ECON 201
advertisement

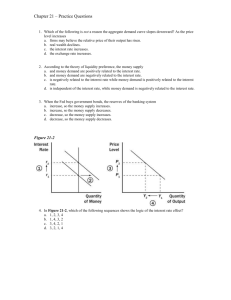
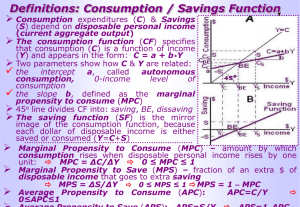
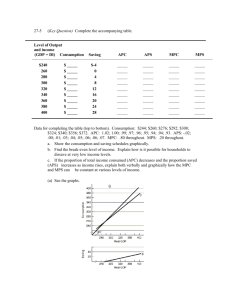
ECON 201 ABBREVIATIONS Prof. M. Naples A Ap AD AE APL AS AVC ATC C Ca c CCA DD DM e G i I Ia Ig In Ip I(i) IM IMa K LF Autonomous Aggregate Expenditures Planned Autonomous Aggregate Expenditure Aggregate Demand Aggregate Expenditure (A + mpe Yd) Average Product of Labor (labor productivity) Aggregate Supply Average Variable Cost Average Total Cost Consumer Expenditures Autonomous Consumption (book uses Co) cash-holding ratio Capital Consumption Allowance (Depreciation) Demand deposits Demand for Money Exchange Rate Government Expenditures on goods and services Interest Rate Real Investment Expenditures Actual Investment Expenditures Gross Investment Expenditures Net Investment Expenditures Planned Investment Expenditures Investment Function; I as function of i Import Expenditures (book uses M) Autonomous imports Capital Stock Labor Force L m MPL MB MC MD MS mpc mpe mpi mps MULT N NW NX P . P Ph q$ r rr S Sa SM T Ta t Leisure money multiplier Marginal Product of Labor Monetary Base Marginal Cost Quantity of Money Demanded Money supply Marginal Propensity to Consume (book also uses b) Marginal Propensity to Expend = mpc - mpi Marginal Propensity to Import Marginal Propensity to Save Expenditure Multiplier Employment Net Worth Net Export Expenditures Price level Inflation Rate (rate of change of price level) Phillips Curve Profit Rate Quantity of Dollars Exchanging on Foreign-Currency Markets total reserve ratio Required Reserve Ratio Saving (out of current income) Autonomous Saving Supply of Money Macro Taxes Autonomous Taxes Income-tax rate U W X xr Y Yd Unemployment Rate Wage rate Export Expenditures Excess Reserve Ratio National Income, National Output, GDP Disposable Income, Take-Home Pay ECON 201 Handout on Expenditure Models Prof. M. Naples Model with consumption as a function of income: C = Ca + mpcYD Since taxes=0, Y = YD, C = Ca + mpcY, AE = C + I + G + NX = A + mpcY Mult = 1/(1-mpc) = 1/mps Model with imports and consumption as a function of income: IM = IMa + mpi(Y) AE = [Ca + I + G + (X-IMa)] + (mpc-mpi)Y = A + mpe(Y) where mpe = mpc-mpi MULT = 1/(1-mpe) = 1/(1-mpc+mpi) = 1/(mps+mpi) Model with lump-sum taxes; imports and consumption as a function of income: YD = Y-T C = Ca + mpc(YD) = Ca - mpc(T) + mpc(Y) AE = [Ca - mpcT + I + G + (X-IMa)] + (mpc-mpi)Y = A + mpe(Y) where mpe = mpc-mpi MULT = same as before: MULT = 1/(1-mpe) = 1/(1-mpc+mpi) = 1/(mps+mpi) Model with income taxes: (for reference only, recognize the multiplier) T = Ta + tY YD = Y-T = Y(1-t) - Ta C = Ca + mpc(YD) = Ca - mpc(Ta) + mpc[Y(1-t)] AE = [Ca - mpcTa + I + G + (X-IMa)] + (mpc(1-t)-mpi)Y = A + mpe(Y) where mpe = mpc(1-t)-mpi MULT = 1/(1-mpc(1-t)+mpi) = 1/(mps+mpi+t(mpc)) so more built-in or induced leakages than lump-sum tax model