Region 6: Prevertebral Region and Pharynx Deep Cervical Fascia
advertisement

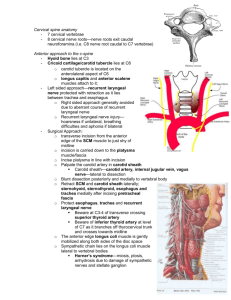
Region 6: Prevertebral Region and Pharynx Deep Cervical Fascia --Investing fascia of the deep cervical fascia (superficial or anterior layer) *splits to inest the trapezius, sternomastoid, omohyoid, and infrahyoids --Prevertebral fascia of the deep cervical fascia (deep or posterior layer) *extends into the axilla as the axillary sheath *surrounds 7 muscles in the prevertebral region: ant. scalene, middle scalene, post. scalene, longus capitus, longus colli, rectus capitus ant., rectus capitus lateralis *the compartment enclosed within the prevertebral layer of fascia is know as the prevertebral region --Carotid sheath *condensation of fascia which encloses the carotid arteries, internal jugular vein, and vagus nerve --Visceral fascia *surrounds the viscera of the neck Spaces in the Head and Neck --Retropharyngeal Space *located behind pharynx *important b/c of downward spread of infection Pharynx --muscular tube lined with mucous membrane that extends from the base of the skull down to the level of C6 --lies posterior to the nose, mouth, and larynx --divided into 3 parts a. Nasopharynx: nasal part *communicates with the nasal cavities through the choanae *auditory/Eustachian tube opens into it *torus tubarius: elevation made by auditory tube *salpingopharyngeal fold: with underlying muscle of same name *pharyngeal tonsils/adenoids: mass of lymphoid tissue embedded in the mucous membrane of the upper posterior wall (enlarged pharyngeal tonsils are known as adenoids) *torus levatorus: fold of mucous membrane produced by the levator veli palatini muslce b. Oropharynx: oral part *posterior to the mouth and tongue *communicates with the mouth through the oropharyngeal isthmus (fauces) *contains the palatine tonsils (located lateral to the tongue, below the soft palate, and b/w the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal folds, lymphatic ring formed by pharyngeal tonsil aove, palatine tonsils laterally, and lingual tonsils below (Waldeyer’s ring) *mucous membrane of the epiglottis is reflected onto the base of the tongue (one median and 2 lateral glossoepiglottic folds, depression b/w them are valleculae) c. Laryngopharynx: laryngeal part *posterior to the larynx *anterior wall includes back of the larynx and piriform recesses *branches of the internal laryngeal nerve and superior laryngeal vessels are located under the mucous membrane of piriform recess --Buccopharyngeal Fascia: contains pharyngeal plexus of nerves --Pharyngeal Muscles a. Constrictors: all of them insert into a median raphe *Superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle: origin from medial pterygoid plate, hamulus, pterygomandibular raphe *Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle: origin from hyoid bone *Inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle: origin from thyroid and cricoid cartilages b. Stylopharyngeus Muscle *origin from styloid process *enters pharynx b/w superior and middle constrictor muscles *inn. by glossopharyngeal nerve c. palatopharyngeus muscle d. salpingopharyngeus muscle: origin from auditory tube --Structures Related to Pharyngeal Constrictor Muscles a. glossopharyngeal nerve and stylopharyngeus muscle: pass b/w superior and middle constrictor muscles b. internal laryngeal nerve and superior laryngeal artery: pass b/w middle and inferior constrictor muscles c. recurrent laryngeal nerve and inferior laryngeal artery: b/w inferior constrictor and esophagus --Nerves Related to the Pharynx a. glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) *exits jugular forament *supplies: carotid sinus (baroreceptors), stylopharyngeus muscle (motor), posterior 1/3 of tongue (with taste and general sense) b. Vagus Nerve (CN X) *exits jugular forament and parallels carotid artery *superior laryngeal nerve --internal branch: pierces the thyrohyoid membrane, sensory and parasympathetic to supraglotti mucosa --external branch: motor to the cricothyroid and inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscles *pharyngeal nerves: motor to pharynx and soft and hard palate * inferior laryngeal nerve/recurrent laryngeal nerve --major motor nerve to intrinsic laryngeal muscles with sensory and parasympathetic nerves to the subglottic mucosa c. Spinal Accessory nerve (CN XI) *exits jugular forament *spinal part: originates from upper cervical spine (motor to SCM and trapezius mm.) d. Hypoglossal Nerve (CN XII) *exits the hypoglossal canal *enters the tongue b/w mylohyoid and hyoglossus muscles *motor nerve to the tongue e. Sympathetic trunk *POSTganglionic fibers in internal carotid nerve or plexus follow the internal carotid artery into head f. pharyngeal plexus *formed by fibers from glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), vagus nerve (CN X), and sympathetic trunk --Blood Vessels Related to the Pharynx a. Carotid arteries *internal carotid arteries --NO branches in neck *External carotid arteries: Anterior Branches --superior thyroid artery --lingual artery --facial artery *External carotid arteries: Medial Branch --ascending pharyngeal artery *External carotid arteries: Posterior Branches --occipital artery --posterior auricular artery *External carotid arteries: Terminal Branches --maxillary artery --superficial temporal artery b. Internal jugular vein *retromandibular v. + posterior auricular form the external jugular v.