of a nucleotide. Do not forget to completely annotate this schematic representation. 1 2 Using the same “square/triangle/circle’ code, schematize below the double stranded DNA of a healthy individual at the GAG codon. Orient and annotate this double stranded DNA. The point mutation described above results in a modification of the amino acid sequence of the globin protein. The table below compares the amino acid sequence of the globin A from a healthy individual with the corresponding amino acid sequence of the globin S from an individual suffering from drepanocytosis. Portion of the globin A amino acid sequence from a healthy individual Portion of the globin S amino acid sequence from a sick individual Val His Leu Thr Glu Leu Val His Leu Thr Val Leu 2 4 Write below the developed formula of the tripeptide Thr Glu Leu (from globin A) at pH1. Threonine Glutamate Leucine pKa (α-COOH) 2,6 2,2 2,4 pKa (α-NH3+) 10,4 9,7 9,6 pKa (lateral chain) 4,3 5 Write the dissociation equilibria of the tripeptide Thr Glu Leu from globin A and calculate its isoelectric point. 3 The modification of the globin amino acid sequence resulting from the point mutation leads to a modification of the protein isoelectric point. 6. Which method would you use to separate globin A from globin S? (Describe the principle of this separation method and name it.) The modification of the globin amino acid sequence resulting from the point mutation also leads to a modification of the protein 3D structure. Hemoglobin S indeed polymerizes into rigid fibers, which deform the red blood cell plasma membrane of sick individuals. 7 Draw below a schematic representation of a portion of a normal cell plasma membrane, including all the components of this plasma membrane. Do not forget to completely annotate this scheme, including the various compartments that you have represented. 4 The lipidomic analysis performed on this plasma membrane showed the presence of 1 palmityl 2 oleyl 3 β D-glucopyranosyl glycerol among the lipid components. 8 Write below the semi-developed formula of β D-glucopyranose. 9 Write below the semi-developed formula of palmitic acid at pH 1. Do not forget to number the carbons and provide its fatty acid nomenclature. 10 Write below the semi-developed formula of oleic acid at pH 1. Do not forget to number the carbons and provide its fatty acid nomenclature. 5 11 Write the semi-developed formula of 1 palmityl 2 oleyl 3 β D-glucopyranosyl glycerol. To which lipid family does it belong? 12 On the formula written in question 11, draw a hydrogen bond that can be established between the lipid and one water molecule. 6