Webinar PowerPoint - Network for Business Sustainability
advertisement

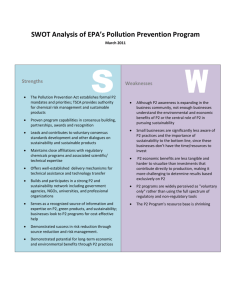
09/08/09 1 What is Sustainability? Broad definition • Consideration of social, environmental and economic impact Many subtopics • E.g. ethics, corporate social responsibility, poverty alleviation, stakeholder engagement Network for Business Sustainability Managers NBS Researchers Strategy Teaching Materials Systematic Reviews • Embedding Sustainability in Organizational Culture Research Insights • For Employee Buy-In, Supervisors Trump the CEO • Reward Honesty, Not Performance, of Chinese Suppliers Thought Leader Forum • Buying Furniture on iTunes: Creative Destruction in a World of “Locavore” Production (Gerry Davis) • Our Baboon Moment: How Business Can Create Peace (Tim Fort) Accessing NBS content • www.nbs.net • Subscribe to receive new content Guest Speakers Mike Valente Marie-France Turcotte Ted London Schulich School of Business, York University University of Quebec at Montreal Ross School of Business, University of Michigan Mike Valente Assistant Professor of Organization Studies Schulich School of Business, York University Teaching Sustainability and Strategy Mike Valente Schulich School of Business Business Sustainability refers to the achievement of economic viability (profitability) while operaHng within the capacity, or contribuHng to the integrity, of social, ecological, and economic systems Business Sustainability Economic Social Environmental Examples of Systems Ecological Systems Social • Biodiversity • Health system • Replenishment cycle • Maintenance of social equity • Water and dry systems • Maintenance of social jusHce • Ice systems • Humanity’s food system • Species reproducHon • Basic service distribuHon Economic • Economic growth • Financial system • Flow of goods/services • Wealth creaHon • Wealth distribuHon Strategic Adoption Levels of Sustainability Extraneous Sustainability Paradigm Culture/Identity - Sustainability absent - Philanthropy Positioning - Public relations/marketing - Reactive/defensive Core Operations - Little or no products/services - Expertise in avoiding sustainability Episodic Sustainability Paradigm Culture/Identity - Identity conflict, hypocrisy - Fragmented Positioning - Range of markets - “We are green too” Core Operations - Product/division level - Pockets of the organization Embedded Sustainability Paradigm Culture/Identity - TBL (shared value) - Defines who we are Positioning - Customer value proposition - Industry leader Core Operations - Company level - Sustainability processes source of SCA Student Exercise • Come to class with your assessment of how strategic sustainability is to a firm of your choice. • How does your chosen company’s commitment to sustainability measure up to competitors in the industry? • What would the company have to do to better embed sustainability into their strategy? • Instructor tools – Positioning strategy – Core competencies related to sustainability • Products • Processes • Identity/reputation Value CreaHon and Value Capture Successful Strategy Almost Perfect Competition WTP WTP Total Value Created Price Cost Opp. Cost Consumer Value Firm Value Supplier Value Price Total Value Created Firm Value Cost Opp. Cost Case: Patagonia Wealthy outdoors people, environmentalists, demand for authenticity Value Created Low advertising, low defect rates, supplier relations WTP Price Cost Opp. Cost Quality, innovative design /material, product guarantee, authentic Create demand for environmental raw materials, innovation Marie-France Turcotte Professor, Department of Strategy, Social Responsibility and Environment Chair of Social Responsibility and Sustainable Development University of Quebec at Montreal Embedding Sustainability in Corporate Culture Stéphanie Bertels 09/08/09 1 Embedding Sustainability in Corporate Culture Stéphanie Bertels 09/08/09 1 Embedding Sustainability A full academic report on Embedding Sustainability in Organizational Culture is available at www.nbs.net/knowledge/culture Étapes ApplicaHon • Assignment to apply Culture Wheel practices: – How are Culture Wheel practices are applied in a case study of Patagonia? – How could the practices be modified for implementation at your organization? Principles and management tools used by Patagonia To what prac:ce(s) does it correspond in the culture wheel? « Philosophy classes » for Raise awareness managers Re-envision Learn Life Cycle analysis for supply material decision-­‐ making Integrate in business processes Engaging with large Trigger compeHtors to create the Share supply market in Invite biological co\on Could it be What adapta:ons implemented in would be needed? your organisa:on? Yes/No Change the name of these strategic sessions addressing sustainability Yes/No … Yes/No … Advice • Well suited for teaching about implementing strategy • Get students involved through their own experience and through cases • Remind them that practices from other organizations must be adapted to their specific context (organizational culture) Embedding Sustainability Limits of the classics stakeholder models 24 Stakeholder Management : Framework and Philosophy Engaging Stakeholders Step 1: Get to know your community A full academic report on Stakeholder Engagement is available at www.nbs.net/topic/stakeholder Limits of the classics stakeholder models Power sleeping dominant définitive dangerous requesting Urgency discretionary dependant Legitimacy Engaging Stakeholders Step 2: Choose your engagement strategy A full academic report on Stakeholder Engagement is available at www.nbs.net/topic/stakeholder Engaging Stakeholders Step 3: Plan your engagement process A full academic report on Stakeholder Engagement is available at www.nbs.net/topic/stakeholder Advice • Well suited : – For teaching the political dimensions of strategy – As a guide for an assignment • If time allows, before presenting the guide, have the students discover the complexity of the relationships among stakeholders UnHl we meet again… • Visit http://nbs.net/knowledge/strategy-teaching/ • Webinar recording • Chat function to share resources • For questions related to NBS resources, contact Chelsea (chelsea.hicks@nbs.net) • The webinar is now over. Please complete the webinar when you exit.