Developmental Stages: Infancy to Adolescence Guide
advertisement
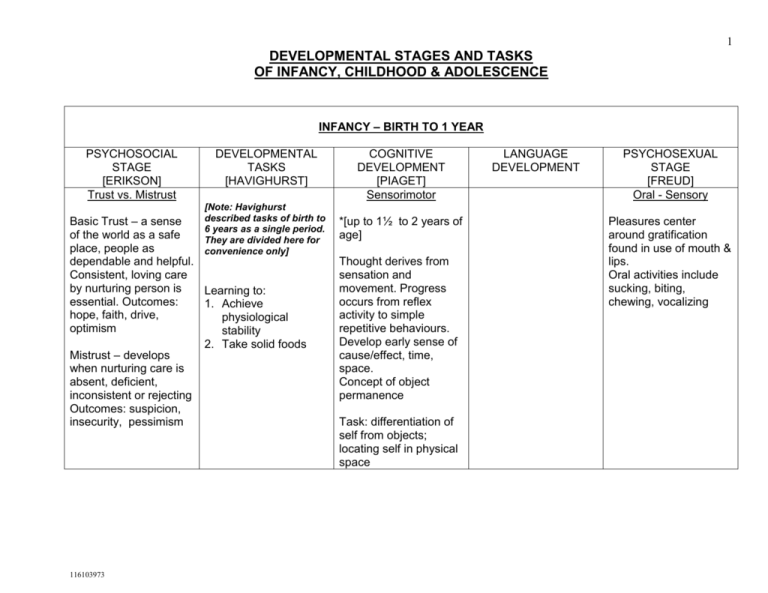
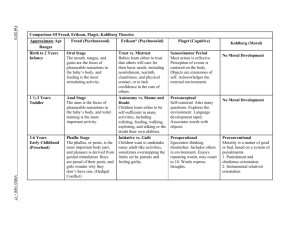
1 DEVELOPMENTAL STAGES AND TASKS OF INFANCY, CHILDHOOD & ADOLESCENCE INFANCY – BIRTH TO 1 YEAR PSYCHOSOCIAL STAGE [ERIKSON] Trust vs. Mistrust DEVELOPMENTAL TASKS [HAVIGHURST] [Note: Havighurst described tasks of birth to 6 years as a single period. They are divided here for convenience only] Basic Trust – a sense of the world as a safe place, people as dependable and helpful. Consistent, loving care by nurturing person is Learning to: essential. Outcomes: 1. Achieve hope, faith, drive, physiological optimism stability 2. Take solid foods Mistrust – develops when nurturing care is absent, deficient, inconsistent or rejecting Outcomes: suspicion, insecurity, pessimism 116103973 COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT [PIAGET] Sensorimotor *[up to 1½ to 2 years of age] Thought derives from sensation and movement. Progress occurs from reflex activity to simple repetitive behaviours. Develop early sense of cause/effect, time, space. Concept of object permanence Task: differentiation of self from objects; locating self in physical space LANGUAGE DEVELOPMENT PSYCHOSEXUAL STAGE [FREUD] Oral - Sensory Pleasures center around gratification found in use of mouth & lips. Oral activities include sucking, biting, chewing, vocalizing 2 TODDLER – 12 to 36 MONTHS PSYCHOSOCIAL STAGE [ERIKSON] Autonomy vs. Shame & Doubt Autonomy – centers around increasing ability to control body, self and environment. Want to “do” for self. Sense of self-reliancy & adequacy develops from being permitted to make choices. Outcomes: willpower, self-control Shame & Doubt – arises when child is made to feel selfconscious, ashamed or is made dependent in areas in which is capable of taking control. Outcomes: selfconsciousness, lack of control 116103973 DEVELOPMENTAL TASKS [HAVIGHURST] Learning to: 3. walk 4. talk 5. control elimination of body wastes COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT [PIAGET] Sensorimotor [to age 1½ to 2] -uses active experimentation to achieve goals -awareness of cause/effect -awareness of spatial relationships -imitation, domestic mimicry Preconceptual [age 2-4 years] -egocentric thought – self as standard of judgment –unable to take viewpoint of others -begin to think & reason conceptually – increasing use of language –thinking is transductive (relating particular to particular) LANGUAGE DEVELOPMENT PSYCHOSEXUAL STAGE [FREUD] Anal - Urethral Interest centers around anal sphincter. Develop ability to withold or expel fecal material at will. Climate surrounding toilet training influences child’s personality. Associated traits include possessiveness, retentiveness, aggressiveness, pronounced messiness or tidiness, punctuality or shame. 3 PRESCHOOL – AGE 3-5 YEARS PSYCHOSOCIAL STAGE [ERIKSON] Initiative vs. Guilt DEVELOPMENTAL TASKS [HAVIGHURST] Learning to: Initiative: sense of confidence that allows child to plan, take action & test what kind of person he/she can be. Reinforced by freedom, opportunity, encouragement Outcome: purpose & direction 6. learn sex differences & sexual modesty 7. relate oneself emotionally to parents, siblings & other people 8. form simple concepts of social & physical reality 9. learning to distinguish right & wrong, developing a conscience Guilt: occurs when made to feel bad about initiatives made Outcomes: guilt, anxiety, fear, dependence 116103973 COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT [PIAGET] Preconceptual [to 4 yr.] as above Pre-operational or Intuitive [ 4-7 yr.] -transition to increased symbolic functioning -ability to think in terms of classes, see relationships, deal with number concepts -defines objects in terms of their use -still egocentric; unable to see another’s point of view LANGUAGE DEVELOPMENT PSYCHOSEXUAL STAGE [FREUD] Phallic – Locomotion -interest focussed around genital area -recognize differences between sexes -identification with parent of same sex -Oedipal or Electra complexes, penis envy, castration fears 4 PSYCHOSOCIAL STAGE [ERIKSON] Industry vs. Inferiority Industry: characterized by sense of confidence and competence in ability to produce, build, make. Needs & wants real achievement. Child learns to compete & cooperate and to use rules. Outcomes: method, competency Inferiority: may feel inadequate if too much or too little is expected of child or if they feel they cannot live up to standards set for them Outcomes: feelings of inadequacy 116103973 DEVELOPMENTAL TASKS [HAVIGHURST] SCHOOL AGE – 6 – 12 YEARS COGNITIVE LANGUAGE DEVELOPMENT DEVELOPMENT [PIAGET] 1. learning physical skills necessary for ordinary games 2. building wholesome attitudes toward self as growing person 3. learning to get along with age-mates 4. learning appropriate masculine or feminine roles 5. developing fundamental skills in reading, writing, calculating 6. developing conscience, morality, scale of values 7. developing concepts necessary for everyday living 8. developing attitudes toward social groups and institutions 9. achieving personal independence Pre-operational [to 7 yr] as above Concrete Operational -development of logical reasoning -thinking is tied to what is observable -concepts of reversability, conservation -thinks in terms of numbers, classes, relations -beginning deductive reasoning -overcoming egocentrism -no longer fooled by appearances PSYCHOSEXUAL STAGE [FREUD] Latency -resolution of phallic conflicts -attention turned from sexuality to tasks of socialization -quiescent period of sexuality