Human Behavior in the Social Environment Anissa Taun Rogers
advertisement

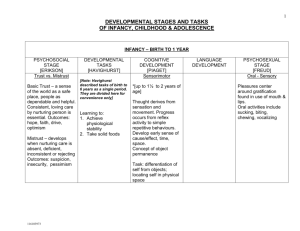
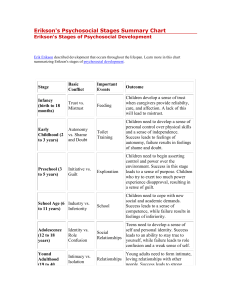
Human Behavior in the Social Environment Anissa Taun Rogers Question Bank 10/08/2009 Chapter 3 Multiple Choice 1. The disease model a. Is concerned with individual illness and dysfunction (p49) b. Assumes people take an active role in their development c. Places a strong emphasis on interactions between individuals and their environments d. Explains development across the life span 2. The disease model is most often used in which of the following settings? a. Medical clinic b. Mental health clinic c. Hospital d. All the above (p49-52) 3. Why do social workers need to understand the disease model? a. To help them communicate with clients’ health care providers (p49) b. It provides reliable diagnostic criteria for assessing mental illnesses c. It focuses on strengths of the client d. It assumes people are active agents in their development 4. Why do social workers tend to use the term “client” versus “patient”? a. To demedicalize the client-worker relationship (p52) b. They don’t want to be confused with the medical profession c. It is agency policy d. All the above 5. A common assessment tool based on the medical model is: a. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th edition (p52) b. Biopsychosocial assessment c. Global assessment of functioning d. Intelligence Quotient (IQ) 6. “Individuals are passive agents in their development” is an underlying assumption of: a. The medical model (p50) b. Psychosocial development theory c. The humanistic perspective d. Social learning theory Human Behavior in the Social Environment Anissa Taun Rogers Question Bank 10/08/2009 7. Psychosocial and environmental problems are covered under which Axis in the DSM-IV? a. Axis II b. Axis III c. Axis IV (p52) d. Axis I 8. In Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, hypothetical-deductive reasoning occurs in which stage of development? a. Concrete operations stage b. Formal operations stage (p56) c. Sensorimotor stage d. Preoperational stage 9. Which of the following is a limitation of Piaget’s theory of cognitive development? a. It disregards what is normal or average b. It overestimates variations c. It ignores sociocultural factors (p58-59) d. It provides useful guidelines around child cognitive development 10. Which of the following is a psychodynamic theory? a. Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development (p59) b. Piaget’s theory of cognitive development c. Bandura’s social learning theory d. Existentialism 11. According to Freud, the conflict in which boys fall in love with their mothers is called: a. Oedipus complex (p61) b. Electra complex c. Fixation d. Reality principle 12. Which is a common defense mechanism in which individuals blame others for their own shortcomings and mistakes? a. Denial b. Sublimation c. Withdrawal d. Projection (p61) Human Behavior in the Social Environment Anissa Taun Rogers Question Bank 10/08/2009 13. Which is a common defense mechanism in which individuals consciously satisfy unacceptable needs and desires through socially acceptable activities? a. Denial b. Sublimation (p61) c. Reaction formation d. Repression 14. What is a chief limitation of Freud’s theory? a. It overemphasizes sexual drive b. It diverges from the medical model c. It frequently does not apply to client situations (p63) d. It is outdated 15. In Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development, identity vs. identity confusion occurs with what age group? a. Adolescence (p65) b. Young adulthood c. Children 6–12 years old d. Adulthood 16. Which theory that says that people have a biological blueprint that dictates how they grow and reach maturity? a. Classical conditioning b. The epigenetic principle (p64) c. Operant conditioning d. The medical model 17. Bandura’s social learning theory suggests that: a. People are passive agents in their learning b. People respond conditionally to stimuli c. People are active agents in their learning (p70) d. People rarely think about the ramifications of their actions 18. What term is used in social learning theory to express individuals’ expectations that they can successfully perform a variety of tasks? a. Self-efficacy (p70). b. Resilience c. Empowerment d. Motivation 19. The focus on the meaning of life and people’s views on existence is a tenet of: a. Existentialism (p73) Human Behavior in the Social Environment Anissa Taun Rogers Question Bank 10/08/2009 b. Psychodynamic theory c. Social learning theory d. Unconditioned response 20. According to Rogers’s person-centered therapy, self actualization is attained when all the following are achieved EXCEPT: a. Our self-concept is congruent with our experiences b. We have positive regard from others c. We have positive self-regard d. We accept the presence of incongruence in our lives (p74) 21. Rewarding a child after they have completed a household chore is an example of: a. Negative reinforcement b. Positive reinforcement (p69) c. Neutral reinforcement d. Unconditioned stimulus 22. In classical conditioning, a naturally occurring reaction is called: a. Unconditioned stimulus b. Conditioned stimulus c. Unconditioned response (p68) d. Conditioned response Short Answer 23. Describe the limitations of the medical model. (p53-55) 24. What does self-fulfilling prophecy refer to? (p54) 25. In reference to Piaget’s theory, describe the differences between accommodation and assimilation. (p57) 26. Discuss the limitations of Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development. (p67) 27. Explain classical conditioning. (p68) 28. Explain reinforcement and punishment according to B.F. Skinner’s work. (p69-70) 29. Explain the type of learning called modeling. (p70) 30. Define systematic desensitization and provide an example. (p71) 31. Describe the pros and cons of the Humanistic Perspective. (p75)