Leaving certificate Chemistry pass level Revision notes
advertisement

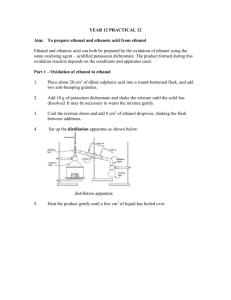
Deirdre Brennan MPC Leaving certificate Chemistry Pass level Revision notes Q.1 Making ethene Making ethyne Glass wool soaked in ethanol Aluminium oxide /white solid Suck back Turns bromine water colourless-test for unsaturation Turns KMn04 purple to colourless- test for unsaturation Called a dehydration reaction Food ripening Burns with luminous flame Water Calcium carbide/grey solid Acidified copper sulphate to remove impurities Turns bromine water colourlessunsaturation test Burns with luminous sooty flame Oxy acetylene Welding Sooty flame caused by lack of 02 1 Deirdre Brennan Making ethanal MPC sodium dichromate(orange 6+) ethanol anti bumping granules conc sulfuric acid added slowly in ice as reaction is exo colour change to (green 3+) distilled immediately to stop ethanal turning to ethanoic acid ice water-stop ethanal evaporating, boiling point = 210C water in at bottom, out at top excess ethanol to stop ethanal turning to ethanoic acid impurities = water, ethanol, ethanoic acid, redox reaction Test for presence of ethanal is fehlings (I) + (II). Blue to red (Identifies C=0) 2 Deirdre Brennan MPC Making ethanoic acid 2008 Making soap sodium dichromate in excess(orange 6+) ethanol anti bumping granules conc acid added slowly as reaction is exothermic colour change to (green 3+) refluxed first and then distilled water in at bottom, out at top excess sodium dichromate to allow ethanol to fully oxidize to ethanoic acid. impurities = water, ethanol, ethanal redox reaction use Bunsen burner instead of hot plate as ethanoic acid bp = 1180C Precautions:add ethanol mixture drop by drop into flask+keep flask cooled under running water Fat Sodium hydroxide Ethanol which is solvent Anti-bumping granules reflux then distil to remove ethanol filtered through brine to precipitate out soap wash with cold water to remove NaOH The ionic part of the soap molecule is water-soluble while the non-polar hydrocarbon part is soluble in oil and grease. Reflux apparatus used to ensure that the hydrolysis of the fat is as complete as possible. If the mixture If not refluxed ethanol would be lost. Base hydrolysis 3 Deirdre Brennan Extracting clove oil MPC Clove oil contains component molecules whose boiling points are quite high. Heating them to their boiling point would be destructive. The component molecules found in clove oil are often relatively non-polar and will therefore be more soluble in the non-polar solvent than in water. One of the major components of clove oil is eugenol, an aromatic compound that can burn skin. Gloves should be worn when handling the product of the experiment. 4 Deirdre Brennan MPC Q.2 Titrations HCl and Na2C03 titration label pipette, burette, wash bottle, volumetric flask standard solution-one whose concentration is known exactly volume of Sodium carbonate solution measured using pipette volume of HCl solution measured using burette How do you make a standard solution of sodium carbonate? o Weigh out quantity of Standard solution in a clock glass o Dissolve in deionised water o Transfer this volume + any remaining Standard solution using wash bottle into a 250ml volumetric flask o Bring to the calibrated mark with deionised water. o Stopper , invert and shake 20 times indicator = methyl orange ratio 2: 1 acid: base V A MA = V B M B NA nB Q.2 hydrochloric acid sodium hydroxide titration 2007 2005 2002 1. label pipette, burette, wash bottle, volumetric flask 2. standard solution-one whose concentration is known exactly 3. volume of Sodium hydroxide solution measured using pipette 4. Describe correct procedure for rinsing and filling a pipette Rinse with deionised water Using a filler fill to the calibrated mark with base Empty the base from the pipette by tipping the last drop at the side of glass 5. Describe correct procedure for rinsing and filling a burette rinse with deionised water using a funnel fill burette to 0 with acid. Make sure you read level of meniscus Open tap to allow acid to fill bottom of burette 6. volume of HCl solution measured using burette 7. describe how you would make a salt 8. indicator = methyl orange 9. end point = permanent pink 10. ratio 1: 1 acid: base 11. calculation 5 Deirdre Brennan MPC Example: 25ml of 0.1M NaOH neutralized 20ml of xM concentration of HCL. Find x? V acid =20 M acid =x n acid =1 V base=25 M base=0.1 n base =1 VA MA = V Na 20 x 1 B MB nB X = 25 x 0.1 1 concentration of HCl = 0.125m/l conc of HCL in g/l = 36.5 x .125 = 4.6 g/l Mr of HCl = 1 + 35.5 = 36.5g 6 Deirdre Brennan MPC Rates of Reaction experiments can come up in various questions Making oxygen from hydrogen peroxide and manganese dioxide 1. Draw the diagram on page 211 2. catalyst is a chemical that speeds up or slows down the rate of a chemical reaction but does not change itself. 3. Rate of reaction is the change in concentration of a reactant per unit time. 1. Catalysis Three types Heterogenous = reaction involving gas/liquid, gas/solid, solid/liquid Homogenous = gas/gas, solid/solid, liquid/liquid Autocatalysis= where product of experiment becomes a cataylst 2. Three types of metals that are used in catalytic converters Palladium, rhodium, platinum 3. Lead damages a catalytic converter Metal Potassium Lithium Barium Strontium Copper Q.5 Revision of flame tests Colour purple Crimson Green Red Green 7 Deirdre Brennan Sodium Chloride Sulphate Carbonate Nitrate MPC Yellow Revision of anion tests Add silver nitrate Add barium chloride Add HCl Add iron sulphate and sulphuric acid 8 White ppt White ppt Fizzing occurs brown ring Deirdre Brennan MPC Q.4 Calculating ppm (parts per million) Calculating % of element in compound Bomb calorimeter OIL RIG Equilibrium constants calculate the pH of an acid/base Anion tests Endothermic/exothermic reactions Atomic radii increase going down group. Atomic radii decrease going across a period. Uses of organic compounds o Methanoic acid= ant stings o Propanone= nail varnish remover o Ethanoic acid = vinegar o Benzoic acid= food preservative o Methyl benzene = safe solvent o Ethene gas= food ripening o Ethyne gas= welding o Ethanol = beer/wine o Methane = home heating Temporary hard water = Calcium carbonate permanent hard water = calcium sulphate Calculations on ppm ( mg/l) A 100cm3 sample of seawater contains 0.022g of SS. Calculate the conc. Of SS in ppm Step 1. Change grams to milligrams 0.022g X 1000 = 22mg in 100cm3 Step 2. Find 1cm3 22÷ 100 = 0.22mg/ml 0.22 X 1000 = 220mg/litre Step 1 : Find relative molecular mass of MgSO4 24 +32 + 16(4) = 120g Step 2 : 24/120 x % = 20% Calculate % of magnesium in ( MgSO4) 9 Deirdre Brennan MPC Question 5 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Scientist John Dalton Rutherford J.J Thompson Chadwick Bohr Crookes Millikan Newlands Dobereiner Mendeleev Moseley Humphrey Davy Becquerel Marie Curie Boyle(plunger) 16. J Charles(hot balloon) 17. Avogadro 18. Arrhenius Discovered Atomic theory Nucleus, proton electron Neutron Electrons orbit nucleus in fixed paths Cathode ray tube Charge/mass of electron Octaves Triads Gaps/atomic mass Atomic number Discovered many elements such as Na/Mg/K Radioactivity Radium/polonium 1.At constant temp a 2.fixed mass of gas , the 3.vol is 4. inversely proportional to 5.pressure p = 1/v air 1.At constant pressure a 2.fixed mass of gas , the 3.vol is 4. directly proportional to 5.temperature on Kelvin scale ( T ∞ V) 1 mole = 6 x 10 23 atoms Definition of an acid/base Atomic number = no. of protons in nucleus of an atom Mass number = no. of protons and neutrons in nucleus of an atom Electronegativity= it’s the force of attraction that an atom has for the shared pair of electrons in a covalent bond. Relative atomic mass= is the mass of an atom compared to 1/12 the mass of the carbon-12 isotopes. 10 Deirdre Brennan Shapes of molecules Molecule Methane ( CH4) MPC Drawing Water (H20) Ammonia(NH3 ) Boron trichloride (BCl3) Ethyne ( C2H2) Covalent bonding= electrons are shared Ionic bonding= electrons are taken/given Valency = group number of that element Radioactivity 1. Alpha Particle(helium nuclei) 2 neutrons+ 2 protons . 2. Beta Particle-high energy electron- it’s a neutron that turns into a proton and a high energy electron is emitted 11 Deirdre Brennan MPC 3. Gamma readiation-high electromagnetic radiation when nucleus changes shape. Uses •Smoke Detectors contain a weak source made of Americium-241. Carbon-14 Dating Cancer treatment Sterilising 12 Deirdre Brennan MPC Q.6 Hydrocarbons are compounds that contain hydrogen and carbon only. 1. Fuels are organic compounds and when they are combusted they release large quantities of energy. 2. LPG is liquid petroleum gas. 3. Octane number is ability of a fuel to reduce knocking 4. Aromatic compound has a benzene ring 5. hydrogen is a fuel for space rockets but is very explosive 6. Lead used to be used for increasing octane number but causes health problems. 7. Isomerisation, catalytic cracking , dehydrocyclisation and adding oxygenates(ethanol has octane no of 111, excellent fuel) are ways to increase octane number 8. Adding oxygenates lower pollution 9. MTBE( methyl tertiary butyl ether) 10. 2,2,4 trimethyl pentane octane no is 100 Fraction Refinery gas petrol Naphtha Kerosene diesel Lubricating oil Fuel Oil Bitumen Use Domestic gasb Motor fuel Petrochemical industry(Plastics) Aviation fuel Motor fuel Reduce wear of engines ships Tar 13 Deirdre Brennan MPC Revising Question 8 Formula Name C2H50H Ethanol C2H2 Ethyne CH3CHO Ethanal CH3COOH Ethanoic acid CH3 CH2 0Na Sodium ethanoate CH3 CH2 Cl 1, chloro ethane Shape tetrahedral planar planar tetrahedral tetrahedral tetrahedral CH2BrCH2Br CH3 CH3 C2H4 tetrahedral tetrahedral Planar Formula C2H50H C2H2 CH3CHO CH3COOH CH3 CH2 Cl CH2BrCH2Br CH3 CH3 C2H4 1,2 dibromoethane ethane ethene Mechanism Ethane going to ethanol is called an addition reaction Ethanol going to ethane is called an elimination reaction CH2 CH2 (ethene) going to CH3 CH2 Cl is called an addition reaction C2H50H going to CH3COOH is called oxidation reaction. Bond type Saturated Unsaturated Unsaturated Unsaturated saturated Saturated saturated unsaturated Questions on water(generally question 9) Treatment of water for drinking Stages What happens Screening Large insoluble solids removed Flocculation Aluminium sulfate added to water to help suspended solids to clump together Sedimentation Suspended solids allowed to settle to bottom of tank. Filtration Water passed through beds of sand and gravel to remove suspended solids Fluorination Put in to prevent tooth decay Chlorination Kills bacteria pH adjustment Lime or acid added Stages Primary Secondary tertiary Treatment of sewage What happens Sewage passed through grids to remove dense solids. Sewage then put into sedimentation tanks where suspended solids allowed sink to bottom. Sewage allowed to be broken down by bacteria Removal of phosphates and nitrates 14 Deirdre Brennan MPC Sewage causes eutrophication which causes fish kills and polluted river water. Phosphates and nitrates cause over enrichment of water causing eutrophication. Silage effluent and human effluent from septic tanks can cause eutrophication. Temporary hardness in water removed by boiling. Hardness in water caused by Mg2+ and Ca 2+ ions. Temporary hardness caused by limestone. Permanent hardness caused by Calcium sulphates (CaS04) from rock such as gysum. What is the % of Ca in CaC03? A 100cm3 sample of sea water contains 0.022grams of suspended solids. Calculate the conc. Of suspended solids in ppm. Biochemical Oxygen Demand. The five day Biochemical Oxygen Demand of a water sample is the amount of dissolved oxygen taken up by bacteria in measured after 5 days incubation in the dark at 20 0C. Acids & bases •Arrhenius acid is a substance that breaks down in water to produce H+ ions. •Arrhenius base is a substance that breaks down in water to produce OH- ions. •Strong Base is Sodium Hydroxide (used for cleaning drains)(NaOH) •Weak base is ammonia.(NH3) •Strong acid is HCl, H2SO4, HNO3 •Weak Acid is vinegar(ethanoic acid) •pH is the measure of acidity or basicity •pH measured using universal indicator •BL acid is proton donor •BL base is proton acceptor •Neutralisation is reaction between an acid and a base that makes salt and water. •Everyday example is rubbing wasp sting with vinegar to neutralise the base •Putting lime on soil to neutralise acidic soil. limitation of pH scale not accurate for concentrated solutions Calculate the pH of a 0.01M solution of NaOH pH = -log10[0.01]= 14-2 = 12 Concentration of a solution of 4.0g/l of sodium hydroxide is Calculate the pH? •Step 1 : 4/40 = 0.1M •Step 2 pH = -log10[0.1]= 14-1 = 13 Calculate the pH of a 0.01M solution of H2S04 pH = -log10[0.01 x2]= 1.7 15 Deirdre Brennan MPC Le Chatelier’s principle states that when a stress is applied to a system the system moves to relieve the stress. What does the symbol tell us? Chemical equilibrium is a state of dynamic balance where the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction. Rates of Reactions The rate of a reaction is the change in concentration per unit time of any one reactant or product. The rate of reaction at a particular instant in time is called the instantaneous rate. Factors affecting reaction rate (i) Nature of reactants Ionic reactions are fast because they merely involve the coming together of oppositely charged ions. Covalent reactions are usually slower at room temperature, because they involve breaking covalent bonds. (ii) Particle size (iii) Concentration The rate of a chemical reaction increases with increased concentration. When sodium thiosulphate is reacted with HCl , a precipitate of sulphur is formed. This sulphur is in the form a cloudy yellow suspension. By increasing the concentration of the sodium thiosulphate solution the rate at which the sulphur appears increases also. (iv) Pressure Increased pressure increases reaction rate. (v) Temperature All reactions are faster at higher temperatures.. When sodium thiosulphate is reacted with HCl , a precipitate of sulphur is formed. This sulphur is in the form a cloudy yellow suspension. By increasing the temperature of the reaction solution the rate at which the sulphur appears increases also. (vi) Catalysts catalyst is substance that alters the rate of a chemical reaction but is not consumed in the reaction. (a) General properties of catalysts 1. Catalysts are recovered from a reaction unchanged with the same chemical properties. 2. Catalysts are specific. Enzymes are biological catalysts that have very specific functions. 3. Catalysts needed in small amounts to function. 4. Equilibrium is reached quicker by using a catalyst. 5. Catalysts can be destroyed by catalytic poisons. Arsenic inhibits the action of certain enzymes in the body. 16 Deirdre Brennan MPC (b) Catalytic Converters Platinum, Palladium and Rhodium Toxic fumes from cars : CO and NO are adsorbed onto the surface of these metals C0 to CO2 NO to NO2 . Collision Theory and Activation Energy A chemical reaction between two substances is the result of their molecules colliding together. These colliding molecules must possess a minimum amount of energy for a reaction to occur. When an effective collision occurs bonds are broken and new bonds are formed. The Activation Energy is the minimum energy which colliding particles must have for a reaction to occur. Chromatography is a separation technique in which a mobile phase carrying a mixture moves in contact with a stationary phase. Stationary phase = filter paper Mobile phase= solution e.g methanol + food colouring/felt-tippedmarkers/mixture of indicators TLC used for separating out impurities in drugs Mass spectrometry Used to find relative molecular mass of compound HPLC High performance liquid chromatography Used to detect growth promoters in food/concentration of caffeine in drinks Gas Chromatography Used in detecting alcohol/drugs in urine samples 17 Deirdre Brennan MPC Q.10+ 11 Gas Laws Boyle’s law states that at constant temperature the volume of a fixed mass of gas is proportional to its pressure. Charle’s law :At constant pressure, the volume of a fixed mass of gas is directly proportional to its temperature measured in the Kelvin scale. Avogadro’s Law states that equal volumes of gases contain equal numbers of molecules under the same conditions of temperature and pressure. Combined gas law solves the problem of the relative molecular mass of a volatile gas How confident am I that I have learnt and know my notes on the experiments Mandatory Experiments 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) Flame tests Preparation and properties of Ethene Preparation and properties of Ethyne Determine the heat of Neutralisation of HCl and NaOH Preparation and properties of Ethanal Preparation and properties of Ethanoic Acid Preparation of Soap Chromatography 9) 10) 11) 12) Determination of total suspended and dissolved solids in water sample + pH To standardise a HCl solution using a standard solution of Na2C03 To prepare a sample of sodium chloride by neutralizing with NaOH with HCl. Benzoic acid 13) 14) Extracting clove oil Anion tests 15) 16) 17) 18) Equilbrium reactions(looking at Le Chatelier’s principle. Looking at rate of production of oxygen To show how concentration and temp. affect the rate of a reaction. Find relative molecular mass of volatile gas 18