Chordate Evolution: Active Reading Worksheet
advertisement

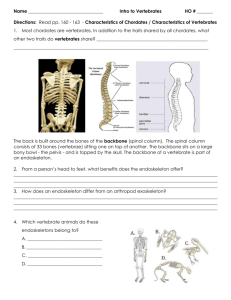
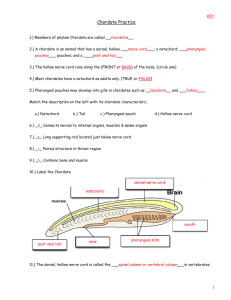
Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ Skills Worksheet Active Reading Section: Chordate Evolution Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. A major group of deuterostomes are the chordates. Chordates have a very different kind of skeleton, one that is completely internal, called an endoskeleton. During the development of the chordate embryo, a stiff rod called the notochord develops along the back of the embryo. The evolution of an internal skeleton was an important step that led to the evolution of vertebrates. The endoskeleton, to which muscles attach, made it possible for animals to grow large and move quickly. Chordates also share three other characteristics. They have a single, hollow, dorsal nerve cord with nerves attached to it that travel to different parts of the body. Chordates also have a series of pharyngeal pouches in the throat at some stage of development. These give rise to structures in the head and neck, including gills in fish and the inner ear in humans. Another chordate characteristic is a postanal tail, which is a tail that extends beyond the anus. All chordates have all four of these characteristics at some time in their life, even if it is only briefly as embryos, as in humans. SKILL: READING EFFECTIVELY Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided. 1. The prefix endo- means “inside or within.” Using the meaning of this prefix, define the word endoskeleton. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. What capabilities were made possible for animals due to the evolution of an internal skeleton? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 3. Where do pharyngeal pouches develop in chordates? _______________________________________________________________ 4. Where does the notochord develop in chordates? _______________________________________________________________ Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Biology 15 Introduction to Animals Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ Active Reading continued In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. _____ 5. The evolution of an internal skeleton was an important step that led to the evolution of a. vertebrates. b. deuterostomes. c. invertebrates. d. amoebas. _____ 6. A member of the phylum Chordata is a a. protostome. b. deuterostome. c. jawless fish. d. arthropod. _____ 7. An endoskeleton is a(n) a. notochord. b. nerve cord. c. external skeleton. d. internal skeleton. _____ 8. The development of which characteristic made it possible for animals to grow large and move quickly? a. dorsal nerve cord b. notochord c. endoskeleton d. exoskeleton _____ 9. Pharyngeal pouches in fish give rise to which structures? a. fins b. gills c. scales d. teeth _____ 10. Humans have postanal tails a. all of their lives. b. briefly at birth. c. only as embryos. d. until puberty. Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Biology 16 Introduction to Animals