Document
advertisement

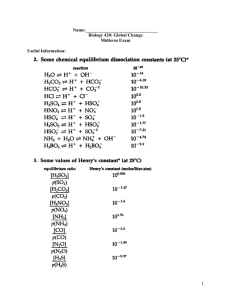
GEOS 115 Intro to Oceanography Test #2- Review What are the characteristic of active and passive continental margins? Be able to define what, continental shelf, slope, submarine canyon, rise, abyssal fan, abyssal plain are What is a Turbidity currents?What are turbidite deposits? What is graded bedding? Where are the thickest ocean sedimentary deposits found ? Define trenches, seamounts, guyots and mid ocean ridges? Where are they found? What are ophiolites? What is continental crust made of, how thick is it? What is oceanic crust made of, how thick is it? What are their densities? What are Hydrothermal vents? What exists near hydrothermal vents? What are black smokers? Be able to identify mid ocean ridges and different trenches on a map as well as different ocean basin features. Be able to draw and label all features across a cross-section of the sea floor from the shoreline to the mid-ocean ridge and to a trench. Name the reef type associated with a sunken volcanic island. The thickest ocean sedimentary deposits are found where? What are methane hydrates, why are they important? What are some examples of example of lithogenous, biogenous, hydrogenous and cosmosgenous sediments? Where are Calcareous sediments and silicious sediments found? What is the CCD, what is its relevance? What are some economic resources found in the oceans (think phosphate, sand and gravel, metals etc) What conditions are necessary for coral reef growth? What can a sediment core tell us about past oceanic conditions? What are the salts that are commercially extracted from seawater? Be able to identify the 4 ocean basins and 6 seas on a map Extra credit questions based on Volcanoes of the Deep What is the salinity of the average open ocean? How is it measured? Where do the salts in the oceans comes from? What is residence time? What is the residence time of some of the common ions in the oceans? What is the normal pH of seawater? What are the major ions of seawater? What is photosynthesis? What is density? What are covalent bonds? Hydrogen bonds? What is a Secchi disk? How does the pH of seawater vary? How does salinity vary? What is heat capacity? How does it vary between land and sea? How fast does sound travels in seawater? How does the addition of salt to water change its properties? At what temperature does seawater of average salinity freeze? What wavelengths of light penetrate deepest in the ocean? What is a buffer? What is an iceberg? What are the Layers of the atmosphere? (thermosphere, mesosphere, stratosphere, and troposphere) At what velocities do different areas of the earth rotate? What are the horse latitudes, doldrums? Where are they found? What are the different circulation cells? Where are they? Be able to DRAW them on a globe. How are offshore breeze an on shore breezes produced? How is atmospheric pressure measured? How are winds named? What is the Coriolis Effect? How does it affect air masses in the Northern/Southern Hemisphere? What effect do increased levels of carbon dioxide have in the atmosphere? What other greenhouse gases exist? What is the orographic effect? What is a rain shadow? What is the jet stream? What is the gaseous composition of the atmosphere? What is a monsoon? How is it produced? What is a hurricane? How are they produced? Where do they preferentially form? What is a storm surge? Why are they dangerous?